The Week in Quantum Computing - June 17th 2024 - Atom, Quantum Transformers, Unitary Fund's results and Majorana's
Issue #190
The Week in Quantum Computing. Brought to you by Sergio Gago (@piratecto).
Hello and welsome to the new subscribers! (For some reason there is a lot of you that came last week… there is some correlation between memes and snarky comments and smart public!).
Today I wanted to start a bit differently: Why am I in this industry? Why do I work in Quantum Computing?
If you have a few hours available. I really recommend you to listen / watch this Acquired podcast with the first years of Microsoft and how they build an industry at the beginning of microcomputers. Why am I in Quantum? Well, because a lot, many of the things that Microsoft did a few decades ago are recplicating or will replicate today. Not everything will be the same but as humans we know how history always repeats itself. If you are in the Quantum industry and have to decide where to use 4 hours this week, or what to listen to in your commute.. let it be this.
(Podcast and other formats here: https://www.acquired.fm/episodes/microsoft And also from other firms. I love the Acquired podcast).
Quick Recap
IQM Quantum Computers secured French government funding to establish Europe's first industrial-scale quantum processor production facility. This €150 million project marks a major stride in Europe's quantum technology industry, particularly positioning France at the forefront. OTI Lumionics and Nord Quantique have partnered on a $5 million CAD project to test new quantum computing applications for materials science, aiming to enhance efficiencies in advanced materials development. On the research front, a team from the University of New Mexico and Google Quantum AI has developed a FTQC protocol using large spincat codes, demonstrating the potential of qudits for robust quantum computation. In a similar vein, a study by Harvard researchers introduced pseudomagic quantum states, offering a potential pathway to achieving the quantum advantage. IonQ and South Carolina Quantum launched a Faculty & Researcher Learning Series, aiming to integrate quantum technologies into research and curricula.
In recognition of quantum science's potential, the United Nations declared 2025 as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology. This initiative aims to inspire the next generation of scientists and aligns with the 100th anniversary of modern quantum mechanics and will be coordinated by APS. Dutch company MicroAlign secured €1M in seed funding to commercialize its high-accuracy fiber arrays, a crucial component in quantum computing. Quixer is a primer on quantum transformer models. Very far from real implementation but a very interesting research line. The Unitary Fund has reached 100 micro grants. See their infographic below because the work this organization for quantum open source is magnificent.
Quantum Computing and Telecom Industry - Infinity report
Inifinity Quantum just released their Quantum Telecom Industry report with some interesting insights. You can download it here.
- The report, contributed by Quantum Delta NL, highlights the significant progress made in the telecom industry's adoption of quantum technology.
- Quantum technology developments are not only related to computing but also to quantum communication, quantum networks, and the quantum internet.
- There are already 25+ different quantum network deployments underway in Europe in domains such as telecom, government, security, and others.
- Quantum technologies are at a pivotal point for the telecommunications industry, providing compelling use cases but requiring support and investment.
- The European telecom industry is exploring use cases for quantum technologies, including communications and security, sensors, computing, clocks, and simulation.
- Key market opportunities within the telecom sector to develop quantum technology customer bases include government bodies, financial institutions, critical infrastructures, energy companies, the defence sector, the space sector, and the technology sector.
- Infinity has identified more than 100 quantum startups, scaleups, and SMEs servicing the telecommunications and telecommunications infrastructure space.
- 42 of these companies have raised a total of EUR 1.9Bn, with a median funding round size of EUR 7.4Mn.
- 35% of vendors have their HQ in North America, 32% in Continental Europe, 14% in Great Britain & Ireland, and 12% in Asia.
- More than 50 enterprises are serving as consumers in the telecommunications and telecommunications infrastructure space.
- 50% of these enterprises are located in continental Europe; 30% in North America; 11% in Great Britain & Ireland; 9% in Asia.
- Quantum key distribution (QKD) is the most popular technology being deployed as the industry evaluates the practicality of quantum communication.
- The increasingly fractured nature of global political relationships places quantum technologies in the same category as AI and defence tech.
- The EU is relatively forward-thinking when it comes to quantum technologies, commissioning the Nostradamus consortium led by Deutsche Telekom to explore the potential of QKD for pan-EU communications.
The Week in Quantum Computing
Quantum computing firm Atom Computing secures $10m from Danish export fund
Quantum computing startup Atom Computing has secured funding from the Danish government. The Export and Investment Fund of Denmark (EIFO) this week announced an investment of 70 million DKK ($10.21 million) in Atom. State-owned EIFO is the national promotional bank and export credit agency of Denmark. Invest in Denmark, also involved in the deal, is part of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Denmark.
Quantum x Climate: Steelmaking
Karan Mario Jude Pinto, an editor for Entangle Quantum, discusses the potential of quantum computing in the steelmaking industry to enhance energy and material efficiencies, thereby positively impacting the climate. His insights are based on a visit to one of the world's largest steel plants in Gwangyang, South Korea. Pinto emphasizes the unique nature of the deep tech growth cycle and its transformative opportunities for hard-to-abate heavy industries. The main implication of the text is the potential role of quantum computing in revolutionizing energy-intensive industries and contributing to climate change mitigation.
https://medium.com/entangle-quantum/quantum-x-climate-steelmaking-4b0971a98833
University of New Mexico and Google Quantum AI Develop Robust Quantum Computing Protocol
Researchers at the University of New Mexico and Google Quantum AI have developed a fault-tolerant quantum computation (FTQC) protocol using large spincat codes, surpassing the fault-tolerant threshold of standard qubit-based encodings. The team demonstrated the protocol's practical application in neutral-atom quantum computing with qudits encoded in the nuclear spin of 87Sr. This method corrects dominant error sources and could lead to improved thresholds and reduced resource overhead in quantum information processing. The protocol represents a significant advancement in quantum computing, demonstrating the potential of qudits with multiple levels for more robust quantum computation.
France to have Europe’s first industrial scale quantum processor manufacturing facility
The Finnish company, IQM Quantum Computers, has received French government funding to establish Europe's first industrial-scale quantum processor production facility. Announced at the Choose France summit, the €150 million project forms part of the France 2030 investment plan. While quantum tech giants like IBM and Google dominate in the US, European facilities have largely been confined to universities and research institutions. This move represents a significant stride in Europe's quantum technology industry, positioning France at the forefront of the continent's quantum computing advancement.
OTI Lumionics Selects Nord Quantique to Test New Quantum Computing Applications for Materials Science
OTI Lumionics, a leader in developing advanced materials for consumer electronics, has partnered with Nord Quantique, a pioneer in quantum error correction, to test new quantum computing applications for materials science. The collaboration, backed by a $5 million CAD investment, aims to improve efficiencies in advanced materials development with potential applications in semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, and specialty chemicals. OTI Lumionics VP Scott Genin highlighted Nord Quantique's unique architecture as potentially the only one suitable for running electronic structure or vibronic spectra calculations. The partnership will leverage Nord Quantique's fast computational speeds and low energy consumption to identify new materials, reduce time-to-market, and lower overall development costs.
Pseudomagic quantum states: A path to quantum supremacy
A study in Physical Review Letters by Harvard Ph.D. student Andi Gu and postdoc Dr. Lorenzo Leone from Freie Universität, Berlin, introduces pseudomagic quantum states, enhancing quantum computing's power. Unlike stabilizer states, pseudomagic states possess high stabilizerness, making them appear complex and non-classical, yet they are computationally indistinguishable from random quantum states. This makes them less resource-intensive to construct. The researchers suggest that pseudomagic states could improve quantum cryptography, provide insights into quantum chaos and scrambling, and build more efficient fault-tolerant quantum computers.
https://phys.org/news/2024-06-pseudomagic-quantum-states-path-supremacy.html
IonQ and South Carolina Quantum (SCQ) Launch Faculty & Researcher Quantum Learning Series
Quantum computing leader IonQ, in partnership with South Carolina Quantum (SCQ), has launched a Faculty & Researcher Learning Series, aiming to introduce quantum technologies, resources, and applications into research, courses, and curricula. Clemson University will be the first to integrate the series, offering free sessions to faculty and researchers. This follows a March agreement between IonQ and SCQ to accelerate the integration of quantum technologies in academia and business across South Carolina. The state has previously invested millions into SCQ to boost workforce development and applied research in quantum computing.
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/ionq-south-carolina-quantum-scq-120000117.html
The United Nations Proclaims 2025 as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology
The United Nations (UN) has declared 2025 as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology (IYQ), recognizing quantum science's potential to drive sustainable development and global communications innovations. The IYQ initiative aligns with the 100th anniversary of modern quantum mechanics, underlying many significant technologies like transistors, lasers, and LEDs. The proclamation follows a multiyear effort by an international coalition of scientific organizations, including ICFO. The American Physical Society will administer the campaign, with worldwide events aimed at building a vibrant, inclusive global quantum science community. Riche-Mike Wellington, Chief Programme Specialist at the Ghana Commission for UNESCO, emphasizes the initiative's aim to inspire the next generation of scientists. Quantum science and technology are poised to address the world's most pressing challenges and support the UN's Sustainable Development Goals.
Crushing Errors in Quantum Computers with Q-CTRL's Dr. Yuval Baum
Dr. Yuval Baum of Q-CTRL discusses advancements in quantum computing, focusing on error reduction. Q-CTRL, a quantum technology company, is developing solutions to stabilize quantum states, improving the reliability of quantum computers. Dr. Baum emphasizes the need for error management in quantum computing, a field that is currently facing significant challenges due to the fragile nature of quantum states. He suggests that advancements in this area could greatly enhance the performance and practical applications of quantum computers. The conversation underlines the ongoing evolution in quantum computing and the critical role of companies like Q-CTRL in this technological revolution.
Meet Majorana
The future of quantum computing may be closer than expected, thanks to a particle called Majorana. This particle could potentially revolutionize the field of quantum computing, bringing us into a new era of technology. Majorana's unique properties could help solve some of the biggest challenges in quantum computing, accelerating its development and application. This breakthrough could lead to new ways of thinking, creating new connections, and even spawning new industries. The world is in constant transformation, and with Majorana, technology's role in our lives could change dramatically.
https://www.wired.com/sponsored/story/meet-majorana/
Dutch-based MicroAlign secures €1M to develop this key component in advancing quantum computing tech
Dutch company MicroAlign has secured €1M in seed funding for the commercialisation of its high-accuracy fiber arrays, a key component in quantum computing. The funding round was led by Dutch venture capital firms DeepTechXL and PhotonVentures. MicroAlign's technology, which originated from a PhD project at Eindhoven University of Technology, offers a solution for aligning multiple optical fibers, crucial for quantum photonic computing applications. The funding will be used to expand the firm's R&D team and facilities. The company's CTO, Marco Fattori, highlighted that MicroAlign's technology is based on the world's smallest fiber alignment actuator, representing a groundbreaking solution for the industry.
https://siliconcanals.com/crowdfunding/microalign-secures-1m/
China makes breakthrough in quantum computing dilution refrigerator
The Anhui Quantum Computing Engineering Research Center in China has produced the Origin SL1000 dilution refrigerator, a crucial component for constructing superconducting quantum computers. Developed by Origin Quantum Computing Technology, the device marks a significant advancement in dilution refrigeration technology. The Origin SL1000 offers improved spatial capacity and cooling efficiency, able to house 840 extremely low-temperature, high-frequency coaxial cables, making it suitable for 100+ bit superconducting quantum chips. The refrigerator's cooling capacity, a crucial factor for maintaining ultra-low temperatures necessary for quantum computing operations, has been significantly enhanced.
SpeQtral, SafeQuantum, Antaris and QTD Systems work on QKD
SpeQtral, SafeQuantum, Antaris, and QTD Systems have partnered to install a satellite Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) receiver node at 60 Hudson Street, New York City. The goal is to establish secure quantum keys between Singapore, the United States, and Europe, ensuring quantum-safe communications for global financial transactions. SpeQtral plans to launch two QKD satellites, SpeQtre and SpeQtral-1, for global quantum-based symmetric key delivery services. The new satellite ground quantum node will be located at the QTD Systems data center. SpeQtral's CEO, Chune Yang Lum, sees this initiative as a significant step towards creating a secure global communication network leveraging quantum technology.
Diraq achieves record accuracy for device manufactured by existing semiconductor infrastructure
Quantum computing company Diraq, in collaboration with nanoelectronics R&D hub imec, has achieved a record control accuracy of 99.9% for a quantum bit (qubit) using industry-standard CMOS materials on a 300mm silicon wafer. This high level of precision meets the requirements for full-scale, error-corrected quantum computer processors. The qubit device was manufactured by imec, and the high fidelity was made possible by Diraq's advanced qubit control and measurement techniques. Diraq's CEO, Andrew Dzurak, emphasized the importance of their partnership with imec in achieving a fully error-corrected quantum computing system. The company is also planning to design chips with GlobalFoundries, aiming to integrate high-quality qubits with standard CMOS transistors.
https://diraq.com/newsdesk/diraq-produces-device-using-semiconductor-infrastructure
The next administration must be ready for new quantum encryption standards, MITRE advises
MITRE, a top federally-backed research group, has urged the next U.S. presidential administration to prioritize readiness for quantum computing advances. The group warns that quantum computing could soon outperform current encryption methods used to secure data. Quantum computers, still under development, could be available within three to five years, according to an NSA official. MITRE's advisory calls for a new era of cryptographic algorithms, secure against quantum capabilities, and suggests the next administration should assess post-quantum readiness and use expertise from the PQC Coalition. The NSA has set a 2035 deadline for IC systems to adopt these new PQC standards. Quantum computing's potential to revolutionize encryption necessitates proactive preparation.
Paper: Quixer: A Quantum Transformer Model
Nikhil Khatri, Gabriel Matos, Luuk Coopmans, and Stephen Clark have developed Quixer, a quantum transformer model designed for large-scale quantum computers. This novel model uses the Linear Combination of Unitaries and Quantum Singular Value Transform primitives as its building blocks. Quixer has shown promising results in a practical language modelling task, performing competitively with a classical baseline. The researchers also provide resource estimates for running the model on quantum hardware and an open-source implementation for classical simulation. The versatility of Quixer is emphasized, as its parameterized components can be replaced with fixed structures to create new quantum transformers.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.04305v1
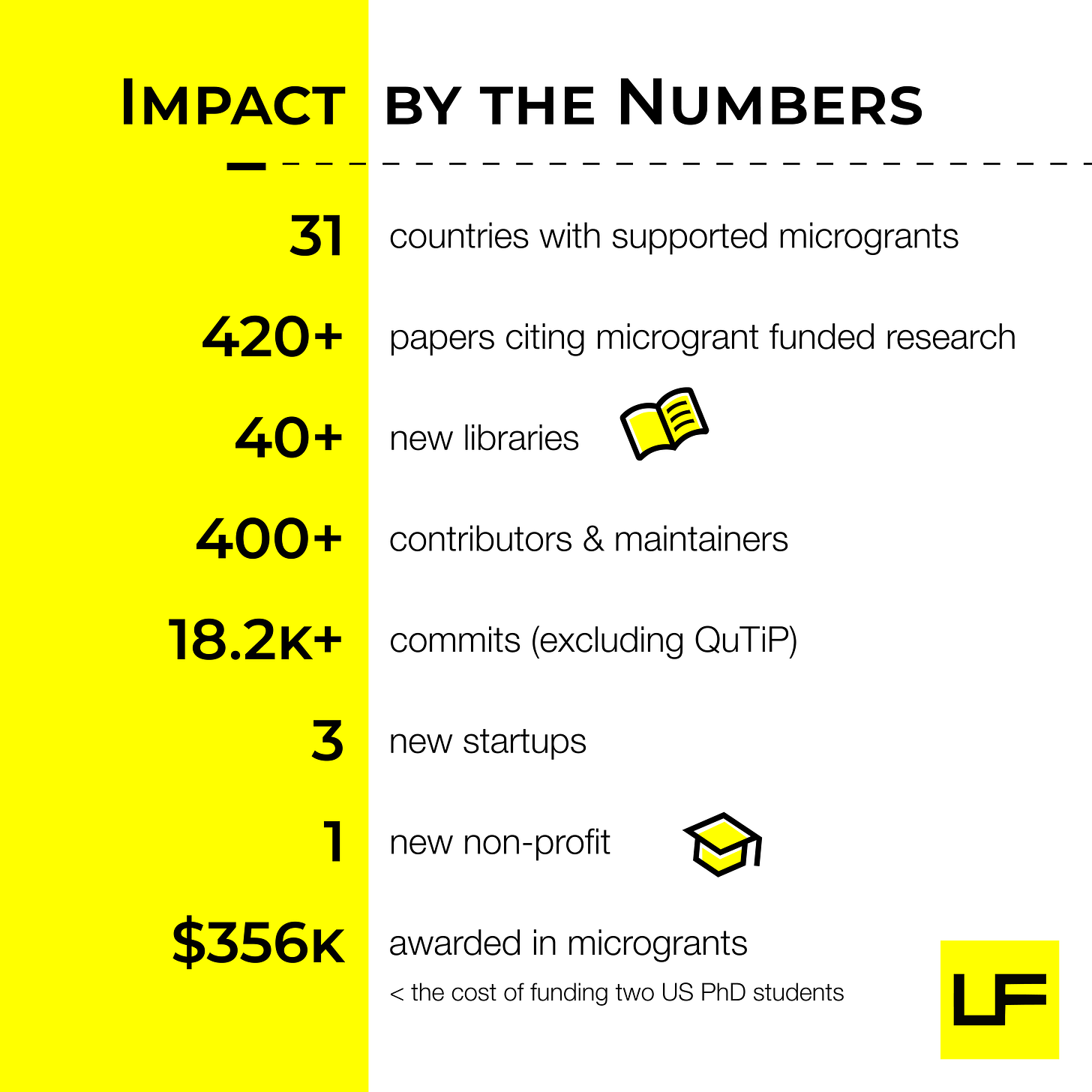
Celebrating a Milestone: Over 100 Microgrants Awarded by Unitary Fund
The Unitary Fund has reached a significant milestone, awarding over 100 microgrants to advance open source quantum technology projects worldwide. The program's core members include IBM Quantum, DoraHacks, OQD, and Scientifica, with support from AWS, Microsoft, Pasqal, QC Ware, IonQ, and SandboxAQ. The microgrants have led to the creation of 40 different libraries, three startups, and one nonprofit. They have also resulted in over 420 research papers, benefiting thousands of researchers. A survey of recipients revealed that 87% of microgrants led to career advancements and additional resources, while over 51% were awarded to individuals from historically underrepresented groups in STEM. The Unitary Fund's microgrants are fostering a vibrant, multiplying effect within the quantum ecosystem.
https://unitary.fund/posts/2024_microgrant_impact/
Quantum computers are like kaleidoscopes - why unusual metaphors help illustrate science and technology
Sorin Adam Matei from Purdue University, in his article for The Conversation, suggests that quantum computers can be better understood using the metaphor of a kaleidoscope, rather than traditional binary computing metaphors. He explains that quantum computers handle information probabilistically at atomic and subatomic levels, which is fundamentally different from classical computers that handle binary, deterministic states. Matei emphasizes that the uniqueness of quantum computers calls for an unusual metaphor. He also warns that using common metaphors can lead to conceptual confusion. In sum, the kaleidoscope metaphor captures the essence of quantum computing - it's about observing the pattern at the moment you choose to look.
Unlocking the Future of Quantum Computing: Interview with Dr. Paul Terry
The interview with Dr. Paul Terry delves into the future of quantum computing. Dr. Terry discusses the potential advancements and challenges in this field, offering insight into the next steps for quantum technology.