Quick Recap
Physicists from the University of Innsbruck and the Max Planck Institute introduced a new metric to evaluate quantum computers' ability to solve many-body problems, a crucial step in enhancing quantum algorithms. Rigetti Computing completed a $100 million equity offering to strengthen its superconducting quantum computing capabilities. Researchers led by Haoran Liao made strides in quantum error correction, achieving over 85% gate fidelities and creating a 75-qubit GHZ state, the largest reported to date. Quantinuum, in collaboration with Harvard and CalTech, advanced non-Abelian quantum computing with topological qubits, potentially reducing resource-intensive challenges. Alice & Bob launched Felis 1, a logical qubit emulator to advance fault-tolerant quantum computing. Investment trends in 2024 reflect a focus on quantum hardware and midstack solutions, with $7.06 billion raised across 296 funding rounds. SemiQon's cryogenic transistor promises to enhance scalability by reducing heat dissipation, and South Korea's increased investment in quantum projects highlights global interest.
The Week in Quantum Computing
Many body physics with Quantum Computers - The Metric
Physicists from the University of Innsbruck and the Max Planck Institute have developed a new metric to assess quantum computers' ability to solve many-body problems, a critical challenge in quantum physics. The metric, detailed in a recent study, evaluates quantum systems' performance in simulating complex interactions among multiple particles. "This metric provides a clearer understanding of quantum computers' capabilities," says lead researcher Peter Zoller. This development is significant as it addresses a fundamental issue in quantum computing, potentially enhancing the design and application of quantum algorithms. As quantum computing progresses in 2024, such metrics could be pivotal in bridging theoretical potential and practical application, marking a step forward in solving complex quantum phenomena.
Rigetti Announces Successful Completion of $100 Million At-the-Market Equity Offering
Rigetti Computing has successfully completed a $100 million at-the-market equity offering, aiming to bolster its position in superconducting quantum computing. CEO Dr. Subodh Kulkarni highlighted the significant interest from national labs and academic institutions in on-premises quantum computers for R&D. Rigetti's systems boast gate speeds of 60-80ns, outperforming other modalities like ion traps. The funds will support working capital, capital expenditures, and efforts to enhance 2-qubit gate fidelity and scale qubit count. Rigetti's proprietary quantum-classical infrastructure and multi-chip quantum processor are pivotal in its strategy. As Dr. Kulkarni stated, the company is poised to sustain operations through 2026, reflecting the growing momentum and potential in quantum computing.
Paper: Achieving computational gains with quantum error correction primitives: Generation of long-range entanglement enhanced by error detection
In a recent study by Haoran Liao et al., researchers have demonstrated significant advancements in quantum error correction (QEC) on superconducting processors. By employing QEC primitives without logical encoding, they achieved over 85% gate fidelities across up to 40 lattice sites, outperforming existing protocols. The team introduced a novel protocol for long-range CNOT gates using a Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger (GHZ) state, incorporating error detection via disentangled qubits. They successfully generated a 75-qubit GHZ state with genuine multipartite entanglement, the largest reported, using only 9 ancilla qubits. This approach reduces error discard rates to 78%, a notable improvement. As Michael J. Biercuk states, "This work showcases the potential of QEC primitives to enhance current quantum devices significantly."
https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.14638v1
A step forward for non-Abelian quantum computing
Quantinuum, in collaboration with Harvard and CalTech, has made significant strides in non-Abelian quantum computing, a promising approach for fault tolerance and resource efficiency. Their recent paper, following work published in Nature, demonstrates control over non-Abelian anyons and prepares the ground state of the "Z3" toric code in qutrit Hilbert space, a first in topological order preparation. This advancement could mitigate the resource-intensive challenges of quantum computing, such as T gates and magic states distillation, which can consume up to 90% of resources. Quantinuum's unique mid-circuit measurement capabilities and Quantum Charge Coupled Device (QCCD) architecture are pivotal in their research, positioning them at the forefront of achieving a universal topological gate set.
https://www.quantinuum.com/blog/a-step-forward-for-non-abelian-quantum-computing
3 Quantum Computing CEOs On The State Of Quantum Today
In November 2024, Microsoft announced a breakthrough in quantum computing with the creation of 24 logical qubits capable of error detection and correction, marking the largest logical entangled state recorded. This advancement is crucial as error correction is a significant hurdle in quantum computing. At the Web Summit in Lisbon, CEOs from Horizon Quantum, Oxford Ionics, and IQM Quantum Computers discussed the industry's challenges, emphasizing the need for integration, scalability, and investment. Joe Fitzsimons of Horizon Quantum highlighted the necessity of overcoming high error rates and developing software infrastructure. Chris Ballance of Oxford Ionics pointed out the engineering challenge of integrating quantum systems. Jan Goetz of IQM stressed the importance of capital for achieving fault-tolerant quantum computing by 2030.
Alice & Bob Enable Companies to Prepare for Practical Quantum Computing with Industry-First Logical Qubit Emulator
Alice & Bob has launched Felis 1, a pioneering logical qubit emulator, aimed at advancing fault-tolerant quantum computing. This tool provides quantum computer scientists with a comprehensive toolbox to work with fault-tolerant algorithms and predict logical qubit behavior. The announcement was made in Paris on November 26, 2024. The significance of Felis 1 lies in its potential to bridge the gap between theoretical quantum computing and practical applications, a critical step towards realizing the full potential of quantum technology.
https://alice-bob.com/newsroom/logical-qubit-emulator-felis-quantum-cloud-alice-bob/
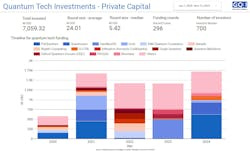
Follow the money: Two stories of quantum tech investment
In 2024, quantum tech investment reached $7.06 billion across 296 funding rounds, highlighting a dichotomy between large deals and shrinking smaller investments. PsiQuantum's $620 million Australian facility underscores this trend. Investors are focusing on quantum hardware and midstack solutions, moving away from pure-play software. IonQ's stable market cap contrasts with Zapata's closure, indicating market volatility. Strategic M&A activities, like IonQ's acquisition of Qubitekk, signal industry maturation. Manufacturing scale-up initiatives, such as IQM's facility in France, mark a shift from exploration to implementation. GQI's projections emphasize quantum-safe cryptography as a near-term catalyst, with quantum sensing targeting a 10% market share by 2027. Public funding remains crucial, bridging private caution and technological momentum, ensuring quantum tech's strategic importance.
Bridging the Quantum Divide: Ensuring Ethical Access in Developing Countries
In 2024, the quantum computing landscape is marked by significant challenges in equitable access, particularly for developing countries. Despite quantum computing's transformative potential, its infrastructure demands—such as cryogenic temperatures and ultra-high vacuum conditions—are prohibitive. This creates a stark contrast with the more accessible AI revolution, where open-source software and affordable hardware have democratized participation. Companies like QURECA and Q-CTRL are pioneering efforts to bridge this gap through accessible workforce development programs. The United Nations' declaration of 2025 as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology underscores the urgency for international collaboration, education, and policy advocacy to ensure global participation in the quantum leap. As we advance, the focus must be on inclusivity, not exclusivity.
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/bridging-quantum-divide-ensuring-ethical-access-j4vrc
SemiQon debuts Cryogenic Transistor
SemiQon has unveiled a groundbreaking cryogenic transistor designed to significantly enhance quantum computing scalability. This innovation addresses a major hurdle in achieving fault-tolerant quantum computers by reducing heat dissipation by 1,000 times, allowing control electronics to be placed inside cryostats without disruption. CEO Himadri Majumdar highlights the transistor's potential to cut both capital and operational expenses, potentially accelerating quantum technology development. The transistor operates efficiently at 1 Kelvin, consuming just 0.1% of the power of traditional transistors, offering substantial energy savings. Erja Turunen from VTT emphasizes its importance in making deep-tech innovation profitable. SemiQon plans to deliver these transistors by 2025, marking a pivotal step toward more efficient and cost-effective quantum computing.
South Korea invests in 24 quantum projects
In 2024, South Korea plans to invest 2,004 billion won in 24 quantum projects, marking an increase of 7 projects and 719 billion won from the previous year. Announced at the Korean Quantum Industry Leaders Forum, organized by KISTI and KQIA, the focus includes quantum computing, communication, and sensing. Notable projects include the Quantum Science and Technology Flagship with 98 billion won for computing and 154 billion won for communication. Jeon Seok-nam from the Ministry of Science and ICT emphasized the strategic importance of these investments, stating they are "priming water" for future developments. As the global quantum race accelerates, South Korea's strategic funding aims to secure a competitive edge in this rapidly evolving field.
https://zdnet.co.kr/view/?no=20241128085823
200 million yen prize for bold ideas in quantum computing test
The New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) has announced a competition offering a 200 million yen ($1.3 million) prize for innovative quantum computing solutions to societal issues in Japan. Scheduled for March 2025, the contest aims to attract diverse talents, including those without prior quantum computing experience, to address challenges like natural disasters and an aging population. Participants can compete individually or in groups, with the top solutions for each issue receiving at least 20 million yen. NEDO's initiative seeks to mitigate talent shortages in quantum computing by encouraging fresh perspectives from various fields.
https://www.asahi.com/ajw/articles/15497153
Vodafone explores quantum computing for network optimisation
Vodafone has partnered with six other prominent companies in Digital Catapult's innovation accelerator to explore quantum computing for network optimization. This initiative underscores the growing interest in leveraging quantum technology to enhance telecommunications infrastructure. While the specifics of the quantum solutions being explored remain undisclosed, the collaboration highlights a strategic move by Vodafone to potentially revolutionize its network capabilities. The involvement of Digital Catapult, a key player in fostering technological innovation, adds credibility to the endeavor. As quantum computing continues to evolve, its application in optimizing complex networks could mark a significant shift in the telecommunications industry.
https://www.telecomstechnews.com/news/vodafone-explores-quantum-computing-network-optimisation/
France to buy Atos supercomputing, quantum business for €625m
In a strategic move, the French government has proposed a €625 million acquisition of Atos' supercomputing and quantum computing business, with an initial €500 million offer and an additional €125 million contingent on meeting specific targets. This acquisition is part of Atos' restructuring efforts, expected to conclude by early 2025. The business, employing around 2,500 people, generated €570 million in revenue in 2023 and is pivotal in European supercomputing, including systems like JUWELS in Germany. The deal underscores France's commitment to advancing its quantum computing capabilities and securing technological sovereignty. As Nick Flaherty reports, this move could significantly impact the European quantum landscape, emphasizing the importance of strategic national investments in emerging technologies.
https://www.eenewseurope.com/en/france-to-buy-atos-supercomputing-quantum-business-for-e1-1bn/
Iceberg Research Slams Quantum Computing (NASDAQ:QUBT) Stock in New Short Report
Iceberg Research has released a critical short report targeting Quantum Computing (NASDAQ:QUBT), maintaining its bearish stance on the stock. This move underscores ongoing skepticism about the commercial viability and near-term profitability of quantum computing ventures. Iceberg's analysis suggests that despite the technological promise, companies like QUBT face significant hurdles in translating quantum advancements into sustainable business models. The report reflects broader industry concerns about the pace of quantum development and its readiness for market disruption. As quantum computing continues to evolve, the tension between scientific breakthroughs and commercial application remains a focal point, highlighting the gap between potential and practical implementation in 2024.
Physicists propose new approach that could unlock barriers to global scale quantum network
In a significant development for quantum computing in 2024, physicists have proposed a novel approach to overcome the limitations of satellite quantum key distribution (SatQKD), which is crucial for establishing a global quantum network. Currently, SatQKD is hindered by daylight noise, restricting its operations to nighttime and thus limiting its potential applications and connectivity. This new method could potentially enable 24/7 operations, enhancing the feasibility of a global quantum network. As quantum networks are pivotal for secure communications and advanced computational capabilities, overcoming this barrier is crucial.
https://phys.org/news/2024-11-physicists-approach-barriers-global-scale.html
Quantum computing as a field is obvious bullshit
In a scathing critique of the quantum computing field, Scott Locklin argues that despite significant investment and research over decades, tangible progress remains elusive. He highlights that no quantum computer has yet achieved a usefully error-corrected qubit, a fundamental requirement for practical quantum computing. Locklin criticizes major companies like IBM, Google, and Microsoft for funding what he deems a "scam," noting that half a million papers have been published without delivering a functional quantum computer. He draws parallels to the unfulfilled promises of nanotechnology, suggesting that quantum computing lacks a clear path to practical implementation. Locklin's skepticism underscores the need for breakthroughs in quantum coherence and error correction to validate the field's potential.
https://scottlocklin.wordpress.com/2019/01/15/quantum-computing-as-a-field-is-obvious-bullshit/
IQM to deploy a quantum computer in Taiwan
IQM Quantum Computers has announced plans to deploy a quantum computer in Taiwan, marking a significant milestone for the region's quantum technology landscape. This initiative is in collaboration with Taiwan's Ministry of Science and Technology and the Industrial Technology Research Institute. The deployment aims to bolster Taiwan's quantum research capabilities and foster innovation in quantum computing applications. IQM's CEO, Jan Goetz, emphasized the importance of this partnership, stating, "This collaboration will accelerate quantum technology development in Taiwan and create new opportunities for researchers and industries." This move underscores the growing global interest in quantum computing and highlights Taiwan's commitment to advancing its technological infrastructure.
https://www.datacenterdynamics.com/en/news/iqm-to-deploy-quantum-computer-in-taiwan/
Kick-off into the quantum age:O2 Telefonica enhances mobile network efficiency and security with quantum technologies on AWS
In a pioneering move, O2 Telefónica has integrated quantum technologies into its mobile network, leveraging Amazon Web Services (AWS) to enhance efficiency and security. This initiative, involving Telefónica SA, AWS, Telefónica Tech, and Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, marks one of the first global efforts to test quantum technologies in a cloud environment. The project aims to optimize network infrastructure in Munich using quantum computing to solve complex optimization problems, such as tower placement, and employs quantum-resistant encryption to secure data. Mallik Rao, O2 Telefónica's Chief Technology & Enterprise Officer, emphasizes the transition to "quantum-safe mobile networks," highlighting the necessity of advanced security in the 6G era. This collaboration underscores the transformative potential of quantum technologies in telecommunications.
Collaborative R&D
In 2024, the National Quantum Computing Centre (NQCC) is spearheading several collaborative R&D projects to advance quantum computing applications across various sectors. Notable initiatives include using quantum algorithms for Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations in aerodynamics, which could revolutionize aerospace design. Another project explores Quantum Machine Learning (QML) for early cancer detection, potentially transforming healthcare diagnostics. The NQCC is also investigating quantum solutions for fraud detection in financial transactions and optimizing renewable energy systems. These projects aim to demonstrate quantum advantage in real-world applications, addressing complex computational challenges.