The Week in Quantum Computing - January 8th
Issue #168
The Week in Quantum Computing. Brought to you by Sergio Gago (@piratecto).
Quick Recap
Lovely first week of the year! Two great papers dig deeper into the challenges of quantum (and AI-Quantum) computing. A piece in Nature and a paper titled “Quantum House of Cards”. Both are worth a read if you are investing your company’s money or your own. This week was the turn of China to distill a “magic logical qubit” on top a 66-qubit device. Right before releasing their 3rd generation device “Origin Wukong”, developed by Origin Quantum Computing Technology with 72 qubits.
Staying in China. If Alibaba closed recently their quantum operations, now it has been the turn of Baidu following suit. What does this mean for the quantum efforts in China? Deinvesting or smoke and mirrors?
JPMorgan released QOKit—a Python library implementing a fast QAOA simulator that works over cuQuantum. It seems that the best chances we have now are simulating with GPUs. Brenno Boer has left Pasqal to start a company that apparently goes in that direction. Meanwhile Rigetti has launched their Ankaa-2 and a collaboration with Moody’s to work in QML for Finance.
So, even though we have seen fantastic advances in error correction, it does not seem we are necessarily close to advantage yet. Look at the results from the question I asked you a couple of weeks ago:
Dulwich Quantum, with its usual satirical style has reviewed Nature’s paper showing a comparison: What the scientists say vs what quantum CEOs say. Really worth a read:
https://twitter.com/DulwichQuantum/status/1743602089635312081?t=WDYRUDq4NZSUpwZdsrGw0g&s=09
So, for the first proper post of 2024. Do we have quantum business advantage yet?
NO
But keep working on your algorithms, hardware and QEC so we can get it ASAP. Before you make any decision in Quantum, ask yourself: What incentives does the person in front of you have?
The Week in Quantum Computing
China and Russia test ‘hack-proof’ quantum communication link for Brics countries
The scientists were able to span 3,800km (2,360 miles) between a ground station close to Moscow and another near Urumqi in China’s western Xinjiang region to send two encoded images secured by quantum keys.
https://ift.tt/v1NEViO
Innovation L’ordinateur du futur se construit a Strasbourg
The future of computing is being constructed in Strasbourg at the recently inaugurated European Center for Quantum Sciences (Cesq). Scientists, including Professor Shannon Whitlock and CNRS researcher Tom Bienaimé, are developing a processor that does not rely on the traditional binary coding (0/1) of bits but uses quantum objects, specifically atoms. This quantum technology, controlled by lasers, positions the Cesq in the global competition to establish the computing standard of tomorrow. The future of computing may well be rooted in quantum science, with Strasbourg leading the way.
BlockEnRoll™ Revolutionizes Supply Chain Engineering Offering An Innovative Software Cartridge Architecture With Classical + Quantum Computing Augmentation Features
Turret Labs has launched BlockEnRoll™, a groundbreaking platform aimed at transforming supply chain network engineering. The platform employs a new generation AI+ML Software Cartridge Architecture and integrated Blockchain Platform with Lakehouse Technology. The Software Cartridge Architecture (SCA) allows businesses to expand their supply chain management software alongside existing ERP systems, offering plug-and-run capability. The platform includes IoT sensor validation, Blockchain verification, Data Lakehouse based AI+ML intelligence, and Quantum-As-A-Service technology. It also provides scalability, modularity, and integration with third-party applications such as Microsoft Dynamics 365 SCM, Oracle SCM, and IBM SCIS. This innovation from Turret Labs signifies a generational transformation in supply chain engineering.
Wow. That is a mouthful… I wonder if there is anything this platform does NOT have.
The AI-quantum computing mash-up: will it revolutionize science?
Quantum machine learning, an amalgamation of artificial intelligence and quantum computing, is being explored by technology giants like Google and IBM, as well as startups like Rigetti and IonQ. Academic institutions like CERN are also investigating its potential. The aim is to leverage quantum computers to enhance classical machine-learning models. However, it remains uncertain whether quantum machine learning offers advantages over traditional methods. Researchers have developed quantum algorithms over the past two decades that could potentially increase machine learning efficiency, but some have failed to deliver on their promise. The focus is now shifting towards applying quantum machine-learning algorithms to inherently quantum phenomena.
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-04007-0
Cloud-based Quantum Computing Market projected to reach USD 6,289.8 Million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 35.5% during the forecast period of 202 : 030 : says MarketDigits in its latest study
The global cloud-based quantum computing market is expected to surge from USD 750 million in 2023 to USD 6,289.8 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 35.5%, according to a report by MarketDigits. The study highlights the increasing demand for advanced computational capabilities and faster data operations as key drivers. Major players in the market include Accenture, Amazon Web Services, Baidu, Cambridge Quantum Computing, and D-Wave Quantum Inc. North America, particularly the US and Canada, dominates the market due to the presence of key quantum computing companies and significant R&D initiatives. The research emphasizes the transformative potential of cloud-based quantum computing across various industries.
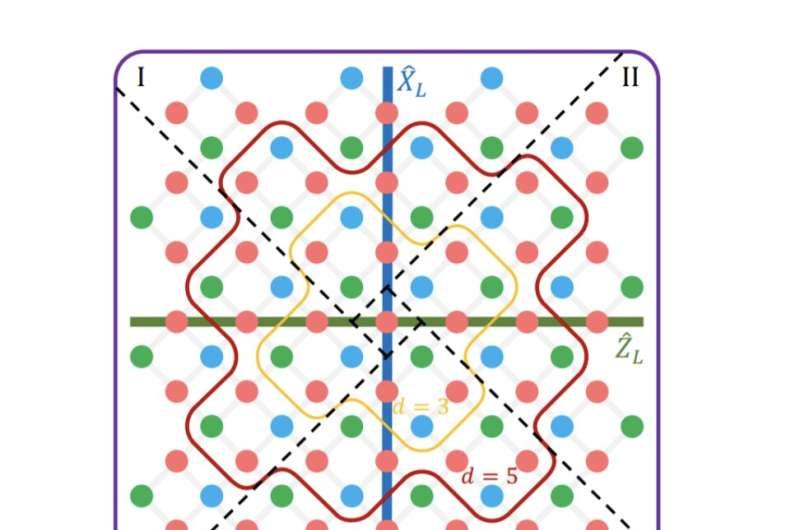
A logical magic state with fidelity beyond distillation threshold realized on superconducting quantum processor
Researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China, Henan Key Laboratory of Quantum Information and Cryptography, and the Hefei National Laboratory have successfully prepared a logical magic state with fidelity surpassing the distillation threshold on a superconducting quantum processor. The team achieved this milestone on the Zuchongzhi 2.1, a 66-qubit quantum processor, by preparing three logical magic states with high fidelities, exceeding the state distillation protocol threshold. Professor Xiao-Bo Zhu, a co-author of the study, stated that their protocol outlines a scalable strategy for preparing high-fidelity raw magic states, marking a critical step towards fault-tolerant quantum computing.
https://phys.org/news/2023-12-logical-magic-state-fidelity-distillation.html
Predictions for 2024. What exciting developments could happen in Quantum Computing in the Coming 12 Months?
The Quantum Mechanic predicts significant advancements in quantum computing for 2024. Qubit count is expected to double from 1,000 to 2,000 by the year's end. IBM Quantum Computing, with its popular Qiskit platform, is predicted to maintain its leading position, despite competition from Amazon's AWS Braket. The NISQ era of error-prone quantum devices may be concluding, with more logical error-corrected qubits being developed by Quera Computing. Zapata AI, partnered with Amazon, Google, IBM, NVIDIA, and others, aims to become publicly listed. Quantum computing is expected to gain mainstream coverage, with public quantum companies like IBM, Google, Intel, IonQ, Rigetti, D-Wave, and soon Zapata AI, gaining visibility. Despite the predicted rise in quantum hype, the Quantum Mechanic also anticipates an increase in anti-hype.
https://quantumzeitgeist.com/predictions-for-2024/
Paper: The Quantum House Of Cards
Xavier Waintal's paper, "The Quantum House Of Cards", critically examines the technical challenges that quantum computing faces. Despite the potential of quantum computers to tackle complex problems like drug discovery and encryption, they currently struggle with basic tasks like multiplying 3 by 5. Waintal discusses the whole stack of technologies needed to build a quantum computer, from the top layers (algorithms and applications) to the bottom ones (hardware, control electronics, cryogeny), including the crucial intermediate layer of quantum error correction. The paper, supported by the Simons Foundation, underscores the significant hurdles that must be overcome for quantum computers to fulfill their promised potential.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.17570v1
Paper: Overcoming the Coherence Time Barrier in Quantum Machine Learning on Temporal Data
A team of researchers led by Fangjun Hu, Saeed A. Khan, and Nicholas T. Bronn have developed a machine learning algorithm, NISQRC, to overcome the coherence time barrier in quantum machine learning on temporal data. The algorithm balances input encoding steps and mid-circuit measurements, enabling processing of temporal data over durations not limited by the finite coherence times of constituent qubits. The NISQRC algorithm also overcomes information scrambling or thermalization in monitored circuits. Validated through experiments on a 7-qubit quantum processor and numerical simulations, the team demonstrated that the test signal length can be arbitrarily long, not limited by the coherence time. This advancement could redefine the boundaries of quantum processing capabilities.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.16165v1
Paper: Tensor Networks for Explainable Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Borja Aizpurua and Roman Orus have developed an unsupervised clustering algorithm based on Matrix Product States (MPS) for enhancing the explainability of machine learning algorithms in cybersecurity. Their research, supported by the Simons Foundation, shows that MPS can match traditional deep learning models like autoencoders and GANs in performance while offering superior model interpretability. The approach allows for the extraction of feature-wise probabilities, Von Neumann Entropy, and mutual information, providing a unique narrative for anomaly classification and boosting transparency in AI decision-making processes. This development signifies a critical step towards understanding the rationale behind AI decisions in cybersecurity.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.00867v1
Baidu to donate quantum computing lab, equipment to Beijing institute
BEIJING, Jan 3 (Reuters) - China's Baidu (9888.HK) plans to donate a quantum computing laboratory and equipment to the government-backed Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences (BAQIS), a company spokesperson said on Wednesday.
Both parties are currently working out the details, the spokesperson added.
Baidu's move followed that of its peer Alibaba (9988.HK), which in November had said it would wind down its quantum computing laboratory and team within its research arm amid a broader company restructuring, donating both the lab and related experimental equipment to Zhejiang University.
Quantum-Enhanced Machine Learning with Moody’s Analytics
Rigetti Computing, a pioneer in full-stack quantum computing, has announced a collaboration with Moody's Analytics to develop quantum machine learning methods for the financial sector. The partnership builds on Rigetti's initial findings, shared in April 2023, of their novel approach to forecasting recessions using machine learning techniques developed with Moody's and Imperial College London. In 2024, they plan to use higher-dimensional datasets from various macroeconomic areas, leveraging Rigetti's 84-qubit Ankaa™ system. Sergio Gago, MD of AI and Quantum Computing at Moody's, highlighted the partnership's value in advancing their quantum computing strategy. Rigetti's CEO, Dr. Subodh Kulkarni, emphasized the importance of industry collaboration for improving quantum computing systems for real-world applications.
https://medium.com/rigetti/quantum-enhanced-machine-learning-with-moodys-analytics-543d37df0549
Flawed proof rocks quantum information theory
The discovery of a flaw in the proof of a 15-year-old lemma has rocked the community of researchers who study quantum information. Results that built on the finding are also broken.
A small prize is on offer to anyone who can recover the original proof, although efforts so far have been unsuccessful.
“It has set back a little our understanding of entanglement,” says CQT Principal Investigator Marco Tomamichel, an Associate Professor at the NUS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, who found the mistake. He has been working to spread news of the problem and explore its consequences with a team of international experts that includes the researchers behind the original proof.
https://www.quantumlah.org/about/highlight/2023-12-flawed-proof-rocks-quantum-information
Quantum computing startup PASQAL’s CCO leaves to start his own company
Benno Broer, Chief Commercial Officer (CCO) of French quantum computing startup PASQAL, has left the company to launch Science Rockstars, a stealth-mode firm active in high-performance computing, scientific software, and AI. Broer joined PASQAL in 2022 after the company acquired his quantum software firm, Qu&Co. His replacement is Joël Kremer, former head of sales at US SaaS company CloudBlue. PASQAL, which has raised $140m, is developing quantum computing hardware and software, a challenging and costly endeavor. The company is currently collaborating with industrial partners like EDF Energy, Siemens, and Johnson & Johnson to explore potential applications of quantum computing.
https://sifted.eu/articles/pasqal-cco-leaves/
Rigetti Announces Public Availability of Ankaa-2 System with a 2.5x Performance Improvement Compared to Previous QPUs
Rigetti Computing has announced the public availability of its 84-qubit Ankaa-2 quantum system, offering a 2.5x performance improvement over previous quantum processing units (QPUs). The Ankaa-2 system, now accessible via Rigetti Quantum Cloud Services, achieved a 98% median 2-qubit fidelity, indicating high-quality qubit operations. The improved performance is attributed to a new chip fabrication process, superconducting PCB technology, and electronics improvements. Rigetti CEO, Dr. Subodh Kulkarni, emphasized the importance of high-quality qubits in building powerful quantum computers, while CTO David Rivas noted the company's progress in qubit performance and their strategy for building higher performing QPUs. The launch of Ankaa-2 follows the release of Novera, Rigetti's first commercially available QPU.
Quantum Computing and Its Promise for the Future of Space
Dylan Taylor, Chairman & CEO of Voyager Space Holdings, discusses the potential of quantum computing in revolutionizing space exploration. Quantum computers, operating on qubits, can perform complex calculations at unprecedented speeds, optimizing spacecraft trajectories, enhancing our understanding of fundamental physics, and improving secure communications for space missions. However, challenges remain, including the need for environmental stability and the development of suitable software and algorithms. Researchers are exploring the development of quantum computers specifically designed for space, and advancements in error correction techniques could mitigate quantum decoherence. Taylor concludes that the union of quantum computing and space exploration could redefine our understanding of the universe.
https://www.newsweek.com/quantum-computing-its-promise-future-space-1855557
Cross-platform comparison of arbitrary quantum processes
Researchers Congcong Zheng, Xutao Yu, and Kun Wang developed a protocol for comparing the performance of arbitrary quantum processes across different quantum platforms. The method uses Local Operations and Classical Communication (LOCC) to construct quantum state preparation and measurement circuits. The protocol was applied to five quantum devices from IBM and Baidu's "Qianshi" quantum computer. Results showed the protocol successfully compares the performance of quantum processes implemented on different quantum computers and scales more favorably with the number of qubits compared to full quantum process tomography. This work paves the way for collaborative efforts in cross-platform comparison of quantum computers.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41534-023-00797-3
La startup española con la que Mahou-San Miguel, Cepsa y Moody's Analytics abrazan la computación cuántica
Spanish startup QCentroid, co-founded by CEO Carlos Kuchkovsky and Antonio Peris, is facilitating quantum computing for companies like Mahou-San Miguel, Cepsa, and Moody's Analytics without the need for expensive hardware or specialized expertise. The company's technology allows clients to execute, compare, and distribute quantum algorithms. Kuchkovsky, who also represents the digital industry's employers' association in Spain (AMETIC) on the advisory board of the European Commission for Quantum Technologies, believes Spain has the potential to become a top-five global power in quantum technologies. QCentroid's 2024 plans include expanding partnerships with climatetech companies and increasing their talent team.
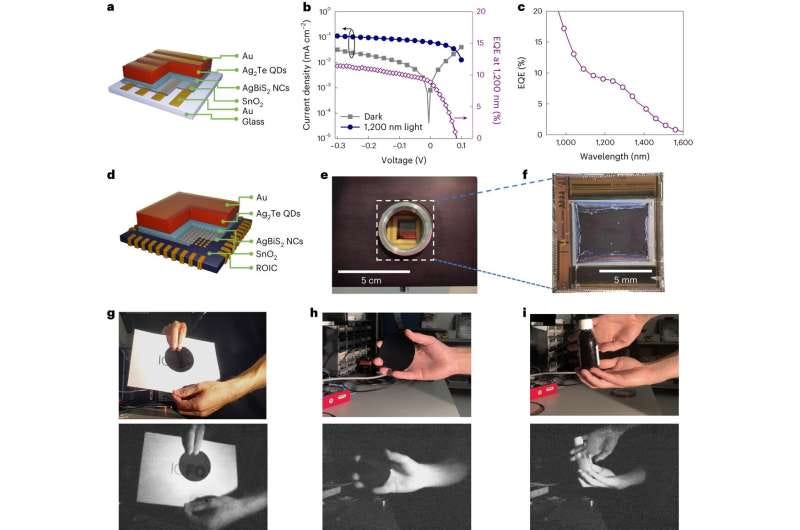
Non-toxic quantum dots pave the way towards CMOS shortwave infrared image sensors for consumer electronics
ICFO researchers, in collaboration with Qurv, have developed non-toxic, shortwave infrared (SWIR) image sensors based on colloidal quantum dots (CQDs). The team, led by ICREA Prof. Gerasimos Konstantatos, produced phosphine-free silver telluride (Ag2Te) quantum dots, which exhibit strong quantum-confined absorption similar to traditional heavy-metal quantum dots. This breakthrough enables the use of SWIR CQD technology in mass-market applications, as heavy-metal quantum dots are subject to RoHS regulations. The researchers' photodiodes demonstrated superior performance, surpassing previous phosphine-based techniques, and were successfully integrated into a CMOS-based image sensor. This development could revolutionize vision systems in consumer electronics, automotive, and robotics applications.
https://phys.org/news/2024-01-toxic-quantum-dots-pave-cmos.html
Accelerating Quantum Optimization Research by Algorithm-Specific Scalable GPU Simulation
Quantum computing is poised to revolutionize computational finance. Among many quantum computing algorithms proposed to date, Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) is one of the most commonly considered due to its ability to tackle a wide class of combinatorial optimization problems from graph coloring to portfolio optimization. While QAOA is hard to analyze theoretically, simulation can be used to gain understanding of QAOA performance. Such numerical studies are of particular importance in optimization, since only a handful quantum algorithms with provable speedups are known. For a numerical scaling analysis to be robust, it must consider sufficiently large systems. This motivates the use of high performance computing for these simulations.
https://www.jpmorgan.com/technology/technology-blog/quantum-optimization-research
Quantum Hype Suppression
Brian N. Siegelwax, an independent Quantum Algorithm Designer and writer for The Modern Scientist, discusses the prevalent hype in quantum news. Drawing inspiration from Jack Krupansky's work, he observes that every quantum news item contains at least one hype indicator. Siegelwax suggests using search engine news feeds, such as Google and Bing, to filter out the hype. He categorizes hype into five levels and identifies hypewords and weasel words often used in quantum discourse. Hypewords include terms like "best-in-class", "breakthrough", and "disruptive", while weasel words are speculative, such as "could", "might", and "should". The piece underscores the need for discernment in consuming quantum news.
https://medium.com/the-modern-scientist/quantum-hype-suppression-2a93ea1df4c7
UCLA Acquires Westside Pavilion to Create State-of-the-Art Research Park
UCLA has acquired the Westside Pavilion, a 700,000-square-foot property, to transform into a research hub, the UCLA Research Park. The Park will host the California Institute for Immunology and Immunotherapy, focusing on advanced biomedical research, and UCLA’s Center for Quantum Science and Engineering, dedicated to quantum computing research. The project is partly funded by a proposed $500 million investment from the state of California, with $200 million already allocated. Google, which previously leased part of the property, also supported UCLA’s acquisition. The initiative aligns with UCLA’s 2023-28 Strategic Plan to deepen ties to LA and use research to advance the common good. The transformation symbolizes UCLA's commitment to fostering cutting-edge research and innovation.
Quantum computing is taking on its biggest challenge: noise
In the race to establish quantum computing, IBM's Jay Gambetta has led a significant initiative to combat the biggest challenge in the field: noise. Quantum systems are extremely delicate, with even minor disturbances causing errors and halting computations. For years, researchers believed they would have to work with this noisy circuitry, but recent breakthroughs have shown promise in suppressing and mitigating quantum errors. Skeptics like University of Helsinki professor Sabrina Maniscalco are now confident about entering the "quantum utility era" soon. Gambetta, who heads IBM's quantum computer development, has also pioneered the world's first cloud-access quantum computer, which went live in 2016. This signifies a major step towards making quantum computing more accessible.
https://www.technologyreview.com/2024/01/04/1084783/quantum-computing-noise-google-ibm-microsoft/
UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar spearheading quantum computing development in the Middle East
Quantum computing is rapidly advancing, sparking a global race for innovation, with the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar emerging as key players in the Middle East, according to research from Frost & Sullivan. Quantum technology, which promises to revolutionize cybersecurity, scientific research, cryptography, finance, supply chains, logistics, and drug discovery, will be a focal point at the Intersec 2024 conference. Frost & Sullivan's Rajarshi Dhar highlighted the technology's potential to solve complex problems more efficiently. The firm predicts a significant surge in the quantum cryptography market in the next five years, largely driven by businesses and the government and defence sectors.
UNM launches innovative quantum photonics graduate program with $3 million NSF grant
The University of New Mexico (UNM) has launched a new Quantum Photonics and Quantum Technology (QPAQT) graduate program, made possible by a $3 million grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF). The program, named NRT-QL: Quantum Photonics Interdisciplinary Training to Advance Quantum Technologies, aims to equip students with a versatile skill set in quantum technology, enabling them to excel in a broad spectrum of basic research and applications within the field. According to Victor Acosta, director of QPAQT, the program is a significant step forward in quantum science and technology education. The first cohort is set for 2024, with core coursework beginning in 2025.
Siemens collaborates with sureCore and Semiwise to pioneer quantum computing ready cryogenic semiconductor designs
Siemens Digital Industries Software is partnering with sureCore and Semiwise to develop cryogenic semiconductor designs that can operate at near absolute zero temperatures, a key component for quantum computing systems. Using Siemens' advanced analog/mixed-signal IC design technology, Semiwise has created cryogenic CMOS circuit designs, which are being used by sureCore to develop their CryoIP product line. This collaboration could lead to significant advances in performance and power efficiency for next-generation integrated circuits. Paul Wells, CEO of sureCore, highlighted the importance of this partnership, stating that it has enabled them to build robust cryogenic IP cores tailored for quantum applications. The initiative represents Siemens' commitment to advancing the quantum computing domain.
https://newsroom.sw.siemens.com/en-US/siemens-eda-quantum-crygogenics/
Single Quantum expands to the US
Single Quantum, the pioneer in single photon detection technology, is expanding its operations to the US. The company's multi-channel Single Quantum Eos system, adopted by over 200 worldwide labs, is used in various applications, including quantum communication, Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), LiDAR, and bio-imaging. Single Quantum's COO, Dr. Jessie Qin-Dregely, has been appointed as Fellow of the Netherlands Academy of Engineering. The company's interleaved SNSPD accurately detects photons through a multipixel approach, perfect for time-multiplexed experiments. Single Quantum's photon detectors played a crucial role in a groundbreaking experiment that observed a nonlinear interaction using low laser powers and a single atom, resulting in a publication on Nature Physics.
https://singlequantum.com/whats-new/latest-news/
China's 3rd-gen superconducting quantum computer goes into operation
China has launched its third-generation superconducting quantum computer, Origin Wukong, developed by Origin Quantum Computing Technology. Powered by a 72-qubit indigenous superconducting quantum chip named Wukong, it is China's most advanced programmable and deliverable superconducting quantum computer. Kong Weicheng, deputy director of the Anhui Quantum Computing Engineering Research Center, highlighted the integration of the third-generation quantum computing control system, significantly enhancing operational efficiency. Jia Zhilong, another deputy director, revealed the Wukong chip's 198 qubits, composed of 72 computational and 126 coupler qubits. The quantum leap in technology symbolizes the computer's powerful and versatile capabilities, akin to its namesake, the mythical Sun Wukong.
https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202401/07/WS6599f6f2a3105f21a507ae67.html
How good is the new device? Apparently not super good: Read evaluation by Brian here: https://medium.com/the-modern-scientist/origin-quantums-wukong-6aa1f79ab436