The Week in Quantum Computing - April 29th 2024 - Pasqal and Welinq, Rigetti, IBM, China, Europol... and Rock'n Roll
Issue #183
The Week in Quantum Computing. Brought to you by Sergio Gago (@piratecto).
Quick Recap
The ICFO team led by Professor Leticia Tarruell has developed QUIONE, the only quantum-gas microscope capable of imaging individual atoms of strontium quantum gases. Meanwhile China goes live with 504 qubis and available in the cloud. In the business realm, Pasqal and Welinq have teamed up to develop quantum interconnects for neutral-atom quantum computing, aiming to solve the challenges of qubit scaling. In cybersecurity, the Quantum Safe Financial Forum, established by Europol's EC3 and the EC3 Advisory Group on Financial Services, is working towards transitioning the financial sector to Post Quantum Cryptography by 2030. On the funding front, the European Commission has pledged €112 million to research and innovation in AI and quantum technologies under Horizon Europe's 2023-2024 work programme. A collaboration between the University of Cambridge, the Wellcome Sanger Institute, and EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute has been awarded up to $3.5 million to explore the potential of quantum computing in genomics.Xiaotian Xu, Kuan-Cheng Chen, and Robert Wille have introduced HamilToniQ, an open-source, application-oriented benchmarking toolkit for Quantum Processing Units. Rigetti launches Novera, their QPU partner program.
McKinsey Quantum Technology Monitor
McKinsey has published a new update on their quantum monitor. Too lazy to read the whole thing? Here’s a summary.
- Quantum technology saw strong momentum in 2024, with significant technological advances and robust funding.
- Despite a 27% decrease in private and corporate funding for QT start-ups, public investments increased by over 50% in 2024.
- Four sectors - chemicals, life sciences, finance, and mobility - are likely to see the earliest impact from quantum computing and could gain up to $2 trillion by 2035.
- The majority of funding (62%) went to companies founded five or more years ago, indicating a shift in investments towards more established start-ups.
- Countries like Germany, the United Kingdom, and South Korea have announced significant new funding for QT development.
- There was a notable increase in quantum technology programs offered by universities, with the European Union leading in the number of graduates in QT-related fields
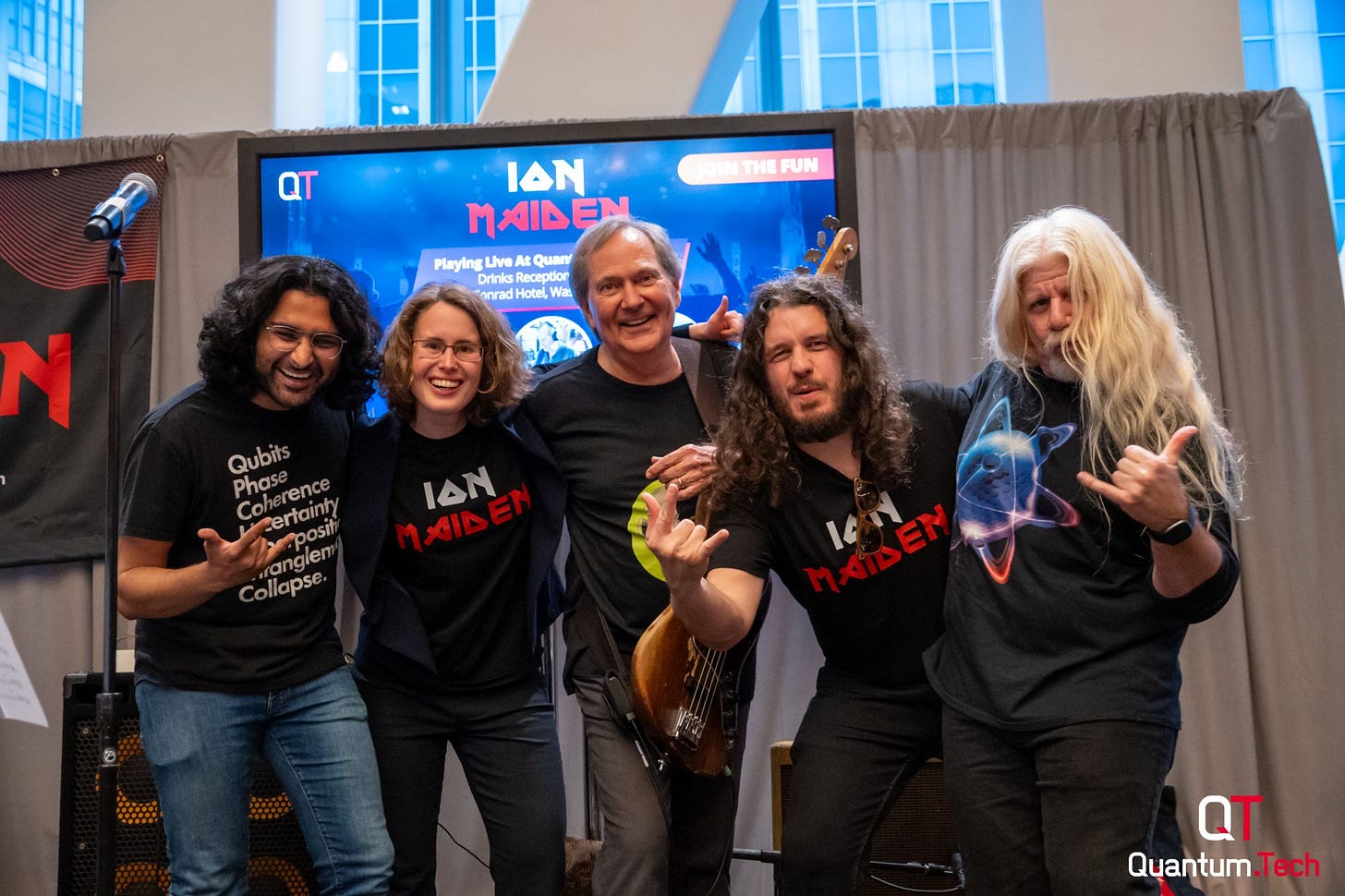
A Quantum Band is born
Shameless promotion :) . But at QuantumTech US 2024, the “Ion Maiden” band was born. What a pleasure to play with the amazing Quantum professionals and amazing musicians Christopher Bishop, Peter Bordow, Marlou Slot and Dhruv Srinivasan. Open for gigs!
Featured
More shameless promotion. Are you interested in Technology Management? Take a look at my new book! The CTO Toolbox. A collection of tools and resources for technology leadership. Your guide to become a Chief Technology Officer (yeah! I had a past before getting into Quantum). All proceeds from the book are donated to the NGOs Teaming.net and MigraCode Barcelona.
The Week in Quantum Computing
My take: Quantum utility for breakthroughs in industries and science
Katie Pizzolato, VP of Quantum Algorithms and Scientific Partnerships at IBM, emphasizes the potential of quantum computing for scientific discovery and industry breakthroughs. She asserts that quantum systems are now more efficient at running quantum circuits than classical computers, citing IBM's demonstration of a 100+ qubit device outperforming classical computers in certain calculations. Early applications include life sciences, physics, materials, and optimization problems, with ongoing projects in aerospace and financial services. Quantum computing's future lies in the hands of users across industries, research, and academia, who will identify its advantages. Pizzolato encourages viewing quantum as approachable and less esoteric, and highlights the importance of collaboration between industry players and quantum technical experts.
Why Quantum Computing Will Break Your Heart
Quantum computing, with its potential to solve complex problems at unprecedented speeds, has captured the attention of scientists, researchers, and industry leaders. The technology operates using qubits and superposition, allowing for parallel problem-solving on an astronomical scale. Quantum computing could revolutionize fields such as drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling. However, the technology faces significant challenges including the delicate nature of qubits, which require extreme cold temperatures to function, and the complexity of error correction. Additionally, its practical application is currently limited to research institutions and tech giants, and the technology raises profound ethical and security concerns. Despite the hype, the journey to practical quantum computing may prove disappointing.
https://www.rfglobalnet.com/doc/why-quantum-computing-will-break-your-heart-0001
Cirq vs. Qiskit vs. Q#: 3 Quantum Programming Languages. Which should you choose?
Cirq, Qiskit, and Q# are three leading quantum computing frameworks, each with unique features. Cirq, developed by Google’s Quantum AI team, excels in accurately modeling quantum noise, which is essential for simulating real-world quantum computing behavior. Qiskit, an open-source framework by IBM, offers a comprehensive suite of tools for quantum computing, including the ability to run quantum programs on real quantum hardware. Q#, developed by Microsoft, integrates quantum algorithms into classical workflows, advantageous for hybrid quantum-classical computations. The choice between these frameworks depends on the specific requirements of the quantum computation task, the need for noise modeling, the complexity of the quantum computations, and the availability of quantum hardware.
Announcing the birth of QUIONE, a unique analog quantum processor
ICFO researchers, led by Professor Leticia Tarruell, have developed QUIONE, the world's only quantum-gas microscope capable of imaging individual atoms of strontium quantum gases. QUIONE's unique capability is aimed at quantum simulation, boiling down complex systems into simpler models. The strontium gas was brought to the quantum regime, placed in an optical lattice for atom-atom interaction, and imaged using single atom techniques. Strontium's unique properties make it a popular element for quantum computing and simulation. The team also confirmed the strontium gas was a superfluid, a quantum phase of matter that flows without viscosity.
https://phys.org/news/2024-04-birth-quione-unique-analog-quantum.html
Pasqal and Welinq partnership
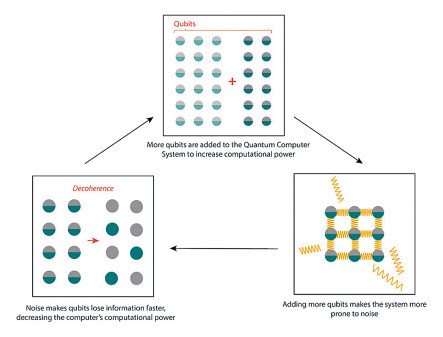
Quantum computing leaders, Pasqal and Welinq, have announced a partnership to develop quantum interconnects for neutral-atom quantum computing. The collaboration aims to solve the problems of qubit scaling for fault-tolerant quantum computing, with Welinq's innovative quantum interconnect technology allowing for the networking of multiple Quantum Processing Units (QPUs). The companies have outlined a roadmap, with Welinq aiming for an industrial prototype of their neutral atom quantum memory by the end of 2024, and Pasqal targeting a breakthrough with 1000-qubit QPUs. By 2030, they aim to create a thriving quantum computing ecosystem.
https://www.pasqal.com/news/pasqal-and-welinq-partnership/
Banco Santander and Moody’s Join Europol’s Quantum Safe Financial Forum to Combat Quantum Threats by 203
In 2024, Europol's European Cybercrime Centre (EC3) and the EC3 Advisory Group on Financial Services established the Quantum Safe Financial Forum (QSFF) to transition the financial sector to Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC) by 2030. The QSFF includes experts from major European, UK, and American banks, such as Banco Santander, Barclays Bank, Moody’s and Mastercard. The forum's mission is to share best practices and coordinate actions to ensure a safe transition to PQC. Quantum computing poses a potential threat to data security, as it could undermine existing cryptography. The transition to quantum-safe cryptography requires a coordinated effort, involving industry peers, the public sector, and academia.
Paper: HamilToniQ: An Open-Source Benchmark Toolkit for Quantum Computers
Scientists Xiaotian Xu, Kuan-Cheng Chen, and Robert Wille have introduced HamilToniQ, an open-source, application-oriented benchmarking toolkit for Quantum Processing Units (QPUs). The toolkit navigates the complexities of quantum computations, assessing QPU types, topologies, and multi-QPU systems. It evaluates QPUs' performance through quantum circuit compilation and quantum error mitigation, integrating unique strategies at each stage. HamilToniQ's standardized score, the H-Score, quantifies the fidelity and reliability of QPUs, providing a multidimensional view of QPU performance. The toolkit has been validated on various IBM QPUs, confirming its effectiveness and robustness. HamilToniQ contributes significantly to the quantum computing field by offering precise and equitable benchmarking metrics.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.13971v1
Commission invests 112 million in AI and quantum research and innovation
The European Commission has committed €112 million to research and innovation in artificial intelligence (AI) and quantum technologies under Horizon Europe's 2023-2024 digital, industrial, and space work programme. Of this, over €65 million will be invested in AI, with €50 million dedicated to developing new ways of combining data and expanding large AI model capabilities, and €15 million for enhancing AI system reliability and transparency. Additionally, €40 million will be allocated to world-leading quantum technologies, including €25 million for a pan-European network of quantum gravimeters. Furthermore, €7.5 million will be set aside to support projects that uphold European values and prioritize people in the digital transformation.
IBM built the biggest, coolest quantum computer. Now comes the hard part
IBM has constructed the world's largest quantum computer in Westchester County, New York, housed in the Thomas J. Watson Research Center. The system hums away in a conference room, performing complex computations in the realm of quantum mechanics. However, the challenge IBM now faces is to make this advanced technology useful and accessible for practical applications. The focus is on developing interfaces and software that can harness the power of quantum computing. IBM's achievement marks a significant milestone in the field of quantum computing, but it's clear that the journey to fully realize its potential is just beginning.
https://www.fastcompany.com/90992708/ibm-quantum-system-two
Quantum Computing Meets Genomics: The Dawn of Hyper-Fast DNA Analysis
A collaboration between the University of Cambridge, the Wellcome Sanger Institute, and EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute has been awarded up to $3.5 million to explore the potential of quantum computing in genomics. The team aims to develop algorithms for quantum computing that could expedite the production and analysis of pangenomes, which capture the genetic diversity in a population. This project is one of 12 selected for the Wellcome Leap Quantum for Bio (Q4Bio) Supported Challenge Program.
https://scitechdaily.com/quantum-computing-meets-genomics-the-dawn-of-hyper-fast-dna-analysis/
QUANTUM AND AI: THE HEDGEHOG AND THE FOX [The High Tech Frontier with Arthur Herman]
Arthur Herman's article discusses the potential synergy of AI and quantum computing. Currently, AI is rapidly spreading across the global economy, while quantum computing, despite being worked on by Google, Intel, Microsoft, IonQ, and others, is progressing slower. However, Herman suggests that the unpredictable nature of quantum science, based on the quanta, the most basic unit of energy and reality, could make it the more agile player in the future. He proposes that AI could help cut through the "noise" of quantum computing, while quantum computing could enhance AI's calculations. The combination of both technologies could lead to advancements in areas such as biotech research, industrial robotics, space exploration, and power grids.
https://mbiz.heraldcorp.com/insight/view.php?ud=20240425050363
McKinsey quantum report: Steady progress in approaching the quantum advantage
Quantum technology (QT) could generate up to $2 trillion in value by 2035, according to the third annual Quantum Technology Monitor by McKinsey. Despite a 27% decrease in private sector funding for QT start-ups, public investment rose by over 50%, led by Germany, the United Kingdom, and South Korea, bringing the global public funding total to around $42 billion. Most funding went to established start-ups, reflecting a focus on scaling. Meanwhile, the number of graduates in QT-related fields and universities offering QT programs increased, with the European Union leading in graduate numbers.
Telefonica, IDEMIA and Quside announce partnership to unveil pioneering Quantum-Safe Connectivity for IoT devices
Telefonica, IDEMIA and Quside have formed a strategic partnership to develop a quantum-safe solution for IoT devices. The collaboration aims to bolster security and resilience within IoT ecosystems, safeguarding both device infrastructure and data from potential quantum attacks.
Demonstration of heralded three-photon entanglement on a photonic chip
Researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China have demonstrated a large cluster state that could advance quantum computation in photonic systems, specifically three-photon entanglement. Photonic quantum computers, which use light particles for information processing, could potentially surpass traditional quantum computers in speed and data transmission over long distances. The study, published in Physical Review Letters, employed a strategy of fusing small resource states into large-scale cluster states suitable for measurement-based quantum computing. This achievement marks a significant step towards realizing fault-tolerant photonic quantum computing.
https://phys.org/news/2024-04-heralded-photon-entanglement-photonic-chip.html
Exponential Quantum Speedup for the Traveling Salesman Problem
Researchers from TCG Centres for Research and Education in Science and Technology, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, and Istituto Nazionale di Ottica have developed a bounded-error quantum polynomial-time (BQP) algorithm that provides an exponential speedup for the Traveling Salesman Problem. This problem, known to be NP-hard, involves finding the shortest route across a network of cities. The team's quantum algorithm significantly reduces the problem's complexity to $O(N^3\log(N)\kappa/\epsilon + 1/\epsilon^3)$, where $\epsilon$ and $\kappa$ represent error and the condition number of the matrix encoding all Hamiltonian cycles, respectively. This innovative approach could revolutionize how we solve complex computational problems.
https://eprint.iacr.org/2024/626
Revolutionizing Quantum Devices: Terra Quantum Introduces the 'Flowermon' Qubit
Terra Quantum has announced the discovery of the "flowermon" qubit, a significant advancement in quantum computing. The development was led by Dr. Valerii Vinokur, CTO, and Dr. Florian Neukart, CPO of Terra Quantum. The "flowermon" qubit, designed from high-temperature superconductor, suppresses noise effects, resulting in an increased coherence time and quantum processor stability. Unlike traditional qubits that require precise fabrication and environmental controls, the "flowermon" qubit uses a simpler design, simplifying the manufacturing process and improving scalability. The primary applications for the “flowermon” qubit would be creating more stable quantum processors and enabling complex quantum algorithms.
https://www.azoquantum.com/Article.aspx?ArticleID=513
China launches 504-qubit quantum chip, open to global users
The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has developed a 504-qubit superconducting quantum computing chip, setting a record for qubits in China. The chip, named "Xiaohong", has been delivered to QuantumCTek Co., a leading quantum company in China. According to Liang Futian, an associate professor at the CAS, the chip's performance is expected to match international quantum computing platforms like IBM. Wang Zhen, deputy general manager of China Telecom Quantum Group, announced plans to develop a quantum computer with the Xiaohong chip, accessible globally via a cloud platform.
https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202404/26/WS662b15dfa31082fc043c431e.html
MIT scientists tune the entanglement structure in an array of qubits
MIT researchers have developed a technique to efficiently generate entanglement among an array of superconducting qubits, a fundamental resource needed for quantum computing. The team, led by PhD candidate Amir H. Karamlou and Professor William D. Oliver, used microwave technology to control a quantum processor composed of superconducting circuits, generating highly entangled states and shifting those states from one type of entanglement to another. The research, which appears in "Nature", also demonstrated the ability to simulate the complex volume-law entanglement, which is key to realizing a quantum advantage, but is challenging to simulate using a classical computer.
https://news.mit.edu/2024/mit-scientists-tune-entanglement-structure-with-qubits-array-0424
Is quantum computing an enabler for the decarbonisation of aviation?
Airbus is exploring the potential of quantum computing in two key areas: aircraft design and operational efficiency. The company's Silicon Valley innovation center, Acubed, conducted a study in 2023 on quantum trajectory optimization, which could help optimize an aircraft's trajectory in real time, considering air traffic restrictions and weather patterns. In 2022, Airbus demonstrated a use case of quantum computing for efficient cargo loading using IonQ's quantum computer. The company is also investigating the use of quantum computing in simulating the complex chemistry of hydrogen fuel cells for aeronautic applications.
Unveiling a new quantum frontier: Frequency-domain entanglement
Scientists from Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea, led by Professor Heedeuk Shin, have introduced a new form of quantum entanglement called frequency-domain photon number-path entanglement. This advancement involves a frequency beam splitter that alters the frequency of individual photons with a 50% success rate. The team successfully created a two-photon NOON state within a single-mode fiber, doubling the resolution of its single-photon counterpart. This development, as highlighted by first author Dongjin Lee, transforms the concept of interference from spatial paths to different frequencies, and enriches our understanding of the quantum world, potentially impacting quantum sensing and secure communication networks.
https://phys.org/news/2024-04-unveiling-quantum-frontier-frequency-domain.html
Rigetti Computing Launches the Novera. QPU Partner Program
Rigetti Computing has announced the launch of the Novera™ QPU Partner Program. The initiative aims to enable high-performing, on-site quantum computing by creating an ecosystem of quantum computing hardware, software, and service providers. The program includes partners such as Bluefors, Quantum Machines, Zurich Instruments, Q-CTRL, Strangeworks, Classiq, Horizon Quantum Computing, TreQ, ParTec AG, and Riverlane. The Novera QPU is a 9-qubit quantum processing unit based on Rigetti's Ankaa™-class architecture. Rigetti CEO, Dr. Subodh Kulkarni, sees the Novera QPU as a unique opportunity to support the development of on-premises quantum computing capabilities worldwide.
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/rigetti-computing-launches-novera-qpu-123000571.html
Japan Tightens Export Controls on More Chip and Quantum Tech
Japan said it plans to expand restrictions on exports of four technologies related to semiconductors or quantum computing, the latest in a global push to control the flow of strategic tech.
https://www.bnnbloomberg.ca/japan-tightens-export-controls-on-more-chip-and-quantum-tech-1.2065573
Quantum Computing Faces Unique Challenges in Debugging, Calls for Specialized Tool
Quantum computing's complex and unintuitive phenomena pose unique challenges for software developers, particularly in the area of debugging. Quantum bugs, arising from incorrect gate sequences and mishandling of measurement processes, necessitate specialized debugging techniques. However, there is a lack of effective tools and guidance for detecting and fixing these bugs, compounded by a lack of integration between quantum programming tools. Studies of real examples and the development of new debugging methods, such as assertion-based debugging, are steps towards addressing these challenges. The future of quantum computing hinges on the development of more effective debugging tools and techniques, as outlined by Olivia Di Matteo in her publication, "On the need for effective tools for debugging quantum programs". Quantum computing's growth is tied to the collaborative efforts of the quantum software community in overcoming these challenges.
Charting a path to quantum-safe transformation through industry initiatives
IBM is leading the charge in quantum-safe transformation, co-developing three of the four algorithms selected by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) for standardization in 2024. IBM is also a key player in quantum-safe consortia, which aim to facilitate the adoption of quantum-safe cryptography. The company recently announced the formation of the Emerging Payments Association Asia (EPAA) work group on post-quantum cryptography, alongside founding members EPAA, HSBC, AP+, and PayPal. Furthermore, IBM has partnered with GSMA and Vodafone to establish the Post-Quantum Telco Network (PQTN) task force, and is a founding member of the Post-Quantum Cryptography Coalition (PQCC).