The Week in Quantum Computing - June 3rd 2024 - Singapore, Q*Bird, Alice & Bob meet Riverlane
Issue #188
The Week in Quantum Computing. Brought to you by Sergio Gago (@piratecto).
Quick Recap
Hamamatsu Photonics has developed a scientific camera, the ORCA-Quest, that is gaining traction in quantum computing due to its unique "photon-number resolving". Quantum security startup Q*Bird secured €2.5M in funding to expand its quantum security product, Falqon. Chris Ferrie published and released for free his new book: "What You Shouldn't Know About Quantum Computers" aiming to demystify quantum computing for a broad audience (in line with his company Quokka for training purposes). Riverlane and Alice & Bob have partnered to integrate Riverlane's quantum error correction stack within Alice & Bob's quantum computing system. Olivia Di Matteo and her team have proposed an abstraction hierarchy to support quantum software engineering, emphasizing a holistic view of the abstraction hierarchy. The big investment news: Singapore is set to invest close to S$300 million over the next five years into quantum technology research and talent, as part of the National Quantum Strategy initiative.
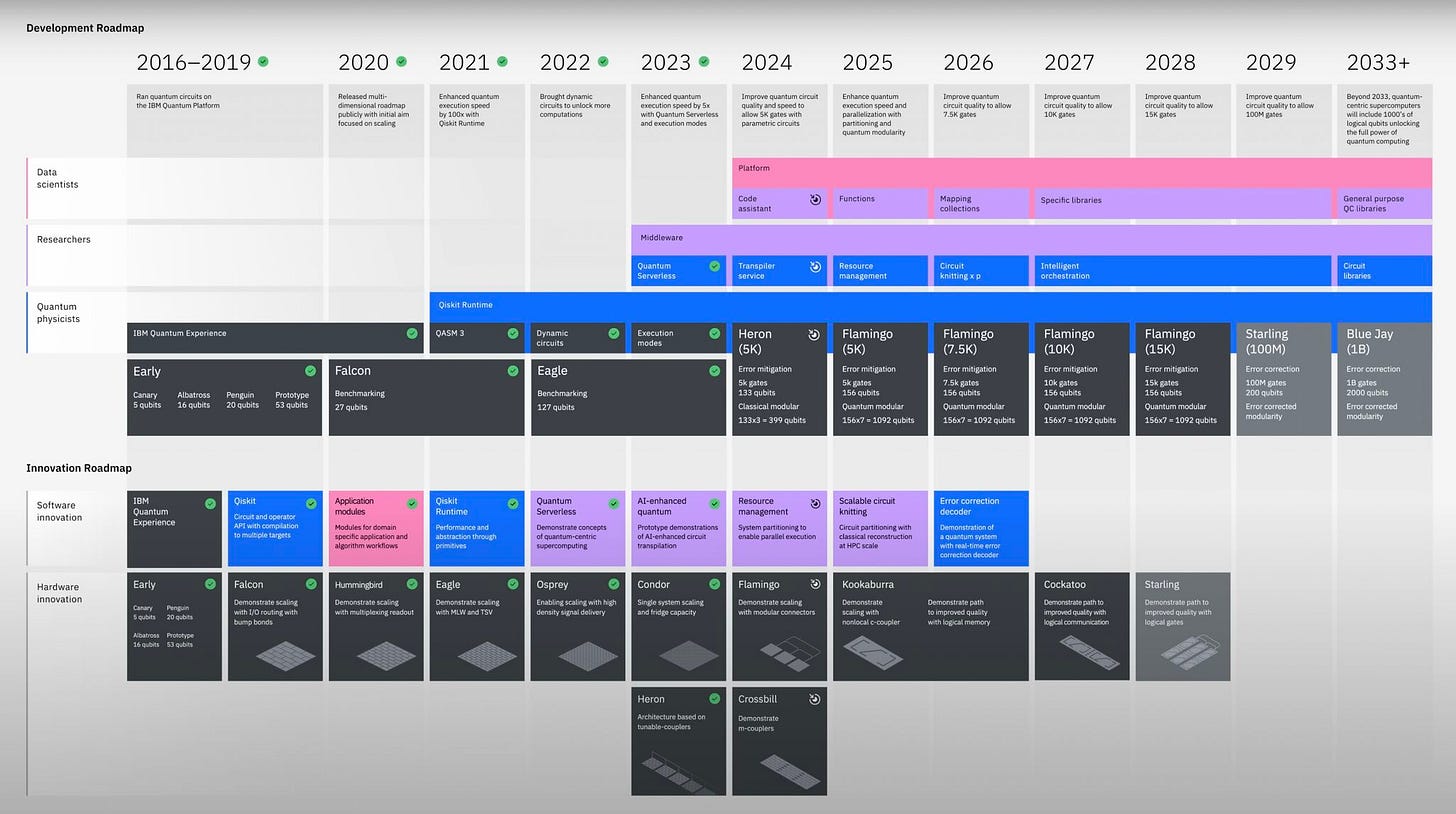
IBM released a couple of weeks ago an update on their roadmap eyeing revenue from quantum advantage cases in as little as 2 years using their modular structure and error correction. Put that work together with some of the systems developed by companies like Kipu Quantum, or the work from Q-Ctrl and we are getting very very close from epiphany.
How Distributed quantum entanglement works with Photonic’s work?
The Week in Quantum Computing
The ORCA-Quest quantitative CMOS camera: a core building block for quantum systems
Hamamatsu Photonics has developed the ORCA-Quest, a scientific camera that is gaining traction among quantum computing researchers and engineers. The camera, which was commercially released in 2021, is a quantitative CMOS (qCMOS) with unique "photon-number resolving" functionality, allowing it to accurately measure the number of photoelectrons generated on each pixel in a 9.4 megapixel array. The camera's unique pixel structure, which includes deep-trench structures in the semiconductor layers, ensures that each photon impacting a pixel registers exclusively on that pixel.
Q*Bird raises €2.5M to secure businesses against cyber threats and future quantum attacks
Quantum security startup Q*Bird has secured €2.5M in funding to expand in the quantum security market. The Delft-based company, founded in 2022, aims to protect data communications and digital infrastructure with its patented technology. Q*Bird's unique quantum cryptography product, Falqon, offers provable security against all attacks, including those from future quantum computers. The company is currently testing its technology at the Port of Rotterdam and has secured a launch customer for Falqon. Q*Bird's co-founder and CEO, Ingrid Romijn, aims to become the largest supplier of quantum networking equipment globally. The funding round was led by QDNL Participations and Cottonwood Technology Fund, with participation from InnovationQuarter. The funds will be used to scale up Falqon sales and develop more quantum security products.
Book: What You Shouldn't Know About Quantum Computers
Chris Ferrie's free book, "What You Shouldn't Know About Quantum Computers" is available on arXiv and aims to demystify quantum computing for a broad audience, from CEOs to high school teachers. The book, which includes a foreword by Scott Aaronson, challenges misconceptions and seeks to deepen understanding of quantum computing's potential and limitations.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.15838v1
"Quantum Computing Progress and Market Potential Highlighted at ISC 2024: Insights from UC's Kathy Yelick and Leading Tech Companies"
At the ISC 2024 conference, around 20 sessions were dedicated to quantum computing (QC), including a keynote by Kathy Yelick, Vice Chancellor for Research at the University of California. Yelick highlighted the significant progress in error correction and the ongoing debate over different types of qubits. However, she also pointed out that QC is not yet ready to replace traditional computing. A panel discussion on QC technologies featured representatives from QuEra, IBM, IQM, and Quantinuum, who shared their views on the most promising QC technologies. According to Hyperion, the worldwide QC market is predicted to exceed $1 billion in 2025.
https://www.hpcwire.com/2024/05/22/isc-2024-a-few-quantum-gems-and-slides-from-a-packed-qc-agenda/
Paper: An Abstraction Hierarchy Toward Productive Quantum Programming
In a paper titled "An Abstraction Hierarchy Toward Productive Quantum Programming", Olivia Di Matteo and her team propose an abstraction hierarchy to support quantum software engineering, analyzing the current state of quantum software stack using programming models. They also discuss the overlaps across programming, execution, and hardware models found in current technologies, and apply this hierarchy to solve the eigenvalue estimation problem in two distinct ways. The paper emphasizes that progress in quantum programming hinges on a holistic view of the abstraction hierarchy, rather than focusing solely on its components.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.13918v1
RIVERLANE AND ALICE & BOB JOIN FORCES TO ACCELERATE QUANTUM ERROR CORRECTION
Riverlane, a global leader in quantum error correction technology, and Alice & Bob, a developer of fault-tolerant quantum computers, have partnered to integrate Riverlane's quantum error correction stack within Alice & Bob's quantum computing system based on cat qubit technology. Alice & Bob's cat qubit, a unique superconducting qubit, is designed to be protected from bit-flips, reducing the error correction challenge and enabling the construction of a large-scale, error-corrected quantum computer with 200 times fewer hardware resources than other approaches. Dr Theau Peronnin, CEO of Alice & Bob, said they chose to partner with Riverlane due to their promising quantum error correction technology. The collaboration was announced at the France Quantum conference in Paris.
How banks are employing quantum computing
Banks are increasingly utilizing quantum computing to combat cyber risks, according to Jan Bellens, global banking and capital markets sector leader at EY. Large banks such as JPMorgan Chase and Wells Fargo are exploring the technology, which uses quantum bits or qubits for faster data processing. The most prominent application of quantum computing in banking is as a defensive tool against cyber threats. Despite being in its early stages, quantum computing has potential to accelerate various financial services processes, including capital markets and payments. Bellens suggests that the learnings from these explorations should be shared industry-wide, especially in the context of cyber risk mitigation.
Singapore to invest about S$300 million in quantum tech research and talent
Singapore is set to invest close to S$300 million over the next five years into quantum technology research and talent, as part of the National Quantum Strategy (NQS) initiative. The NQS, announced by Deputy Prime Minister Heng Swee Keat, includes plans to design and build the country's own quantum processors. The initiative builds on the S$400 million already invested into quantum research over the past two decades. The NQS also includes a scholarship scheme aiming to develop up to 200 graduates in quantum technology. Singapore's pursuit of quantum technology, despite challenges like high error rates and energy requirements, signals its commitment to this promising field.
Two real-world tests of quantum memories bring a quantum internet closer to reality
Scientists from Harvard University and the University of Science & Technology of China have made significant strides towards the development of a quantum internet. The Harvard team, led by physicist Can Knaut, achieved entanglement between two quantum memories over a 35-kilometer loop through Boston and Cambridge, using a diamond-based quantum memory. Meanwhile, the Chinese team, led by physicist Xiao-Hui Bao, successfully entangled three quantum memories across a 20-kilometer network in Hefei, using a rubidium atom-based memory. Both teams confirmed "heralded" entanglement, crucial for practical applications.
https://www.sciencenews.org/article/quantum-physics-memories-internet
Michael Nielsen on Collaboration, Quantum Computing, and Civilization's Fragility | CWT
Capgemini announces new project with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency on quantum computing for energy transition
NEW YORK–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Capgemini Government Solutions LLC today announced a new initiative with The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) to investigate the use of quantum computing in the field of carbon capture. Beyond pushing the boundaries of technological innovation, this project provides an opportunity for Capgemini to work alongside the U.S. government to advance sustainability efforts and promote a greener future. To support this work, Capgemini will leverage its engineering talent across the globe to navigate the complex ecosystem of carbon capture. As part of this agreement, Capgemini will offer the use of its specialist hybrid intelligence team’s capabilities to tackle high-impact exploratory efforts and identify breakthrough technologies that can accelerate innovation and digital transformation.
JPMorgan Chase, Argonne National Laboratory and Quantinuum Show Theoretical Quantum Speedup with the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm
JPMorgan Chase, Argonne National Laboratory, and Quantinuum have demonstrated a theoretical quantum speedup using the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm. This collaboration between a leading financial institution, a national scientific research lab, and a quantum computing company showcases the potential for quantum computing in solving complex optimization problems, such as those encountered in finance. The team's success in demonstrating quantum advantage could herald a new era of computational capabilities, with profound implications for industries reliant on complex data processing and analysis.
In collaboration with Microsoft, Photonic demonstrates quantum entanglement at telecom wavelengths
Microsoft and Photonic have demonstrated quantum entanglement at telecom wavelengths, marking a significant milestone in quantum networking and computing. This achievement, six months into their collaboration, enables successful transfer of quantum information between physically separated qubits. As Dr. Stephanie Simmons, Founder and Chief Quantum Officer of Photonic, noted, this extends the boundaries of quantum computing beyond isolated systems and emphasizes the potential of their unique architectural strategy. Photonic's spin-photon architecture allows for quantum communication via existing telecom fibers. The next steps involve improving the quality of entanglement distribution and entangling additional quantum devices. Microsoft and Photonic aim to integrate quantum-networking capabilities into everyday operating environments through Microsoft Azure's global infrastructure.
US-returned Chinese physicist and team achieve world first in quantum computing
Chinese physicist Duan Luming and his team at Tsinghua University have built the world's most powerful ion-based quantum computer, achieving a stable trapping and cooling of a two-dimensional crystal of up to 512 ions. This breakthrough marks "the largest quantum simulation or computation performed to date in a trapped-ion system," according to a reviewer of the study published in Nature. Duan, a pioneer in quantum research, returned to China in 2018 after a 15-year stint in the US. The team also conducted a quantum simulation calculation using 300-ion qubits, demonstrating computational complexity far beyond classical computers.
NXP, eleQtron and ParityQC Reveal their First Quantum Computing Demonstrator for the DLR Quantum Computing Initiative
NXP Semiconductors, eleQtron, and ParityQC, part of the QSea consortium, have unveiled the first full-stack, ion-trap based quantum computer demonstrator entirely made in Germany, commissioned by the DLR Quantum Computing Initiative (DLR QCI). The Hamburg-based demonstrator will provide early access to real quantum computing resources to aid in complex applications like climate modeling and global logistics. The QSea consortium combines eleQtron’s MAGIC hardware, ParityQC architecture, and NXP’s chip design and technology. NXP Semiconductors' CTO Lars Reger believes this project will benefit the industry and research communities in Germany, strengthening digital sovereignty in the country and the EU.
Paper: Towards Green AI with tensor networks -- Sustainability and innovation enabled by efficient algorithms
The research paper "Towards Green AI with tensor networks" by Eva Memmel and her team highlights the unsustainable cost of AI progress due to the exponentially increasing computational requirements. The paper proposes the use of tensor networks (TNs), tools from multilinear algebra, in AI algorithms to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy. The authors argue for a shift in evaluating algorithms based on both accuracy and efficiency, demonstrating TNs' potential for Green AI. They also present an experimental setting for kernel ridge regression to analyze efficiency. The paper aims to raise awareness about Green AI's impact on sustainability and AI research.