The Week in Quantum Computing - April 15th 2024 - Nu Quantum, SoftwareQ Collaboration, Quanmatic, ICFO, Quantonation's new fund
Issue #181
The Week in Quantum Computing. Brought to you by Sergio Gago (@piratecto).
Quick Recap
First things first: Happy belated Quantum day!. 4.1356677×10−15 eVs is Planck’s constant. Make that number more palatable and you get a plethora of celebrations, hackathons, articles and other events around the world!
On the news:
Nu Quantum and SoftwareQ partner to work together on a fault tolerant QC framework. Quanmatic's achieves milestone in solving a large-scale optimization problems. The successful transmission of light-matter entanglement over long distances by ICFO researchers brings us closer to a full-fledged quantum internet. On the policy front, Congresswoman Stefanik's introduction of the Defense Quantum Acceleration Act aims to speed up quantum technology adoption in the U.S. Department of Defense. MIT's discovery of "neutronic molecules" could open new avenues for quantum information processing devices. In the startup scene, European quantum computing startups are attracting considerable attention, with investments reaching $781m last year. Kipu Quantum's focus on immediate usability in quantum computing is noteworthy, together with the last funding round by Multiverse. And Quantonation's new €200 million fund, Quantonation II, is set to boost the quantum tech industry further. Finally, the paper of the week: Yilei Chen's development of a polynomial time quantum algorithm to solve the learning with errors problem is a significant advancement in quantum computing applied to cryptography. Another great paper analyzes the next decade in quantum and paves the way for the job “Quantum Engineer” in a similar fashion to today’s “AI Engineers” moving further from “Quantum Researchers”.
Learning With Errors implications
There is a lot of debate online on the LWE (Learning With Errors) problem implications. While the paper is theoretical it postulates a potential way to make lattice based cryptography (most of the post-quantum encryption algorithms) vulnerable. So, elliptic curve algorithms are unsafe thanks to Shor, and lattice unsafe thanks to Chen. Said that, the community is leaning towards keeping Cyrtal-Kyber methods safe for now.
EU PQC Recommendations
In the meantime, the EU has shared one of the fist official recommendations on PQC. This is the summary:
- This recommendation is in line with the EU's strategic importance on cybersecurity and the Digital Decade policy programme.
- The Commission recognizes the potential threat quantum computing poses to current cryptographic standards and the need for stronger safeguards, hence the need for a swift transition to Post-Quantum Cryptography.
- Member States are urged to migrate their current digital infrastructures and services for public administrations and other critical infrastructures to Post-Quantum Cryptography as soon as possible.
- The Commission encourages Member States to develop a comprehensive strategy for the adoption of Post-Quantum Cryptography, ensuring a coordinated and synchronized transition among different Member States and their public sectors.
- The strategy should define clear goals, milestones, and timelines resulting in a joint Post-Quantum Cryptography Implementation Roadmap.
- The Commission recommends the development of common European standards and a framework for identifying and selecting Post-Quantum Cryptography algorithms to be deployed in the digital networks and services across the Union.
- Member States and the Union should continue to cooperate actively with their international strategic partners in the development of international standards in Post-Quantum Cryptography.
- The Commission intends to monitor closely the actions taken in response to the Recommendation and assess the effects of this Recommendation to determine whether additional steps, including proposing binding acts of Union law, are required.
- The purpose of this Recommendation is to foster the transition to Post-Quantum Cryptography for the protection of digital infrastructures and services for public administrations and other critical infrastructures in the Union.
- The Commission recommends that Member States take advantage of existing structures at Union level in the area of cybersecurity and establish a sub-group of the NIS Cooperation Group.
- The Post-Quantum Cryptography Coordinated Implementation Roadmap should be available after a period of two years following the publication of this Recommendation.
- The overall work will be monitored and assessed periodically by the Commission in cooperation with the expert representatives of the Member States.
- Member States should cooperate with the Commission to assess the effects of this Recommendation maximum three years after its publication.
Featured
Qureca has launched a new image, website and LMS covering all their new trainings and support. Upskilling and education at all levels is fundamental in this industry and they are doing an amazing job at that.
Join me at this event. “Ion Maiden” concert included!
The Week in Quantum Computing
Quantum Monte Carlo simulations for financial risk analytics: scenario generation for equity, rate, and credit risk factors
Titos Matsakos and Stuart Nield from S&P Global have published a paper on Quantum Monte Carlo (QMC) simulations for financial risk analytics. The paper explores the use of QMC simulations in scenario generation for equity, rate, and credit risk factors. Monte Carlo simulations, widely used in financial risk management, are computationally expensive due to the number of scenarios required for convergence. The authors propose bypassing the computational cost by incorporating scenario generation into the quantum computation. They assemble quantum circuits to implement stochastic models for various risk factors and integrate these with Quantum Amplitude Estimation. The paper provides a promising approach for both market and credit risk use cases, highlighting the potential of quantum computing in financial risk analytics.
https://quantum-journal.org/papers/q-2024-04-04-1306/
Nu Quantum collaboration with SoftwareQ for first fault-tolerant quantum computer
Quantum networking company, Nu Quantum, and quantum software company, SoftwareQ, are collaborating to build the theoretical framework for the first fault-tolerant quantum computer. The project aims to address the challenge of scaling in quantum computing and is sponsored by the UK and Canadian governments. It is the first step towards creating a multi-core, distributed, error-corrected quantum computing paradigm. Dr Carmen Palacios-Berraquero, founder and CEO at Nu Quantum, stated that the collaboration will guide future development work towards architecting and building a fault-tolerant networked quantum computer.
Quanmatic Successfully Solves NP-hard Combinatorial Optimization Problem with Unprecedented Scale Using Annealing Technology
Tokyo-based Quanmatic Inc., a quantum computing firm, has achieved a major milestone in solving a 100 million-plus bit NP-hard optimization problem using quantum annealing technology. This feat surpasses previous records by a significant margin. The company employed proprietary technology called "revolvers", enabling them to handle larger problems and improve output stability. Dr. Kotaro Terada, Director of Application Development, likened the iterative problem-solving process to "Wyatt Warp enforcing his business with Colt 1873". The achievement follows a series of software releases in 2023, and the company's work with ROHM Co., Ltd. in complex LSI production.
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/quanmatic-successfully-solves-np-hard-040000753.html
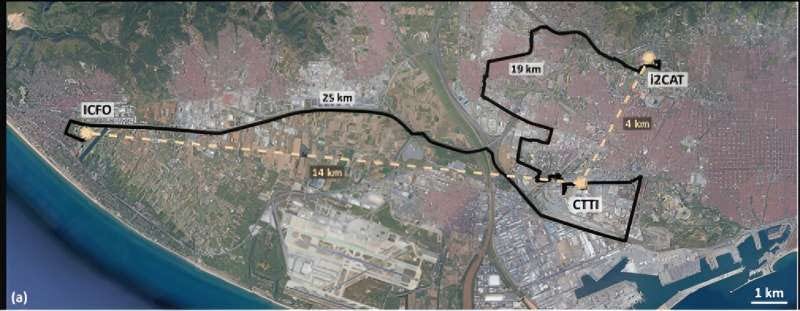
ICFO Researchers Achieve Quantum Leap: Transmit Light-Matter Entanglement Over 50km, Edging Closer to Quantum Internet Reality
Researchers at ICFO led by ICREA Prof. Hugues de Riedmatten have successfully transmitted light-matter entanglement over tens of kilometers of optical fiber, using the metropolitan network of Barcelona. The team demonstrated that photonic qubits maintain their quantum features without substantial decrease even after traveling 50 km in a fiber optic cable. The experiment, which involved the generation of photon pairs and their transmission through optical fiber, is a significant step towards the realization of a quantum repeater node, a key requirement for long-distance quantum communication. The team has also partnered with Cellnex for the realization of an entangled state of remote quantum memories. This achievement brings us closer to the realization of a full-fledged quantum internet.
https://phys.org/news/2024-04-transmitting-entanglement-metropolitan-network-barcelona.html
ICYMI: Stefanik Highlights FY24 Appropriations Investments and Announces Introduction of the Defense Quantum Acceleration Act in Rome, NY
Congresswoman Elise Stefanik announced the introduction of the Defense Quantum Acceleration Act at the Griffiss Institute, Rome, NY. The act aims to speed up quantum technology adoption in the U.S. Department of Defense. Stefanik also highlighted securing over $415 million in FY2024 funding for the Air Force Research Lab through the appropriations process. The funding, which doubles the previous year's investment, will support quantum research, cyber, and Counter-UAS. The announcement was made in the presence of notable figures including NY State Senator Joe Griffo, Oneida County Executive Anthony J. Picente Jr., Rome Mayor Jeff Lanigan, and Griffiss Institute President and CEO Heather Hage.
MIT researchers discover neutronic molecules
MIT researchers have discovered "neutronic molecules", where neutrons adhere to quantum dots solely through the strong force. This unexpected finding has been reported in ACS Nano by MIT graduate students Hao Tang and Guoqing Wang, and MIT professors Ju Li and Paola Cappellaro. The strong force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature, usually has a negligible influence beyond 1/10,000 the size of an atom, making this discovery surprising. This research could lead to new tools for examining properties of materials at the quantum level and potentially open up new avenues for quantum information processing devices.
https://physics.mit.edu/news/mit-researchers-discover-neutronic-molecules/
11 quantum computing startups that VCs are watching in Europe
European quantum computing startups are attracting considerable attention, with investments growing by 3% to reach $781m last year, three times more than North America. The UK and Germany have pledged $4.3bn and $3.7bn respectively to quantum technologies. Key startups include Multiverse Computing, which applies quantum computing to sectors like finance and cybersecurity, and Riverlane, which develops components and software to correct quantum computer errors. Terra Quantum offers quantum services via the cloud, while Pasqal focuses on quantum computers based on neutral atoms. Other notable startups include Arque Systems, Orange Quantum Systems, Haiqu, Alice&Bob, Pixel Photonics, Algorithmiq, and planqc.
https://sifted.eu/articles/quantum-computing-startup-vc-europe/
Interview with Prof. Enrique Solano - Co-founder of Kipu Quantum
Kipu Quantum, co-founded by Prof. Enrique Solano, is focusing on immediate usability in quantum computing. Solano, a critic of the overhyping of quantum computing's future potential, founded Kipu to demonstrate the technology's current capabilities. The startup, based in Berlin, is working on delivering application- and hardware-specific quantum algorithms, with a focus on combinatorial optimization problems. These problems, such as optimizing logistics routes or chemical compound composition, can be solved quickly by quantum computers. Kipu recently secured €10 million in seed funding and uses quantum hardware from IBM, D-Wave, QuEra, PASQAL, IonQ, and Quantinuum to deliver immediate benefits. The company's approach reflects Solano's belief that quantum computing can provide immediate societal benefits.
https://www.optik-bb.de/news/artikel/interview-with-enrique-solano-the-founder-of-kipu-quantum/
Quantonation announces the first closing of its new 200 million fund dedicated to Quantum Technologies
Quantonation has made the first closing of its new €200 million fund, Quantonation II, at €70 million. This early-stage fund is dedicated to Quantum Technologies. Quantonation, already a key player in the Quantum Tech industry, has begun investing globally in new companies from this fund. Their first fund, Quantonation I, exceeded their original target, raising €91 million and investing in 27 companies worldwide, with two exits. Quantonation II is set to continue this trend, with four deals already made. Managing Partner Christophe Jurczak expressed confidence in the quantum industry's future, while investor Bradley M. Bloom highlighted the team's expertise in identifying and accelerating promising innovations. The fund is managed by Quantonation Ventures, headquartered in Paris and Boston.
Quantum Algorithms for Lattice Problems
Yilei Chen from Tsinghua University, Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, and Shanghai Qi Zhi Institute has developed a polynomial time quantum algorithm to solve the learning with errors problem (LWE) with certain polynomial modulus-noise ratios. This breakthrough also yields polynomial time quantum solutions for the decisional shortest vector problem (GapSVP) and the shortest independent vector problem (SIVP) for any size of lattices, a feat previously unattainable. The new algorithm utilizes Gaussian functions with complex variances and windowed quantum Fourier transform with complex Gaussian windows, converting LWE instances into quantum states with purely imaginary Gaussian amplitudes, which are then translated into classical linear equations. This innovation propels the field of quantum computing into uncharted territories.
https://eprint.iacr.org/2024/555
Quantum Computing Market Set to Skyrocket to $5.3 Billion by 2029, Predicts MarketsandMarkets
The Quantum Computing market is poised to surge from $1.3 billion in 2024 to $5.3 billion by 2029, as per a MarketsandMarkets report. This growth is attributed to quantum computers' ability to solve complex problems more efficiently than classical computers. Superconducting qubits, a quantum computing technology, dominate the market. Major players include IBM, D-Wave Quantum Inc., Microsoft, Amazon Web Services, and Google. The healthcare and pharmaceutical industry is anticipated to significantly benefit from quantum computing advancements. The report also indicates a growing trend towards on-premises quantum computing. North America, housing several key players, contributes significantly to the industry's rapid growth.
How Switzerland is preparing for the quantum computing revolution
The Geneva Science and Diplomacy Anticipator Foundation (GESDA) is preparing Switzerland for the anticipated quantum computing revolution. GESDA, founded by the Swiss government, believes quantum computing will be the next big tech disrupter, succeeding artificial intelligence (AI). The foundation aims to establish governing rules for quantum computing and ensure Switzerland's central role in the international response. Peter Brabeck-Letmathe, chairman of GESDA, emphasizes the importance of anticipation, citing AI's rapid development that outpaced policy-making. GESDA recently launched the Open Quantum Institute at CERN, positioning Switzerland as an "honest broker" for this new technology. Quantum computing is expected to be 1000 to 10,000 times more powerful than current computing capabilities.
Breakthrough promises secure quantum computing at home
Oxford University Physics researchers have made a breakthrough in secure, cloud-based quantum computing, as detailed in a study published in Physical Review Letters. The team, led by Professor David Lucas, has demonstrated a scalable, practical method for "blind quantum computing", allowing users to access remote quantum computers securely, process confidential data with secret algorithms, and verify results without revealing useful information. This development could soon allow millions of individuals and companies to harness the power of quantum computing. The research was funded by the UK Quantum Computing and Simulation (QCS) Hub, with contributions from the Paris-Sorbonne University, the University of Edinburgh, and the University of Maryland
https://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2024-04-11-breakthrough-promises-secure-quantum-computing-home-0
Recommendation on a Coordinated Implementation Roadmap for the transition to Post-Quantum Cryptography
The European Commission has issued a recommendation for member states to develop a comprehensive strategy for the adoption of Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC). The aim is to ensure a coordinated and synchronised transition among different member states and their public sectors. The strategy should define clear goals, milestones, and timelines, leading to a joint PQC Implementation Roadmap. The ultimate goal is the deployment of PQC technologies into existing public administration systems and critical infrastructures through hybrid schemes that may combine PQC with existing cryptographic approaches or Quantum Key Distribution.
Paper: Quantum Algorithms: A New Frontier in Financial Crime Prevention
A research paper by Abraham Itzhak Weinberg and Alessio Faccia explores the potential of quantum algorithms in combating financial crimes. The authors highlight Quantum Machine Learning (QML) and Quantum Artificial Intelligence (QAI) as robust solutions for detecting and preventing financial crimes, including money laundering, financial crime detection, cryptocurrency attacks, and market manipulation. Leveraging quantum computers' computational capabilities, these quantum approaches can overcome limitations of classical methods, enhancing financial risk management. By exploiting the quantum advantage, financial institutions can improve risk identification and mitigation, leading to more robust strategies.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.18322v1
Paper: Challenges of Quantum Software Engineering for the Next Decade: The Road Ahead
The paper "Challenges of Quantum Software Engineering for the Next Decade: The Road Ahead" by Juan M. Murillo and 15 other authors, discusses the evolution of quantum computers and the complexity of software they can run. The authors argue for mature software engineering approaches to ensure efficiency, maintainability, reusability, and cost-effectiveness of quantum software. They highlight the difficulty of applying classical software engineering solutions to quantum software, leading to the emergence of Quantum Software Engineering as a distinct discipline. The authors, active researchers in the field, are addressing the challenges and analyzing recent research advances in Quantum Software Engineering, identifying needed breakthroughs and future research directions. The evolution and complexity of quantum software necessitate innovative engineering approaches.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.06825v1
Satellite-based entanglement distribution and quantum teleportation with continuous variables
Researchers Tasio Gonzalez-Raya, Stefano Pirandola, and Mikel Sanz have studied the effects of atmospheric turbulence on satellite-based quantum entanglement distribution and quantum teleportation. They observed the degradation of entanglement due to error sources such as diffraction, atmospheric attenuation, turbulence, and detector inefficiency. To improve the fidelity of quantum teleportation, they proposed the use of an intermediate station for state generation or beam refocusing. Their results indicate the feasibility of free-space entanglement distribution and quantum teleportation in downlink paths up to the LEO region, and in uplink paths with the help of an intermediate station.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42005-024-01612-x
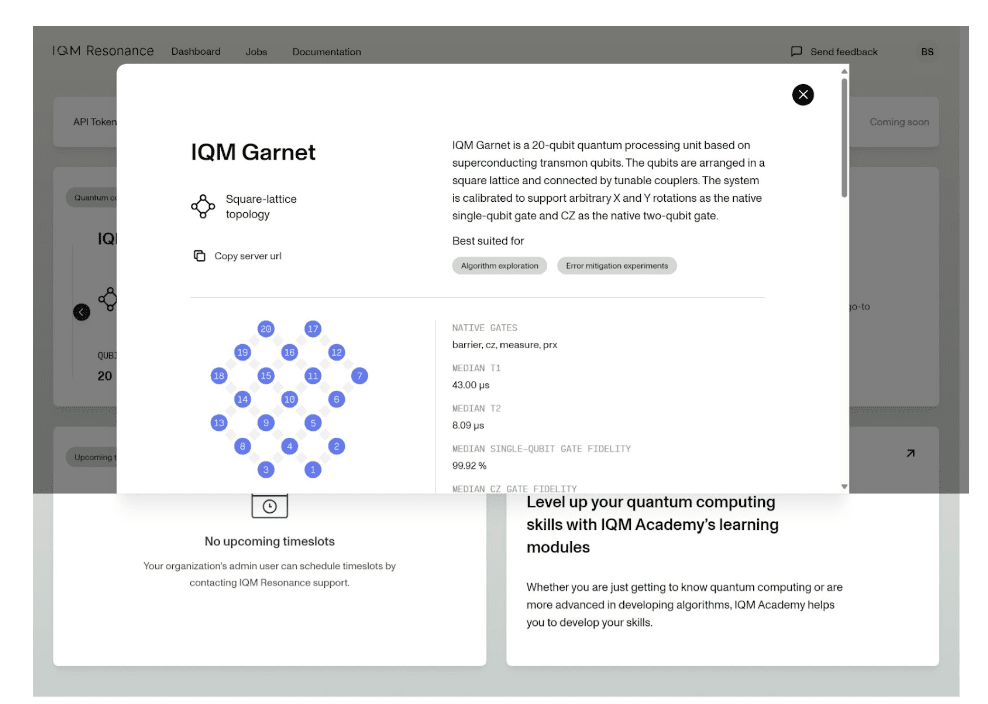
Resonating with IQM Resonance-By Brian Siegelwax
IQM Resonance offers IQM Garnet, a 20-qubit superconducting quantum computer, and IQM Deneb, a 6-qubit all-to-all-connected superconducting quantum computer. Siegelwax highlights the service's benefits, including true reservations, weekly timesharing, cost-effectiveness, and a user-friendly dashboard. He also praises its speed, ability to handle batch jobs, and coherence. However, he notes some limitations, such as constraints on batch circuits and potential dependency-related software issues. Siegelwax concludes that IQM Resonance is a viable option for quantum computing research, emphasizing its ability to complete jobs swiftly and efficiently.
Get set for World Quantum Day 2024
The third World Quantum Day, a global initiative promoting public awareness of quantum science and technology, will be celebrated on 14th April 2024. This date was chosen as "4.14" are the first three digits of Planck’s constant when rounded up. Despite a drop in private investment in quantum technology, which stood at $1.2bn in 2023, up to $50bn in public cash has already been invested globally in quantum science. Mauro Paternostro from Queens’ University Belfast suggests that the most advanced quantum technology is quantum sensing.
https://physicsworld.com/get-set-for-world-quantum-day-2024/
Quantum Kernels May Enhance Credit Scoring, Boosting FinTech and Neobank Competitiveness
A study by Falcondale LLC and Fintonic suggests Quantum Kernels could significantly improve credit scoring systems, particularly for smaller financial entities like Neobanks and FinTechs. The study introduced a novel approach, the Systemic Quantum Score (SQS), which demonstrated improved performance over data-intensive algorithms and the ability to extract patterns from fewer data points. Quantum computing techniques could optimally exploit scarce data, enhance data classification, and improve class separability, potentially speeding up machine learning techniques. This could greatly impact key business processes such as default detection or score assignment.
America is the undisputed world leader in quantum computing even though China spends 8x more on the technology but an own goal could soon erode U.S. dominance
Despite China investing eight times more in quantum computing, the U.S. remains the global leader in this field, thanks to a combination of world-class research universities, government funding, and a supportive policy environment. A key player is IonQ, a quantum computing company founded by academics from Duke and the University of Maryland, which became the first publicly-traded quantum hardware and software company, valued at $2 billion. However, this dominance could be threatened by changes to the Bayh-Dole Act, which allows universities to own patents on their inventions, potentially imposing price controls on federally-funded inventions. This could disincentivize private sector investment, jeopardizing U.S. national security and economic stability, given the transformative potential of quantum computing.