The Week in Quantum Computing - July 15th 2024 - Lufthansa, Zapata AI, and D-Wave, Quantum Algos, Riverlane, Planck and Plancq
Issue #194
The Week in Quantum Computing. Brought to you by Sergio Gago (@piratecto).
Quick Recap
Pick your algorithm:
That comes from a fantastic paper on algorithm families, categorization and which use cases they tackle. This paper is a must read regardless of how deep you are in the field.
The Institute for Quantum Physics at Universität Hamburg and Lufthansa Industry Solutions are working together to create quantum algorithms to optimize airport gate assignments, a problem with over 570 billion possible configurations for just 15 gates and 10 airplanes. Zapata AI and D-Wave Quantum have expanded their partnership to accelerate generative AI platforms, Researchers have classified around 130 quantum algorithms in a comprehensive study, providing insights into trends and promising fields for near-term quantum computing. The Niels Bohr Institute demonstrates a novel, energy-efficient method for generating quantum entanglement using quantum dots, paving the way for scalable quantum technologies. Plank and Plancq are two different companies. Both in Germany but one was acquired this week by Kipu Quantum and the other just received 50M investment. To know which is which you will have to review the newsletter in full! Riverlane has also presented their 3y roadmap on error correction. While Google's Sycamore experiment gets smashed (again) which was meant to happen (remember though, that the experiment had zero business value)
The Week in Quantum Computing
Algorithms for Optimal Airport Operations
The Institute for Quantum Physics at Universität Hamburg and Lufthansa Industry Solutions are collaborating to develop quantum algorithms aimed at optimizing airport gate assignments. Dr. Joseph Doetsch from LHIND highlights the complexity, noting that 15 gates and 10 airplanes yield over 570 billion possibilities. Traditional computers struggle with such calculations, but quantum computing offers scalable solutions. Prof. Dr. Dieter Jaksch emphasizes that this project is pioneering in using quantum computers for this problem. Funded for three years by IFB Hamburg, the initiative aims to establish Hamburg as a quantum computing hub. The project leverages local talent and Hamburg’s funding culture, with real-time solutions already available on classical computers, set to improve with quantum advancements.
https://www.uni-hamburg.de/en/newsroom/presse/2024/pm32.html
German quantum computing startup planqc raises €50m Series A
Munich-based quantum computing startup planqc is today announcing a €50m Series A round, led by the European Family Office CATRON Holding and Germany’s deeptech and climate tech fund (DTCF).
Founded in 2022, planqc — a spinout from the Max Planck Institute in Munich — builds quantum computers using a technique known as “neutral atoms” that involves using lasers to trap and stabilise single atoms to make qubits (stores of quantum information).
https://sifted.eu/articles/planqc-raises-50m-series-a-news
Zapata AI and D-Wave Quantum Announce Expanded Partnership to Accelerate Development and Delivery of Generative AI Platforms
Zapata AI and D-Wave Quantum have announced an expanded partnership to accelerate the development and delivery of generative AI platforms. This collaboration leverages Zapata's Universal Generative AI software and D-Wave's Leap quantum cloud service to enhance model training efficiency and performance. Christopher Savoie, CEO of Zapata AI, emphasized the business value and computational capacity provided by this partnership. Dr. Alan Baratz, CEO of D-Wave, highlighted the transformative potential of combining generative AI with quantum computing. The agreement includes a one-year Enterprise subscription to Zapata's Orquestra platform for scalable AI application development. This partnership aims to drive advancements in AI and quantum computing, enhancing operational efficiency and sustainability.
Paper: A typology of quantum algorithms
Researchers Pablo Arnault, Pablo Arrighi, Steven Herbert, Evi Kasnetsi, and Tianyi Li have classified approximately 130 quantum algorithms in their paper "A typology of quantum algorithms." The study categorizes these algorithms based on the fundamental mathematical problems they address, their real-world applications, and the primary subroutines they utilize. The paper aims to highlight trends, identify promising fields for near-term quantum computing (NISQ era), and pinpoint key algorithmic primitives that enable quantum advantage. The comprehensive analysis spans 60 pages and includes 7 figures, providing a detailed overview of the current landscape of quantum algorithms. This work is pivotal for guiding future research and practical implementations in quantum computing.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.05178v1
The promise of quantum computing in manufacturing
Quantum computing, projected to generate $2 trillion in economic impact by 2035, is set to revolutionize Industry 4.0, particularly in chemicals, life sciences, finance, and mobility, according to a McKinsey report. Erik Garcell highlights that quantum computers, leveraging qubits and properties like superposition and entanglement, can process data at unprecedented speeds. This capability enhances AI, machine learning, and optimization in manufacturing, enabling more accurate defect detection, efficient resource allocation, and advanced simulations. Rolls Royce's work on quantum algorithms for jet engine efficiency exemplifies its potential. Quantum computing also promises significant efficiency and sustainability benefits, such as optimizing energy production based on real-time demand. Companies should start exploring quantum technologies now to stay ahead.
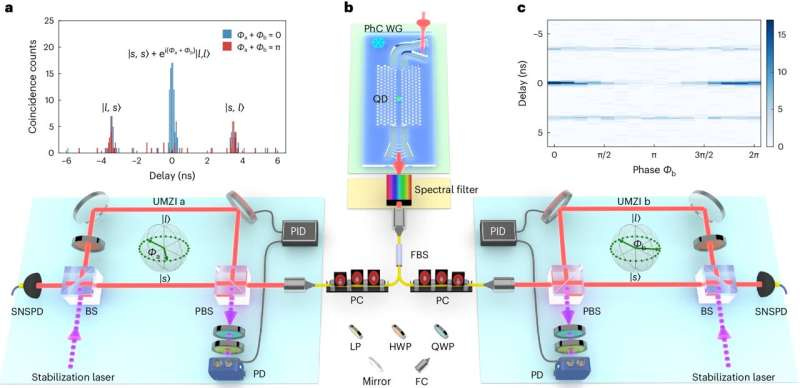
Quantum dot photon emitters violate Bell inequality in new study
A groundbreaking study published in *Nature Physics* by Dr. Shikai Liu and colleagues from The Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen demonstrates a novel method for generating quantum entanglement using quantum dots, which successfully violates the Bell inequality. The method employs ultra-low power levels, approximately 7.2 picowatts, making it about 1,000 times more energy-efficient than traditional single-photon sources. By coupling quantum dots with photonic crystal waveguides, the team achieved a high coupling efficiency of over 90% and a Purcell enhancement of 16. This significant advancement confirms the quantum nature of the correlations between photons, paving the way for scalable and efficient quantum technologies.
https://phys.org/news/2024-07-quantum-dot-photon-emitters-violate.html
Shopping the quantum computer supermarket
Top financial industry players have been investing in quantum computing to gain competitive advantages in speed and accuracy for complex problems like derivatives pricing and portfolio optimization. Quantum computers, which use physical qubits, come in various modalities such as Atom, Ion, NVC, NMR, Photon, and Superconducting. The largest publicly available quantum computers include QuEra Computing's 256-atom "Aquila" and IBM Quantum's 127-qubit superconducting devices. While larger quantum computers exist, they are often restricted. Quantum computers can be accessed via the cloud or leased for intellectual property protection. Quantum annealers, specialized for optimization problems, are also being developed by companies like NEC and Qilimanjaro.
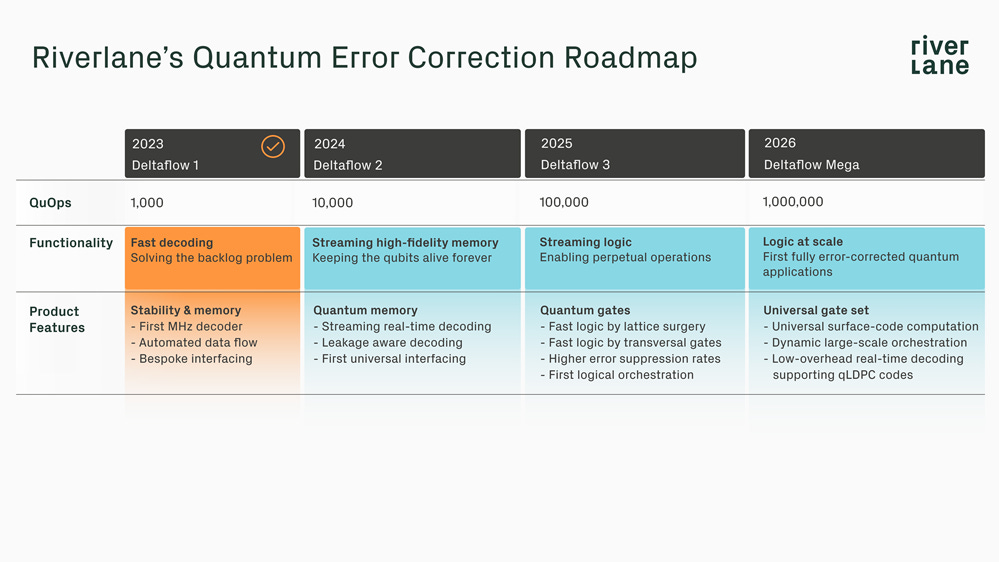
Introducing Riverlane’s Quantum Error Correction roadmap
Riverlane has unveiled its Quantum Error Correction (QEC) roadmap, aiming to achieve a MegaQuOp-scale QEC stack by 2026. This milestone involves performing one million reliable quantum operations, a critical step towards the ultimate goal of TeraQuOp systems by 2035. Key breakthroughs from institutions like Quantinuum, ETH Zürich, Google, Harvard, Yale, IBM, Microsoft, Alice & Bob, and Riverlane have accelerated progress in qubit quality and error correction. Riverlane's Deltaflow Mega will support non-Clifford logic, crucial for fault tolerance. Co-authors Earl Campbell and Maria Maragkou emphasize that achieving MegaQuOp will push quantum computing beyond classical supercomputers, marking a pivotal moment in the field.
https://www.riverlane.com/blog/introducing-riverlane-s-quantum-error-correction-roadmap
The AI Boom is good for Quantum Tech
The AI boom is significantly benefiting quantum technology, according to Quantonation. The demand for computational power in AI has surged, with training models requiring 1000 times more compute and costs rising 100 times over the past four years. NVIDIA dominates this space with a market cap exceeding $3.1 trillion. Quantum computing offers disruptive potential with new algorithms and problem-solving approaches. Companies like Qubit Pharmaceuticals, Multiverse Computing, and Pasqal are already leveraging quantum tech to enhance AI. In 2023, there were over 4,000 publications on quantum machine learning, indicating growing interest but highlighting the nascent stage of the field. The AI boom is expected to drive further advancements and investments in quantum technologies.
https://www.quantonation.com/2024/07/09/the-ai-boom-is-good-for-quantum-tech/
EDF, Alice & Bob, Quandela and CNRS Partner to Optimize Quantum Computing’s Energy Efficiency
EDF, Alice & Bob, Quandela, and CNRS have launched a €6.4 million project to enhance the energy efficiency of quantum computing. This collaboration aims to address the significant energy consumption challenges posed by quantum technologies. The project will leverage EDF's expertise in energy, Alice & Bob's advancements in quantum error correction, Quandela's photonic quantum computing innovations, and CNRS's extensive research capabilities. According to Alice & Bob's CEO, Théau Peronnin, "This partnership is a crucial step towards making quantum computing more sustainable." The initiative underscores the growing importance of energy efficiency in the development of quantum computing technologies.
https://alice-bob.com/newsroom/edf-alice-bob-quandela-cnrs-quantum-computing/
Quantum Computing Pioneers Making Strides in Cybersecurity
USA News Group reports significant advancements in quantum computing for cybersecurity, spotlighting Scope AI Corp. Based in Vancouver, Scope AI Corp. is pioneering quantum encryption methods to combat cyber threats. CEO Dr. Emily Zhang stated, "Quantum computing will redefine our approach to data security." The company aims to leverage quantum algorithms to enhance encryption, making it exponentially harder for hackers to breach systems. This breakthrough is expected to revolutionize cybersecurity, providing robust protection against increasingly sophisticated cyber-attacks. The collaboration between academia and industry is crucial, with institutions like MIT and IBM contributing to research and development. Quantum computing's potential to transform cybersecurity marks a pivotal moment in technology, promising unprecedented data protection.
Chasing quantum magic: Andrea Young receives $2 million award to develop a more stable quantum architecture
Andrea Young, a physics professor at UC Santa Barbara, has been awarded $2 million by the Brown Institute for Basic Sciences at Caltech to advance topological quantum computing. This approach, theorized over two decades ago, aims to create more stable quantum systems by encoding qubits in larger patterns of entanglement. Despite skepticism in the field, Young's recent work with atomically thin crystals has shown promising robustness in nonabelian anyons, potentially leading to the first operational topological qubit. UC Santa Barbara Chancellor Henry T. Yang praised Young's innovative contributions, emphasizing the award's significance for the university's leadership in quantum science. Young acknowledges the project's high risk but is optimistic about its transformative potential.
Will banks be ready for post-quantum chaos?
Banks are increasingly exploring transformative technologies like AI and cryptocurrency, but quantum computing, which could be up to 10 million times faster than classical computers, remains under-discussed. Quantum computers use qubits, allowing for superposition and entanglement, leading to exponential increases in computing power. This technology could revolutionize financial modeling, portfolio optimization, fraud detection, and customer targeting. JP Morgan and Goldman Sachs are at the forefront, focusing on quantum algorithms and applications. JP Morgan's collaboration with Quantinuum has produced research on option pricing and portfolio optimization. Quantum computing's potential to process digital payments faster and improve risk quantification could be a game changer for banks in predicting and managing financial market turmoil.
Quantum in Context: Quantum Companies Rotate in New Leaders
In recent months, several quantum computing companies, including Atom Computing, Infleqtion, Oxford Quantum Circuits, and Quantum Circuits Inc., have appointed new CEOs, while Pasqal and IQM have shifted to co-CEOs. This trend reflects the high-stakes nature of deep-tech startups requiring significant investment. Notable changes include Ben Bloom resuming the CEO role at Atom Computing, which recently secured $27.1M from Denmark's Export and Investment Fund, and Matthew Kinsella taking over at Infleqtion, which raised $110M in 2022. The leadership shifts are driven by various factors, from financial needs to strategic pivots. As the industry evolves, having the right leadership at different stages is crucial for achieving Practical Quantum Advantage.
https://futurumgroup.com/insights/quantum-in-context-quantum-companies-rotate-in-new-leaders/
Pay-as-you-go quantum computer makes QuEra a catch for industry
QuEra, a Boston-based quantum computing startup, has integrated its 256-qubit Aquila machine into AWS Braket, enabling enterprises like BMW, Airbus, and BP to explore quantum applications. CEO Alex Keesling emphasizes the urgency for organizations to adopt quantum technology to avoid falling behind. QuEra's recent $40 million deal with Japan's AIST highlights this trend. Founded in 2018 through MIT and Harvard collaboration, QuEra aims to achieve 100 logical qubits by 2026, significantly advancing fault-tolerant quantum computing. Chief Commercial Officer Yuval Boger notes that quantum computing is closer to practical use than previously thought, with enterprises and national programs increasingly investing in quantum technology. "Quantum is closer than you think," asserts Boger.
https://biforesight.com/quantum/pay-as-you-go-quantum-computer-makes-quera-a-catch-for-industry/
IBM Surpasses Google with Revolutionary 127-Qubit Eagle Quantum Processor
IBM has announced a significant breakthrough in quantum computing with the development of the Eagle processor, which boasts 127 qubits. This achievement surpasses the 53-qubit Sycamore processor by Google, marking a substantial leap in quantum capabilities. IBM's Director of Research, Dario Gil, stated, "Eagle is a key milestone on our path to practical quantum computing." The Eagle processor's architecture allows for more complex computations, potentially revolutionizing fields such as cryptography and material science. IBM plans to make Eagle accessible via its Quantum Network, fostering further research and development. This milestone underscores IBM's commitment to advancing quantum technology and its potential to solve problems beyond the reach of classical computers.
Kipu Quantum Acquires Quantum Computing Platform Built by Anaqor AG to Accelerate Development of Industrially Relevant Quantum Solutions
Kipu Quantum has acquired a quantum computing platform developed by Anaqor AG. This strategic move aims to expedite the creation of quantum solutions with industrial applications. The acquisition underscores Kipu Quantum's commitment to advancing quantum technology and its practical uses in various industries. The integration of Anaqor AG's platform is expected to enhance Kipu Quantum's capabilities in developing cutting-edge quantum computing solutions. This acquisition marks a significant step in the company's mission to leverage quantum computing for real-world industrial challenges.
Iberdrola and Multiverse Computing Announce Pilot Project Success to Optimize Battery Installation in the Grid
Iberdrola and Multiverse Computing have successfully completed a pilot project in northern Spain to optimize grid-scale battery installations using quantum and quantum-inspired algorithms. The project, overseen by Iberdrola's distribution company i-DE, focused on Guipuzkoa's electricity grid and demonstrated that these algorithms matched or outperformed classical solutions in maximizing grid reliability and voltage control. Enrique Lizaso Olmos, CEO of Multiverse Computing, highlighted the potential for quantum computing to help meet sustainability goals while reducing costs. Estibaliz Goñi, i-DE's Process and Technology director, emphasized the importance of such innovations for achieving smart and robust grids essential for the energy transition. This project underscores the critical role of advanced technology in enhancing grid performance and sustainability.
Oxford Ionics breaks global quantum performance records
Oxford Ionics has unveiled the highest performing quantum chip globally, capable of mass production in standard semiconductor plants. Their chips outperform previous records by over twice the performance without error correction, achieving 99.97% fidelity in two-qubit gates and 99.9992% in single-qubit operations. This breakthrough is attributed to their patented Electronic Qubit Control system, which eliminates the need for lasers. Dr. Michael Cuthbert of the UK’s National Quantum Computing Centre hailed this as a pivotal step, while CEO Dr. Chris Ballance emphasized their "rocket ship" approach to solving complex challenges. Oxford Ionics plans to build a scalable 256 qubit chip, marking a significant leap towards practical quantum computing applications.
https://www.oxionics.com/news/oxford-ionics-breaks-global-quantum-performance-records
Artificial intelligence could help make quantum computers a reality
CSIRO's recent study, led by Dr. Muhammad Usman, reveals that AI neural network syndrome decoders can detect and correct errors in quantum processors, addressing a major hurdle in quantum computing. Published in *Physical Review Research*, the research demonstrates that AI can process complex qubit noise from IBM quantum devices, suggesting suitable corrections. Dr. Usman notes, "Our work for the first time establishes that a machine learning-based decoder can, in principle, process error information obtained directly from measurements on IBM devices and suggest suitable corrections despite the very complex nature of noise." This breakthrough indicates that AI could enable full fault-tolerance in quantum computers as physical error rates decrease in the coming years.
https://phys.org/news/2024-07-artificial-intelligence-quantum-reality.html
Paper: Large-scale quantum reservoir learning with an analog quantum computer
Researchers led by Milan Kornjača have developed a scalable, gradient-free quantum reservoir learning algorithm using neutral-atom analog quantum computers. This approach addresses the resource-intensive nature and vanishing gradient issues of current quantum machine learning methods. The team demonstrated competitive performance in binary and multi-class classification, as well as time-series prediction, with system sizes up to 108 qubits, marking the largest quantum machine learning experiment to date. Their findings also highlight a quantum kernel advantage in learning tasks using synthetic datasets. This work underscores the potential of quantum correlations for effective machine learning and suggests further exploration into various quantum hardware and paradigms.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.02553v1
New quantum computer smashes 'quantum supremacy' record by a factor of 100 and it consumes 30,000 times less power
Quantinuum's new 56-qubit H2-1 quantum computer has shattered Google's Sycamore quantum supremacy record by a factor of 100, achieving an XEB score of 0.35, indicating 35% error-free results. This breakthrough, published on June 4 in arXiv, involved collaboration with JPMorgan, Caltech, and Argonne National Laboratory. The H2-1 also consumes 30,000 times less power. Ilyas Khan, Quantinuum's Chief Product Officer, emphasized the focus on universal fault-tolerant quantum computers, noting significant advancements due to long-term investments. Previously, Quantinuum and Microsoft demonstrated logical qubits with an error rate 800 times lower than physical qubits. This milestone suggests fault-tolerant quantum computing may be achievable sooner than anticipated.
https://www.yahoo.com/tech/quantum-computer-smashes-quantum-supremacy-103636811.html