The Week in Quantum Computing - October 7th 2024 - HSBC, Quantinuum, Q-Ctrl, NuQuantum, Australia
Issue #204
Quick Recap
Get ready, I’m putting together 2 weeks of developments in this edition!
In a rush? Just listen to the podcast:
The Week in Quantum Computing - October 7th 2024 - HSBC, Quantinuum, Q-Ctrl, NuQuantum, Australia
This week in quantum computing news, HSBC, in partnership with Quantinuum, has made strides in securing digital assets against future quantum threats by trialing quantum-secure technology for trading tokenized physical gold. This is good because Gartner is forecasting a Q-Day by 2029. A team led by Harald Putterman has developed a hardware-efficient qua…
This week in quantum computing news, HSBC, in partnership with Quantinuum, has made strides in securing digital assets against future quantum threats by trialing quantum-secure technology for trading tokenized physical gold. This is good because Gartner is forecasting a Q-Day by 2029. A team led by Harald Putterman has developed a hardware-efficient quantum error correction method using concatenated bosonic qubits, achieving a minimum logical error per cycle of 1.65% for a distance-5 code. This advancement suggests a promising path toward fault-tolerant quantum computing. Q-CTRL has integrated its Fire Opal software with the QCentroid platform, enhancing quantum optimization workflows and making quantum computing more accessible to businesses and developers. The European Union has allocated €65 million to advance quantum chip technologies, aiming to establish a robust European quantum ecosystem. IonQ has secured a massive contract with Air Force Research Lab, and at the same time achieved ion to ion entanglement, which is a key piece for quantum networking. No wonder their stock price had a great bump this week. Quandela will build “Lucy” in the EU. But IBM went first with their quantum DC in Germany. If you want to understand the new FIPS from NIST, Qcrypt wrote an excellent article. Is Qiskit good? How does it compare with other quantum frameworks? A recent paper proposes a benchmark for quantum solutions. NordVPN goes PQC. Nu Quantum, in collaboration with the UK's National Quantum Computing Centre (NQCC), has launched Project IDRA, a four-year initiative to develop optical networks for distributed quantum computing.
The Week in Quantum Computing
HSBC Pioneers Quantum-Safe Tech for Tokenised Gold
HSBC, in collaboration with Quantinuum, has successfully trialed quantum-secure technology for trading tokenized physical gold, marking a significant step in protecting digital assets from future quantum computing threats. HSBC's initiative, led by Philip Intallura, involves using post-quantum cryptography (PQC) to secure gold tokens, which can be converted into ERC-20 tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. Ilyas Khan of Quantinuum highlights the partnership's role in building quantum-hardened financial services. The trial addresses the "store now, decrypt-later" threat, emphasizing the importance of future-proofing digital assets. This advancement could lead to more secure and efficient cross-platform digital asset trading. The main takeaway is HSBC's pioneering role in integrating quantum-safe technology with tokenized assets to enhance digital financial security.
https://fintechmagazine.com/articles/hsbc-pioneers-quantum-safe-tech-for-tokenised-gold
Title:Hardware-efficient quantum error correction using concatenated bosonic qubits
A team led by Harald Putterman has developed a hardware-efficient quantum error correction method using concatenated bosonic qubits, as detailed in their recent paper. The study, supported by the Simons Foundation, employs a microfabricated superconducting quantum circuit to create a logical qubit memory. This memory combines encoded bosonic cat qubits with an outer repetition code of distance \(d=5\), effectively reducing the physical-qubit overhead typically required for error correction. The approach passively protects against bit flips and corrects phase-flip errors using ancilla transmons. The team achieved a minimum logical error per cycle of 1.65% for the distance-5 code, demonstrating the method's effectiveness. This work suggests concatenated bosonic codes as a promising path toward fault-tolerant quantum computing.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.13025v1
Q-CTRL integrates with QCentroid to enhance quantum optimization workflows for customers
Q-CTRL has integrated its Fire Opal software with the QCentroid platform to enhance quantum optimization workflows. This collaboration allows users to test algorithms effortlessly using no-code and API tools, optimizing performance and managing costs effectively. Fire Opal's AI-driven error suppression improves algorithm success on real hardware by 1000x, enabling scalability for large problems. The integration provides access to a library of use cases, such as risk analysis and chemistry simulations, and supports the MaxCut optimization problem. Heather West from IDC describes this as "frictionless quantum software." This partnership marks a significant advancement in making quantum computing more accessible and effective for businesses and developers. The main takeaway is the facilitation of quantum computing adoption through enhanced integration and user-friendly tools.
EU invests €65 million in quantum chips
The European Union has allocated €65 million to advance quantum chip technologies through the Chips Joint Undertaking (Chips JU). This initiative marks the first call for investment in quantum technologies, focusing on computing and sensing applications. The funding is expected to be matched by participating states, contributing to a total of €200 million over three years. The projects aim to enhance innovation and establish a manufacturing supply chain for quantum chips in Europe. Applications include logistics optimization, drug discovery, cybersecurity, and AI improvements. Proposals are due by January 21, 2025. This investment underscores the EU's commitment to leading in quantum technology development and establishing a robust European quantum ecosystem.
https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/news/eu-invests-eu65-million-quantum-chips
Quantum Computing: Opportunities, Concerns And Impact
The text discusses the transformative potential of quantum computing, highlighting its ability to solve complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers. Key figures include John Preskill, who coined the term "quantum supremacy," and Google, which claimed to achieve it in 2019. IBM and Microsoft are also pivotal players in the field. Concerns about quantum computing include its potential to break current encryption methods, posing security risks. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is working on post-quantum cryptography standards to address these issues. "Quantum computing is not just a faster computer; it's a fundamentally different way of processing information," says Scott Aaronson, a leading quantum theorist. The main takeaway is that quantum computing holds immense promise but requires careful management of its risks.
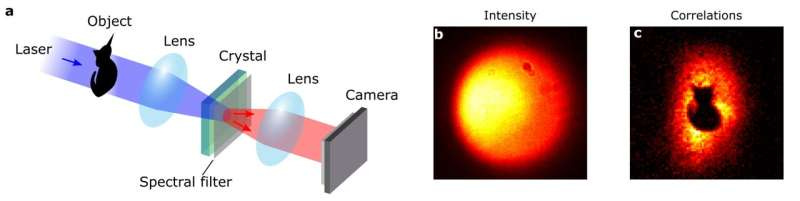
Physicists use quantum correlations of photon pairs to hide images from standard cameras
Hugo Defienne and his team have developed a technique to encode images into the spatial correlations between entangled photons—particles of light linked in such a way that their spatial degrees of freedom are strongly correlated, even over great distances. "Entangled photons are fundamental to many applications, such as quantum computing and cryptography," says Chloé Vernière, Ph.D. candidate under the supervision of Defienne and first-author of the study published in Physical Review Letters. "Hence, it is crucial to be able to tailor the photons' spatial correlations to meet different needs."
https://phys.org/news/2024-09-physicists-quantum-photon-pairs-images.html
World’s first observation of quantum entanglement in quarks
CERN's Large Hadron Collider has achieved the first observation of quantum entanglement in quarks, marking a significant milestone in particle physics. This discovery, published in *Nature*, involved the ATLAS and CMS collaborations and was confirmed through proton-proton collisions at 13 teraelectronvolts. The entanglement was observed between a top quark and its antimatter counterpart, providing new insights into the Standard Model and potential new physics. ATLAS spokesperson Andreas Hoecker highlighted the importance of this finding, stating it "paves the way for new investigations." CMS spokesperson Patricia McBride emphasized its potential to test the Standard Model in unprecedented ways. The main takeaway is that this breakthrough opens new avenues for exploring quantum mechanics and particle physics.
https://cosmosmagazine.com/science/physics/cern-quantum-entanglement-quarks/
Hoja de ruta cuántica para empresas
The "Quantum Roadmap for Businesses" by the Bankinter Innovation Foundation is a crucial guide for organizations to adopt quantum computing, ensuring their competitiveness. It highlights the synergy between artificial intelligence and quantum computing, which promises to transform sectors like healthcare and energy. The guide recommends investing in education, analyzing processes for quantum improvements, building multidisciplinary teams, and collaborating with pioneering institutions. It addresses challenges such as cybersecurity, emphasizing quantum cryptography. Practical cases are presented in sectors like finance and pharmaceuticals. According to the report, "quantum computing can optimize investment portfolios and improve fraud detection." Quantum adoption is essential to stay at the forefront of technology.
https://www.fundacionbankinter.org/noticias/hoja-de-ruta-cuantica-para-empresas/
Quantum Computing: Between Hope and Hype
In a recent talk titled "Quantum Computing: Between Hope and Hype," Scott Aaronson shared insights from his 25-year journey in quantum computing. Hosted by UCLA, the event was part of a US-India workshop on quantum computing and post-quantum cryptography. Aaronson highlighted significant advancements, such as Google's use of the Kitaev surface code to achieve a net gain in logical qubit coherence and Microsoft's collaboration with Quantinuum on trapped-ion architecture. He noted the importance of achieving 99.99% reliability in 2-qubit gates for fault-tolerant quantum computing. Aaronson emphasized the urgency of transitioning to post-quantum cryptography, stating, "Yes, unequivocally, worry about this now." The main takeaway is that quantum computing is transitioning from theoretical to practical, with significant progress expected in the next decade.
https://scottaaronson.blog/?p=8329
G7 cybersecurity group urges financial institutions to prepare for quantum computing
The G7 Cyber Expert Group has issued a statement urging financial institutions to prepare for the advent of quantum computing. The group emphasizes the potential of quantum computers to surpass current computational capabilities, posing significant risks to cybersecurity. Financial entities are advised to develop a comprehensive understanding of quantum technology, assess associated risks, and formulate strategies to mitigate these risks. The statement underscores the importance of proactive measures in safeguarding financial systems against future quantum threats. The main takeaway is the critical need for financial institutions to anticipate and address the cybersecurity challenges posed by quantum computing advancements.
IonQ Announces Largest 2024 U.S. Quantum Contract Award of $54.5M with United States Air Force Research Lab
IonQ has secured a $54.5 million contract with the United States Air Force Research Lab (AFRL), marking the largest U.S. quantum contract for 2024. IonQ has reported $72.8 million in bookings year-to-date, aiming to meet its $75-95 million guidance. The AFRL partnership focuses on advancing quantum networking and system deployability. Peter Chapman, IonQ's CEO, highlighted the company's rapid growth, stating, "No other publicly traded pure-play quantum computing company has nearly doubled revenue each year since going public." The collaboration will enhance U.S. defense capabilities, as noted by Michael Hayduk of AFRL. IonQ's strategic partnerships and technological advancements position it as a key player in quantum computing. The main takeaway: IonQ is significantly advancing quantum computing through strategic government partnerships.
US Implements Controls on Quantum Computing and other Technologies
The U.S. Commerce Department announced new export controls on quantum computing, advanced semiconductors, and additive manufacturing technologies. These controls target key equipment, materials, and software, with specific requirements for foreign nationals. The rule, effective November 5, 2024, seeks public input on potential license requirements. Assistant Secretary Thea D. Rozman Kendler emphasized the importance of international coordination for national security. Carl Williams, a quantum technology consultant, noted the burden these controls place on startups. The controls aim to prevent misuse of critical technologies with military applications. The main takeaway is the U.S. government's strategic move to regulate emerging technologies while balancing national security and international collaboration.
Infleqtion secures $1M grant to advance quantum software
Infleqtion, a quantum information company, has been awarded a $1.15 million Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) grant by the U.S. Department of Energy. This funding is aimed at advancing the development of quantum computing software. The grant signifies a significant investment in the burgeoning field of quantum technology, highlighting the government's commitment to fostering innovation in this area. As quantum computing continues to evolve, such financial support is crucial for companies like Infleqtion to push the boundaries of software capabilities. The main takeaway is that Infleqtion's grant underscores the importance of government backing in accelerating quantum software advancements.
https://www.dailycamera.com/2024/09/27/infleqtion-secures-1m-grant-to-advance-quantum-software/
Signature of the Procurement Contract for Lucy, a New EuroHPC Quantum Computer Located in France
The European High Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (EuroHPC JU) has signed a procurement contract for "Lucy," a new EuroQCS-France quantum computer, with a French-German partnership including Quandela and attocube. Lucy, a MOSAIQ-12 photonic quantum computer with 12 qubits, will be integrated with the GENCI supercomputer Joliot-Curie for hybrid HPC-Quantum workloads. The system, costing EUR 8.5 million, will be co-funded by EuroHPC JU and France, and installed at CEA's TGCC in 2025. GENCI leads the consortium, with partners including Forschungszentrum Jülich and the University Politehnica of Bucharest.
2024 Post-Quantum Cryptography Standards Explained
The transition to NIST's 2024 post-quantum cryptography (PQC) standards marks a significant step in algorithmic security but doesn't fully address the "harvest now, decrypt later" threat posed by quantum computers. Denis Mandich highlights the lack of a backup plan for key exchange algorithms, as SIKE was compromised by a regular laptop. The government recommends "crypto-agile" implementations to allow easy replacement of flawed algorithms. The industry faces challenges with reactive standards and evolving threats, as seen in past cybersecurity breaches like SolarWinds and Intel's SGX vulnerability. Adopting PQC is crucial but not sufficient for quantum-era cybersecurity. The main takeaway: cybersecurity must evolve beyond single points of failure to ensure robust protection in the quantum era.
https://www.qrypt.com/resources/2024-post-quantum-cryptography-standards-explained/
Paper: Benchmarking the performance of quantum computing software
The paper "Benchmarking the performance of quantum computing software" by Paul D. Nation et al. introduces Benchpress, a comprehensive benchmarking suite for quantum computing software development kits. Benchpress includes over 1000 tests to evaluate performance metrics for quantum circuits with up to 930 qubits and approximately 1 million two-qubit gates. It provides a unified execution framework to assess multiple quantum software packages, ensuring transparency and verification of performance claims. The suite's flexibility allows it to adapt to advancements in quantum hardware and anticipate future device architectures' processing costs. As an open-source tool, Benchpress facilitates ongoing improvements and community engagement. The main takeaway is that Benchpress offers a robust, adaptable, and transparent benchmarking solution for quantum computing software.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.08844v1
Lumorti/Quandoom
Lumorti's "Quandoom" is a novel project that ports the first level of the classic game DOOM to a quantum computing framework. The project utilizes a QASM file requiring 70,000 qubits and 80 million gates, although such a quantum computer is not yet available. Instead, the game runs on a classical computer using a lightweight simulator. The simulator, written in 150 lines of C++, achieves 10-20 fps on a laptop. The project is open-source under the MIT license and is a parody inspired by the "anything can run DOOM" meme. Lumorti notes, "There is no quantum advantage, it's just a classical algorithm written in a format compatible with a quantum computer." The main takeaway is that Quandoom humorously explores the intersection of gaming and quantum computing.
https://github.com/Lumorti/Quandoom
Quantum Computing, Inc. Extends Collaborative Agreement with Los Alamos National Laboratory
Quantum Computing, Inc. (QCI) has extended its collaborative agreement with Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). This partnership aims to advance quantum computing technologies and applications. The collaboration focuses on leveraging QCI's expertise in quantum software and LANL's research capabilities to explore new quantum algorithms and solutions. The agreement signifies a continued commitment to pushing the boundaries of quantum computing. "This extension underscores our shared vision to drive innovation in quantum computing," stated a representative from QCI. The partnership is expected to yield significant advancements in quantum computing research and development. The main takeaway is that QCI and LANL are reinforcing their collaboration to further quantum computing innovations and applications.
History of quantum computing: 12 key moments that shaped the future of computers
Quantum computing has evolved from a theoretical concept to a burgeoning industry in under 50 years. Key milestones include Paul Benioff's 1980 proposal of a quantum Turing machine, Richard Feynman's 1981 advocacy for quantum simulators, and David Deutsch's 1985 concept of a universal quantum computer. Peter Shor's 1994 algorithm for efficient factorization and Lov Grover's 1996 search algorithm highlighted practical applications. In 1998, Isaac Chuang demonstrated quantum algorithms on hardware. The first commercial quantum computer was launched by D-Wave in 2011, and IBM's 2016 cloud-based quantum processor expanded access. QuEra set a record in 2023 with the most logical qubits. Quantum computing is poised to tackle problems beyond classical computing's reach.
New Quantum Error Correction Method
Hayato Goto from the RIKEN Center for Quantum Computing in Japan has introduced a new quantum error correction method using "many-hypercube codes," as detailed in Science Advances. This approach leverages the geometric structure of hypercubes to enhance error correction efficiency, potentially advancing fault-tolerant quantum computing. Goto's method allows for parallel placement of logical gates, akin to parallel processing in classical computing, achieving an encoding rate of up to 30%. This surpasses traditional methods in scalability without sacrificing performance. Goto notes, “In practice, this code could be implemented with physical qubit systems such as laser-trapped neutral-atom qubits.” The main takeaway is that Goto's method could significantly improve quantum computing's fault tolerance and efficiency.
https://www.azoquantum.com/News.aspx?newsID=10513
Will quantum computing drive the automotive future?
Quantum computing (QC) is poised to significantly impact the automotive industry, with potential applications in route optimization, material durability, and autonomous vehicle algorithms. Notable advancements include IBM's Q System One and D-Wave's 5,000-qubit chip. Companies like Volkswagen and Bosch are already exploring QC's capabilities, with Volkswagen demonstrating a traffic-management system using D-Wave's technology. The industry anticipates QC's broader commercial viability by 2030, with an economic impact estimated at $2-3 billion by then. Near-term QC applications will focus on hybrid systems combining QC with high-performance computing (HPC). As Ondrej Burkacky, Niko Mohr, and Lorenzo Pautasso note, QC offers "computational improvements that could boost capabilities across the value chain." QC will be a transformative force in automotive innovation.
First IBM Quantum Data Center in Europe Opens; Will Include IBM's Most Performant Quantum Systems
IBM has inaugurated its first European Quantum Data Center in Ehningen, Germany, marking a significant expansion of its quantum computing capabilities. The center, opened with German Chancellor Olaf Scholz, will house IBM's most advanced systems, including the IBM Quantum Heron, which offers a 16-fold performance boost and a 25-fold speed increase over 2022 models. This facility will support over 250 global enterprises and research institutions, such as Crédit Mutuel, Bosch, and Volkswagen, in advancing quantum algorithm discovery. "This state-of-the-art facility will foster innovation," stated Ana Paula Assis, IBM's General Manager for EMEA. The main takeaway is IBM's commitment to enhancing Europe's quantum computing landscape through strategic infrastructure and collaboration.
MAG Aerospace Partners with Zapata AI to Deliver Next-Generation Airborne Surveillance Platform
MAG Aerospace has partnered with Zapata AI to develop a next-generation airborne surveillance platform, enhancing global intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities. Zapata AI, known for its AI solutions, will utilize its Orquestra® Enterprise Solution to integrate advanced sensor fusion technology, improving real-time data processing and decision support. Christopher Savoie, Zapata AI's CEO, emphasized the partnership's potential to "push the boundaries of what's possible for the next generation of airborne ISR." MAG's Chief Strategy Officer, Donald Robinson, highlighted the need for rapid innovation in fast-paced environments. This collaboration marks a significant advancement in ISR technology, leveraging AI to deliver superior tactical decision-making capabilities in complex operational settings.
IBM Develops New Quantum Benchmarking Tool — Benchpress
IBM has unveiled Benchpress, a new quantum benchmarking tool designed to evaluate quantum computing software development kits (SDKs) and stacks. The tool includes over 1,000 tests for quantum circuits with up to 930 qubits and 10^6 two-qubit gates. Benchpress aims to assess quantum circuit construction, manipulation, and optimization across various SDKs, including Braket, Cirq, and Qiskit. IBM claims Benchpress leverages Qiskit's interoperability for a uniform testing environment and can measure SDK memory consumption using Memray. IBM researcher notes, "Benchpress allows for benchmarking that keeps pace with quantum hardware improvements." The main takeaway is that Benchpress offers a comprehensive framework for evaluating quantum software, potentially setting a new standard in quantum benchmarking.
https://www.hpcwire.com/2024/09/26/ibm-develops-new-quantum-benchmarking-tool-benchpress/
Illinois gov. adds $500 million to quantum computing quest
Illinois Governor JB Pritzker has proposed a $500 million investment in quantum computing as part of the state's effort to become a leader in quantum technologies, semiconductors, and AI. The funding includes $200 million for a cryogenic facility, $100 million for a quantum campus, and $200 million in matching funds to attract additional investment. This initiative aligns with Illinois' bid to host the National Semiconductor Technology Center, leveraging its strong network of national labs and universities. Pritzker believes this move will solidify Illinois as a hub for quantum research and development, positioning the state competitively in the global race against countries like China.
https://www.axios.com/2024/02/21/illinois-jb-pritzker-quantum-computing-semiconductors
I'm concerned about qiskit
Mark McGuire expresses concerns over Qiskit 1, IBM's quantum programming language, citing significant changes that may harm its community and usability. He notes that the transition from Qiskit 0 to 1 has rendered educational resources obsolete, impacting both industry and academia. McGuire highlights the abrupt migration requirements, such as replacing "backend.run" with "backend.transpile," which could disrupt existing codebases. He fears the shift from educational focus to production environments might alienate users, eroding Qiskit's community goodwill. McGuire acknowledges a discussion with a Qiskit team member, who explained the strategic shift, but remains worried about the loss of the Qiskit textbook. The main takeaway is that Qiskit's rapid evolution risks losing its foundational community support.
https://medium.com/@-mark-mcguire-/im-concerned-about-qiskit-41f0a6ef7d2f
Paper: Eavesdropping on the BB84 Protocol using Phase-Covariant Cloning: Experimental Results
Researchers Brian Pigott, Elizabeth Campolongo, Hardik Routray, and Alex Khan have conducted an experimental study on the security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol under noisy conditions. The study, supported by the Simons Foundation, investigates the potential for eavesdropping using asymmetric phase-covariant cloning. Despite BB84's theoretical security in noiseless channels, its robustness in practical, noisy environments remains uncertain. The team developed a reproducible test to estimate the information an eavesdropper could extract, highlighting vulnerabilities in current implementations. The findings underscore the need for further exploration of error tolerances in quantum communication systems. The main takeaway is the necessity to reassess the security of quantum protocols in real-world conditions.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.16284v1
New Research Finds Quantum Software Makes Complex Chemistry Research Process Up to 20 Times More Efficient and Could Cut Drug Development Costs
Terra Quantum AG, in collaboration with Prof. Dr. Christoph Bannwarth from RWTH Aachen University, has developed a quantum tensor network-based method that enhances the efficiency of predicting molecular structures by 5 to 20 times compared to classical methods. This advancement, detailed in the paper "Tensor Train Optimization for Conformational Sampling of Organic Molecules" on ChemRxiv, could significantly reduce drug development costs, which currently range from $1 to $2 billion per approved drug. Markus Pflitsch, CEO of Terra Quantum, highlights the potential for accelerating drug design by exploring a wider chemical space. The method does not require training data, offering a data-independent solution for complex molecular analysis. This breakthrough represents a significant leap in computational chemistry efficiency.
https://www.azoquantum.com/News.aspx?newsID=10524
Equal1 and NVIDIA Partner to Develop Quantum-Classical Solutions for Data Centers
Equal1, a spin-out from University College Dublin, has partnered with NVIDIA to develop quantum-classical solutions for data centers. The collaboration aims to create quantum computing use cases and integrate quantum-classical infrastructure for cloud and data center deployments. Equal1's UnityQ quantum system-on-chip will be combined with NVIDIA's CUDA-Q software platform. Jason Lynch, CEO of Equal1, expressed excitement about the collaboration, stating, "We see NVIDIA CUDA-Q as a leading hybrid quantum classical software platform." The partnership was announced during an Enterprise Ireland trade mission to the US, led by Peter Burke TD. Equal1, supported by various investors, is at the forefront of quantum advancements. The main takeaway is the strategic collaboration between Equal1 and NVIDIA to enhance quantum-classical computing integration.
NordVPN announces its first app with post-quantum encryption support
NordVPN has launched its first app featuring post-quantum encryption, initially available for Linux users. This update aligns with the latest NIST standards, aiming to protect against potential quantum decryption threats. NordVPN CTO Marijus Briedis warns of "harvest now, decrypt later" attacks, where cybercriminals store encrypted data to decrypt once quantum computing becomes more advanced. Quantum computers, using qubits, can solve complex problems exponentially faster than traditional computers, posing significant cybersecurity risks. Despite NASA's 2022 statement on the infancy of quantum computing, NordVPN is proactively enhancing encryption to ensure long-term security. Briedis emphasizes, "With this launch, we start a major transition to new-generation encryption." The main takeaway: NordVPN is pioneering post-quantum encryption to safeguard future cybersecurity.
https://www.zdnet.com/article/nordvpn-announces-its-first-app-with-post-quantum-encryption-support/
Nu Quantum’s Platform for Networking Quantum Computers Hosted at the UK's National Quantum Computing Centre
Nu Quantum, in collaboration with the UK's National Quantum Computing Centre (NQCC), has launched Project IDRA, a four-year initiative to develop optical networks for distributed quantum computing. Located at the Harwell Campus, this project aims to overcome technical barriers in quantum entanglement, crucial for scaling quantum computers. Supported by the National Security Strategic Investment Fund, IDRA will enhance the UK's position in quantum technology. Nu Quantum is developing high-efficiency qubit-photon interfaces and Quantum Networking Units, aiming to surpass current academic standards. Carmen Palacios, CEO of Nu Quantum, emphasized the UK's leadership in quantum computing. Dr. Michael Cuthbert, NQCC Director, highlighted the project's role in future quantum data centers. The main takeaway: Project IDRA is pivotal in advancing scalable quantum computing networks in the UK.
https://www.nu-quantum.com/news/idra-nu-quantums-platform-for-networking-quantum-computers-nqcc
Germany backs Australian startup Quantum Brilliance to build a mobile quantum computer
The German government has faith in Australia’s quantum sector to build the world’s first mobile mobile quantum computer, with the nation’s cybersecurity agency, Cyberagentur, awarding a record $58 million (€35 million) contract to Canberra startup Quantum Brilliance and two others.
Potential of quantum machine learning for solving the real-world problem of cancer classification
Quantum machine learning (QML) shows promise in cancer classification, as demonstrated by Mohadeseh Zarei Ghobadi and Elaheh Afsaneh's study published in Discover Applied Sciences. The research utilized QML to classify ten cancer types using gene expression data, revealing that QML achieved results comparable to classical methods. Notably, the Quantum Support Vector Machine (QSVM) outperformed some classical models, identifying novel biomarkers consistent with DNA promoter methylation. The study highlights QML's potential in medical research, suggesting it could enhance early disease detection and patient management. As Ghobadi states, QML "paves the way for future advancements in other disease research and clinical applications." The main takeaway is QML's potential to revolutionize cancer classification and biomarker discovery.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42452-024-06220-6
TU Graz Develops Hardware Architecture for Post-Quantum Cryptography
Researchers at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz), led by Sujoy Sinha Roy, have developed a hardware architecture for post-quantum cryptography (PQC) as part of the PQC-SRC project. This architecture supports NIST-standardized algorithms like Kyber, Dilithium, Falcon, and SPHINCS+, which are crucial for transitioning to quantum-safe cryptography. The team created a unified cryptographic coprocessor, KaLi, to efficiently handle these algorithms, focusing on compact design and physical security. They introduced a data randomization technique, "Kavach," to protect against physics-based attacks. Sinha Roy emphasized the urgency of this work, stating, "When powerful quantum computers are fully developed, they will be able to break encryptions in a few seconds." This development marks a significant step toward secure quantum-era communications.
Quantum computing will render traditional cryptography unsafe by 2029
Quantum computing will render traditional cryptography unsafe by 2029, and fully break it by 2034, making the transition to post-quantum cryptography (PQC) a critical priority. Organizations need to start preparing now to resist future quantum and classical attacks. Transitioning to PQC will be complex, requiring new algorithms, updates to performance standards, and significant organizational effort, akin to the Y2K preparations. Governments are already pushing for PQC adoption, but many companies lack the knowledge and vendor support to implement it. A structured, policy-driven approach is essential to ensure a smooth transition and protect sensitive data.
https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/post-quantum-cryptography
New Album Fuses AI And Quantum Computing, Pushing Music’s Limits
Eduardo Reck Miranda, a pioneer in quantum computer music, has composed an album titled "Qubism" using AI and quantum computing. The album features a unique composition where a quantum computer, running an AI model, responds in real-time to a violin with synthesized sounds, creating a dynamic improvisation. The London Sinfonietta performed "Qubism" with IBM's quantum computer. Miranda, also a scientific adviser for Moth Quantum, is developing tools like Actias Synth, a qubit-enabled sound synthesizer. Moth Quantum plans to release an open-source toolkit for musicians. Ferdi Tomassini, Moth Quantum's CEO, emphasizes the transformative potential of quantum technology in the arts. The album showcases quantum computing's potential to revolutionize music creation and experience.
Modular quantum-to-quantum Bernoulli factory in an integrated photonic processor
A team led by Francesco Hoch, Taira Giordani, and others has developed a modular quantum-to-quantum Bernoulli factory using an integrated photonic processor, as published in Nature Photonics. This approach leverages quantum states for input and output, employing a photonic-path-encoding method. The scheme is universal and oblivious to input bias, overcoming limitations of previous models. The experimental implementation utilized a six-mode, fully programmable integrated photonic platform, demonstrating the feasibility of this method for randomness manipulation in quantum technologies. "Our scheme is modular and universal," the authors note, highlighting its potential for integration into quantum algorithms. The main takeaway is the advancement of quantum randomness manipulation through a robust and programmable photonic platform.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-024-01526-8
IonQ achieves Remote Ion-Ion Entanglement: Paving the Way for Scalable Quantum Networking
IonQ has achieved a significant milestone in quantum networking by demonstrating remote ion-ion entanglement using photonic interconnects, marking the first instance of such entanglement in a commercial setting. This development is crucial for scaling quantum systems, as it enables the connection of qubits across different quantum processing units (QPUs), creating larger, more powerful quantum networks. IonQ's four-step roadmap includes future milestones such as transferring entanglement to computation qubits (Milestone 3) and achieving programmatic entanglement across multiple QPUs (Milestone 4). These advances lay the groundwork for scalable, enterprise-grade quantum computing, pushing quantum systems toward practical, large-scale applications in fields like national security. The implication is that quantum networks, powered by these interconnects, will enable more complex computations and drive the commercialization of quantum technologies, potentially revolutionizing industries reliant on computing power.
Achieving Remote Ion-Ion Entanglement: Paving the Way for Scalable Quantum Networking
UNSW delivers atomic quantum computing breakthrough
Researchers at the University of New South Wales (UNSW) have achieved a significant milestone in quantum computing by demonstrating provable quantum entanglement between two atoms in silicon. This breakthrough is pivotal for the scalability of quantum computers. The UNSW team’s success marks the first time such entanglement has been demonstrated in silicon, which is essential for integrating quantum technology with existing semiconductor infrastructure. This advancement could accelerate the development of practical quantum computing solutions. "This is a major step forward in quantum computing," said a UNSW spokesperson. The main takeaway is that UNSW's achievement in silicon-based quantum entanglement is a crucial development towards scalable quantum computing.
https://www.innovationaus.com/unsw-delivers-atomic-quantum-computing-breakthrough/
A New Phase for Quantum Competition in Europe
Europe is entering a new phase of quantum competition, marked by IBM's first Quantum Data Center launch. Olaf Scholz emphasized collaboration over national silos. Mario Draghi called for €800 billion annual investment and a new EU industrial strategy. The UK, despite Brexit, maintains a strong quantum program but faces collaboration challenges with the EU. The EU's €1 billion Quantum Flagship and initiatives like Horizon Europe aim to boost quantum tech, but coordination remains difficult. The EU seeks technological sovereignty, wary of US and Chinese dependencies. NATO promotes quantum initiatives for collective security. The main takeaway is Europe's strategic push for quantum technology amidst geopolitical and economic challenges, emphasizing collaboration and innovation.
https://quantumcomputingreport.com/a-new-phase-for-quantum-competition-in-europe/