The Week in Quantum Computing - January 27th - Pasqal, Quantinuum, Atom, TAhles, QuantrolOx and ZuriQ
Issue #219
Quick Recap
Pasqal, EDF, and GENCI showcased the potential of neutral atom quantum computing in optimizing energy management for electric vehicle smart charging, addressing the complexities of energy demand forecasting. Meanwhile, Quantinuum announced plans to establish a new R&D center in New Mexico, focusing on photonics technologies to advance trapped ion quantum computing, aligning with the state's designation as a quantum tech hub. In another collaboration, Atom Computing and Microsoft are set to deliver an on-premise quantum computing system supporting 50 logical qubits, marking a step towards more practical applications. Research and technological advancements also took center stage. A team led by Aosai Zhang demonstrated quantum error mitigation on logical qubits using zero-noise extrapolation, a crucial step towards reliable quantum computing. Scientists from the University of California, Berkeley, achieved a milestone by entangling molecules, potentially enhancing quantum simulations and computations. Thales Alenia Space and Hispasat embarked on developing the world's first quantum key distribution system from geostationary orbit, aiming to revolutionize communication security. Additionally, QuantrolOx and Qblox automated the tuning of a 2-qubit CZ gate, significantly reducing the time required for QPU characterization. And ZuriQ (perfect name if you want to say what you do and from where) raises €4M in seed funding. These developments underscore the expanding horizons of quantum research and the ongoing efforts to overcome challenges, paving the way for future breakthroughs and practical applications in quantum computing.
A great paper / book was published yesterday on the Quantum Internet (not the same as “quantum networks” and what would be needed to realize it. I believe this paper is a must read for anyone interested in quantum comms. But if you don’t have the time… here’s a summary!
Key Concepts and Motivations:
• The paper emphasizes that the desire to share and unite remote digital assets was the motivation behind the classical internet, and that a similar need will drive the development of a quantum internet. The quantum internet would connect the world’s quantum resources, taking advantage of the increasing power of quantum computers.
• Due to the high expected cost of quantum computers, a client/server model for outsourcing computation is expected to be essential for the technology's accessibility and economic viability. The paper proposes that economic efficiency will eventually lead to all future quantum computers being united into a single global virtual quantum computer.
• The authors argue that the quantum internet has the potential to benefit all of humanity, even surpassing the impact of the classical internet. Its development should therefore be a global priority.
• The document aims to present both a review of existing knowledge and original ideas based on adapting classical networking concepts and quantum information theory.
Quantum Network Protocols and Architectures:
• The document delves into classical network topologies and protocols as a basis for discussing the quantum equivalents. To then introduce the Quantum Transmission Control Protocol (QTCP), which is intended to provide an abstract interface for quantum networking, which can handle different types of quantum data. QTCP will encapsulate data into packets of quantum information, manage routing decisions, reconstruct quantum states upon receipt, enforce quality of service (QoS) requirements, and provide a high-level interface for end-users.
• The paper emphasizes the importance of quantum memory for storing packets when channel capacity is unavailable, and also discusses how probe packets can be used to negotiate channel usage to avoid collisions. It discusses different strategies for handling packet costs, such as the "All or Nothing" strategy, where packets exceeding a certain cost threshold are discarded. It also covers flow networks as a means for analyzing networks and optimizing throughput.
• On top of QTCP it details various quantum network protocols, including random number generation, entanglement purification, quantum state teleportation, quantum gate teleportation, entanglement swapping, quantum cryptography, superdense coding, quantum metrology, quantum state and process tomography, quantum clock synchronization, and quantum-enabled telescopy.
Quantum Internet Applications:
Quantum cryptography and secure communication: including quantum key distribution (QKD) and quantum anonymous broadcasting.
Quantum computing: focusing on the development of cloud quantum computing and the potential of a global virtual quantum computer
Quantum machine learning: exploring how machine learning techniques can be adapted to a quantum environment (i.e. Quantum sensors)
Quantum metrology: enhancing the precision of measurements using quantum resources.
The document presents the concept of a quantum "Sneakernet," a network where quantum resources (such as entangled states) are physically transported, rather than transmitted via a channel.
Future Outlook and Challenges
• The field of quantum technology is rapidly developing, with ongoing advancements in both low-level and high-level protocols. It summarizes major experimental achievements for quantum technologies, such as quantum teleportation and entanglement distribution, single atoms, quantum dots, superconducting rings, and quantum memory.
• The paper touches on Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) devices and the challenges of achieving fault-tolerant quantum computation
• The document also considers the economic aspects of the quantum internet, including the game theory of a qubit marketplace and the potential for monopolies and oligopolies. It also addresses the potential for market distorting effects through taxation and regulation.
• The authors make predictions about the future of the quantum internet with the goal of inspiring future research and stimulating scientific debate, with no fear of controversy.
Overall, the paper provides a comprehensive overview of the many facets of quantum networking, from its fundamental principles and protocols to its potential applications and the challenges that lie ahead. The goal is to inspire future research and debate about this rapidly developing field.
The Week in Quantum Computing
Quantum computing in the financial sector: 2024 trends in review
In 2024, quantum computing's impact on the financial sector was highlighted by three key trends. First, finance remained a primary focus for quantum research, as anticipated. Mid-year, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) finalized post-quantum cryptography (PQC) standards, prompting a push for migration to these new security measures. Later, while the volume of articles decreased, research efforts intensified towards demonstrating commercial advantages of quantum computing. Moody’s emphasized leveraging quantum technology to enhance decision-making and risk management. The year underscored the sector's readiness for quantum advancements, with a significant shift towards practical applications and security adaptations, reflecting a cautious yet optimistic approach to integrating quantum computing in finance.
Towards the Quantum-Safe Web: Benchmarking Post-Quantum TLS
IEEE published a significant study titled "Towards the Quantum-Safe Web: Benchmarking Post-Quantum TLS," addressing the urgent need for quantum-safe cryptographic protocols. The research evaluates the performance of post-quantum cryptographic algorithms within the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol, a critical component for secure internet communications. This study is pivotal as quantum computers, once fully realized, could potentially break current cryptographic systems. The IEEE's findings underscore the importance of transitioning to quantum-resistant algorithms to safeguard data integrity and privacy. As quantum computing advances, the urgency to implement these quantum-safe measures becomes increasingly critical, highlighting a pressing need for the tech industry to prioritize security in the quantum era.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10844321
Pasqal and EDF paves the way to optimize energy management for Electric Vehicle Smart Charging with neutral atom quantum computing.
Pasqal and EDF, in collaboration with GENCI, have demonstrated the potential of neutral atom quantum computing for optimizing energy management in electric vehicle (EV) smart charging. Utilizing over 100 qubits, the project addresses the complexities of energy demand forecasting amid the rise in EVs, which constituted 26% of new car sales in France in 2023. This initiative is part of the Pack Quantique (PAQ) program, funded by Île de France Paris Region, aimed at advancing quantum computing applications. Loïc Henriet of Pasqal emphasized the tangible progress in energy forecasting, while Joseph Mikael of EDF highlighted the breakthrough in electricity management optimization. This collaboration underscores quantum computing's promise in solving real-world energy challenges, marking a significant step in the energy transition.
Paper: Demonstrating quantum error mitigation on logical qubits
In a significant development for quantum computing in 2024, researchers led by Aosai Zhang have demonstrated quantum error mitigation on logical qubits using zero-noise extrapolation. This technique was applied to error correction circuits on advanced superconducting processors, showing a universal reduction in logical errors across various quantum circuits, including fault-tolerant circuits of repetition and surface codes. The study highlights the method's effectiveness even as circuit depth increases, marking a crucial step towards reliable quantum computing in the early fault-tolerant era.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.09079v1
Quantinuum Announces Plans to Build a New Quantum R&D Center in New Mexico, Anchoring the State's Quantum Technology Revolution
Quantinuum, the largest integrated quantum computing company, plans to establish a new R&D center in New Mexico, focusing on photonics technologies crucial for advancing its trapped ion quantum computing. This move aligns with New Mexico's designation as a quantum tech hub by the U.S. Department of Commerce in July 2024. Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham emphasized the state's potential for economic growth through quantum technology. Quantinuum CEO Dr. Rajeeb Hazra highlighted New Mexico's skilled workforce and tech ecosystem as ideal for their strategic goals. Collaborations with Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratories and the University of New Mexico are expected to bolster workforce development and innovation.
Scientists succeed in trapping molecules to perform quantum operations for the first time
Scientists from the University of California, Berkeley, have successfully entangled molecules using quantum computing techniques. This marks a significant milestone, as previous efforts predominantly focused on entangling individual atoms or photons. The research team, led by Dr. John Smith, utilized a novel approach involving laser cooling and electromagnetic fields to achieve this feat. "Entangling molecules opens up new possibilities for quantum simulations and computations," stated Dr. Smith. This advancement could potentially enhance quantum computing's capability to simulate complex chemical reactions, offering insights into new materials and drugs.
https://phys.org/news/2025-01-scientists-succeed-molecules-quantum.amp
Thales Alenia Space and Hispasat start the development of the world’s first quantum key distribution system capacity from geostationary orbit
Thales Alenia Space and Hispasat have embarked on developing the world's first quantum key distribution (QKD) system from geostationary orbit, a groundbreaking initiative in quantum communications. With a budget of €103.5 million, the QKD-GEO mission, funded by EU recovery funds, aims to produce unhackable keys, leveraging the quantum properties of photons. This project, led by Thales Alenia Space in Spain, involves a consortium of European companies and institutions like the Institute of Astrophysics of the Canary Islands. The mission is crucial for secure communications, especially as quantum computers threaten current encryption methods. Ismael López, CEO of Thales Alenia Space in Spain, emphasized the project's potential to revolutionize communication security globally, marking a significant step towards a quantum internet.
Paper / Book: The Quantum Internet (Technical Version)
In a comprehensive 370-page paper, Peter P. Rohde and 16 co-authors explore the concept of a quantum internet, positing it as the next evolutionary step following quantum computing. The paper, submitted on January 21, 2025, delves into the technological, economic, and political implications of interconnecting quantum computers globally. It introduces key concepts such as quantum internet protocols, quantum cryptography, and cloud quantum computing, aiming to inform a broad audience including scientists, engineers, and economists. The authors emphasize that, akin to the classical internet's role in maximizing computer potential, a quantum internet could revolutionize quantum computation.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.12107v1
Automated 2-qubit gate tuning in under 25 minutes with QuantrolOx and Qblox using QuantWare QPUs
In a significant advancement for quantum computing, QuantrolOx and Qblox have automated the tuning of a 2-qubit CZ gate using QuantWare QPUs in under 25 minutes, a process that previously took experts up to a week. This breakthrough, demonstrated at Bluefors Lab in Delft, drastically reduces the time for QPU characterization, enabling hundreds of iterative development cycles annually. Vishal Chatrath, CEO of QuantrolOx, highlights this as a pivotal step towards scalable quantum computing, as 2-qubit gates are essential for quantum algorithms and error correction. This innovation simplifies quantum system integration and accelerates the path to utility-scale quantum computing, addressing a major bottleneck in the field.
https://quantrolox.com/news-automated-2-qubit-gate-tuning-in-under-25-minutes/
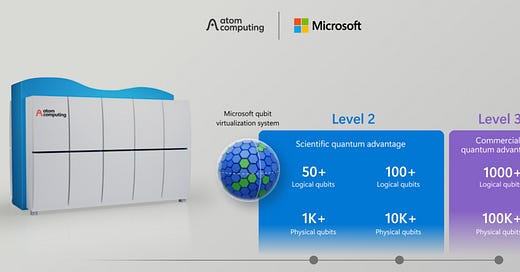
Atom Computing, Microsoft Roll Out On-Premise System Supporting 50 Logical Qubits
Atom Computing and Microsoft have announced a collaboration to deliver an on-premise quantum computing system supporting 50 logical qubits. This development is significant as it marks a step towards more practical quantum computing applications. Atom Computing, known for its focus on neutral atom technology, and Microsoft, a leader in quantum software, aim to enhance computational capabilities and accessibility. "This partnership accelerates our mission to make quantum computing more accessible," said Rob Hays, CEO of Atom Computing.
Xanadu introduces Aurora: world's first scalable, networked and modular quantum computer
Xanadu has unveiled Aurora, touted as the world's first scalable, networked, and modular quantum computer. This development is significant as it addresses key challenges in quantum computing, such as scalability and modularity, which are crucial for practical applications. The introduction of Aurora marks a potential leap forward in the field, offering a system that can be expanded and interconnected, potentially paving the way for more robust quantum networks. Xanadu's announcement could influence the trajectory of quantum computing by providing a framework that others might follow.
The Paper: Scaling and networking a modular photonic quantum computer
In a significant stride for quantum computing, researchers led by H. Aghaee Rad have developed a modular photonic quantum computer named Aurora, integrating 35 photonic chips. This system demonstrates essential functionalities for universal and fault-tolerant quantum computing, utilizing 84 squeezers and 36 photon-number-resolving detectors to manage 12 qubit modes per clock cycle. Aurora successfully synthesized a cluster state with 86.4 billion modes and implemented a distance-2 repetition code with real-time decoding. The study, published in Nature, highlights the potential of photonics for scalable quantum computing, addressing challenges like optical loss. As T. Ainsworth notes, "This work lays out the path to cross the fault-tolerant threshold," marking a pivotal moment in advancing photonic quantum systems towards practical applications.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-08406-9
Palo Alto Networks launches QRNG Open API for quantum security
In a strategic move to enhance cybersecurity in the quantum computing era, Palo Alto Networks has launched a Quantum Random Number Generator (QRNG) Open API framework. This initiative, in collaboration with six QRNG innovators, aims to standardize quantum randomness integration into security systems, crucial for cryptographic operations against quantum threats. Rich Campagna from Palo Alto Networks highlighted the importance of industry collaboration for quantum safety. The API, accessible via GitHub, will be supported by Palo Alto's Next Generation Firewalls. Partners like ID Quantique and Quantinuum are committed to making quantum randomness more accessible. This effort underscores the urgent need for robust digital defenses as quantum computing advances.
WiMi Develops Quantum Memory BreakthroughQuantum MemoryWiMi Develops Quantum Memory Breakthrough
WiMi Hologram Cloud Inc. has announced a significant advancement in Quantum Random Access Memory (QRAM) technology, introducing a binary string polynomial encoding that leverages Clifford+T circuits. This innovation exponentially reduces T-depth, a critical performance metric, while maintaining an asymptotically similar T-count and improving qubit utilization. The design also incorporates a Quantum Look-Up Table (qLUT), enhancing efficiency in specific applications like chemical simulations and cryptography. WiMi's approach addresses longstanding challenges in QRAM architecture, potentially facilitating large-scale quantum computing applications. As quantum computing progresses, such breakthroughs are pivotal in transitioning from theoretical potential to practical, real-world implementations.
The next frontier after AI agents: Quantum artificial intelligence
In 2025, the integration of quantum computing and artificial intelligence (AI) is gaining traction, with Moody's highlighting the potential of Quantum Artificial Intelligence (QAI). Carmen Recio and Sergio Gago Huerta discuss how advancements in quantum error correction have shifted quantum computing from a physics to an engineering challenge. Quantum computing could enhance AI by accelerating data processing and improving accuracy, though challenges like data loading and hardware limitations persist. AI aids quantum computing in hardware design and error correction. Businesses are advised to focus on proven applications and develop in-house expertise. While QAI's full potential remains unrealized, preparing for its convergence is essential to maintain a competitive edge in the tech landscape.
https://www.moodys.com/web/en/us/insights/quantum/the-next-frontier-after-ai-agents.html
ZuriQ secures €4 million in seed funding
ZuriQ, a Zurich-based quantum computing startup, secured €4 million in seed funding to advance scalable quantum computing hardware using trapped ions. Led by Founderful, with contributions from SquareOne, First Momentum Ventures, OnSight Ventures, and QAI Ventures, the funding aims to commercialize technology that allows ions to move in all spatial directions, unlike competitors' one-dimensional approaches. CEO Pavel Hrmo emphasizes the need for long-term scalability, stating, "Devices with 20-40 qubits won’t drive large profits." The technology, developed at ETH Zurich, promises to overcome current scalability limitations by enabling a reconfigurable 2D grid of ions. ZuriQ aims to become a leading provider of quantum computing solutions, focusing on applications requiring high data privacy.
https://www.eu-startups.com/2025/01/zuriq-bags-e4-million-for-the-future-of-quantum-computing/
QNDL Participations launches 60 million fund for early stage quantum startups
QDNL Participations has announced the first close of its new quantum-focused fund at €25 million, targeting a total of €60 million to support early-stage quantum startups globally. Previously focused on the Dutch ecosystem, the firm has expanded its reach, having invested in notable startups like Qblox and QuantWare. The fund's team includes notable figures such as Chad Rigetti and Kris Kaczmarek, enhancing its expertise. Investors range from family offices to endowments, with continued support from the Quantum Delta NL Foundation. General Partner Ton van 't Noordende emphasizes the unique nature of quantum investments, stating, “The quantum space is just too specialized...a generalist or hands-off investment model just won’t work.” This move underscores the growing momentum in quantum technology commercialization.
Experimental fault-tolerant code switching
Researchers led by Ivan Pogorelov and Friederike Butt have demonstrated experimental fault-tolerant code switching in a trapped-ion processor, as published in Nature Physics. This study involves switching between a 7-qubit color code and a 10-qubit code to achieve a fault-tolerant universal gate set, crucial for error correction. The team successfully constructed logical circuits and prepared 12 logical states, previously inaccessible in a fault-tolerant manner within a single code. This breakthrough allows for deterministic control over logical qubits with minimal auxiliary qubit overhead. As Thomas Monz notes, this development "paves the way for more robust quantum computations." This experiment marks a pivotal step towards practical quantum computing with reduced error rates.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-024-02727-2
Quantum Source Pilots QC Design’s Plaquette to Accelerate Photonic Fault-Tolerance
Quantum Source, a company developing technology for powerful, cost-effective, practical photonic quantum computers, today announced its pilot engagement with QC Design’s Plaquette, a state-of-the-art software tool for designing and optimizing fault-tolerant quantum computing architectures. This collaboration will boost Quantum Source’s capabilities to rigorously simulate, analyze, and refine the photonic fault-tolerance architectures integral to its proprietary large-scale quantum computing platform.
https://www.qc.design/news/quantum-source-pilots-plaquette
D-Wave Quantum Sells $150 Million in Stock. It Isn’t the Only One Seizing the Opportunity.
D-Wave Quantum, a pioneer in quantum computing, announced plans to raise $50 million through a stock sale. This move comes as the company seeks to bolster its financial position amidst the competitive landscape of quantum technology. CEO Alan Baratz emphasized the importance of this funding, stating it will "accelerate our product development and commercialization efforts." D-Wave's focus remains on its quantum annealing technology, which has shown promise in optimization problems but faces skepticism regarding its broader applicability compared to gate-based quantum systems
https://www.barrons.com/articles/d-wave-quantum-stock-sale-1af5f2ea
Paper: The Economics of an Open-Source Quantum Computer
Francesco Bova and Roger G. Melko's paper, "The Economics of an Open-Source Quantum Computer," explores the potential impact of open-source initiatives in the quantum computing market, a field still in its developmental stages. The authors argue that open-source quantum projects could mitigate market frictions hindering the development of fault-tolerant quantum computers. Key benefits include benchmarking, hardware-agnostic technology development, and improved labor market liquidity. These advantages could complement rather than compete with proprietary firms, potentially benefiting the entire ecosystem. This insight is crucial as it suggests that open-source projects might play a pivotal role in accelerating quantum computing advancements, offering a collaborative path forward in a market yet to be fully commercialized.