The Week in Quantum Computing - November 13th
Issue #160
The Week in Quantum Computing. Brought to you by Sergio Gago (@piratecto).
Quick Recap
Researchers have successfully mixed diffusion models in quantum circuit synthesis, effectively bypassing the exponential overhead found in classical simulation of quantum dynamics. The Riverlane team has developed a new method for quantum error correction decoders that allows for parallelisation, tackling the data backlog issue and enabling efficient universal quantum computers. On the infrastructure front, Fermilab has launched a new 6,000-sq.-ft quantum research facility named “The Quantum Garage” to advance quantum information science and technology. Quantum technology is projected to generate $850 billion in market value by 2040, according to Olivier Tonneau from VC firm Quantonation.
Wavemaker and Liftt co-lead a $4.7 million funding round for Entropica Labs, French start-up Quandela raising 50 million euros right after delivering their first computer to OVH. And Photonica comes out of stealth getting $100m and a big co-development partnership with Microsoft, that resembles the OpenAI model. Meanwhile IonQ has raised a $500 mixed shelf for potential acquisitions. IQM has announced plans for a 150 qubit device in 2025. A fantastic paper on QKD has been published and a paper that serves as a text book on Quantum Information. Read all that below!
The Week in Quantum Computing
A Bold New Plan for Preserving Online Privacy and Security
Barath Raghavan and Bruce Schneier, propose a solution termed "decoupling", which involves separating private data and limiting the information systems can access. The strategy includes two types of decoupling: organizational (dividing information among organizations) and functional (splitting information among software layers). The authors assert, "We’re all hoping that companies will keep us safe, but it’s increasingly clear that they don’t, can’t, and won’t. We should stop expecting them to." Their proposition is a shift towards users taking security into their own hands.
https://spectrum.ieee.org/data-privacy
Paper: Quantum circuit synthesis with diffusion models
In a recent study, researchers Florian Fürrutter, Gorka Muñoz-Gil, and Hans J. Briegel demonstrated the use of denoising diffusion models (DMs) in quantum circuit synthesis. The team leveraged text-conditioning to guide the model in creating desired quantum operations within gate-based quantum circuits, effectively bypassing the exponential overhead found in classical simulation of quantum dynamics. The model was tested across two tasks: entanglement generation and unitary compilation, and showed proficiency in generating new circuits. The researchers suggest that DMs, with their flexibility and generalization capabilities, could be critical in quantum circuit synthesis, enhancing practical applications and theoretical understanding of quantum computation.
https://scirate.com/arxiv/2311.02041
Parallelisation opens window to useful quantum computers for the first time
The Riverlane team has developed a new method for quantum error correction decoders that allows for parallelisation, enabling efficient universal quantum computers. Quantum computers generate vast amounts of data that must be decoded in real time, a problem that could halt their progress. Riverlane's parallelisation method tackles this data backlog issue, allowing quantum computation at any scale. Details of this solution are published in the Nature Comms paper. The method works across all qubit types, with a focus on superconducting qubits due to their challenging speed for real-time decoding. This development paves the way towards useful quantum computing, overcoming previous concerns about the feasibility of real-time decoding.
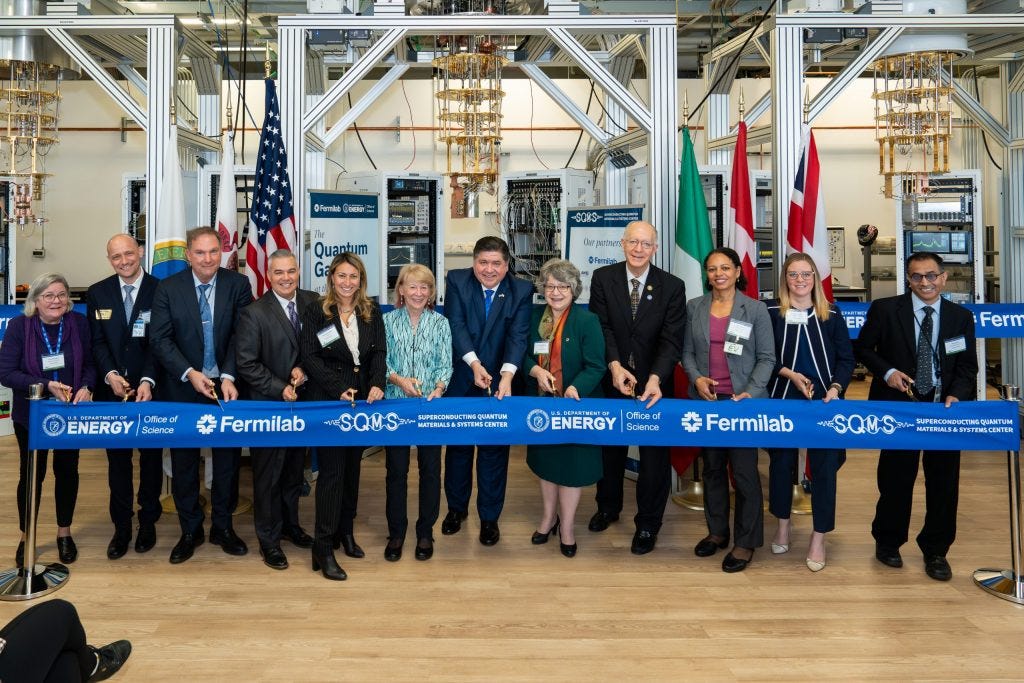
Fermilab’s SQMS Center inaugurates quantum information science and technology facility: “The Quantum Garage”
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab) has launched a new 6,000-sq.-ft quantum research facility named “The Quantum Garage”. The Superconducting Quantum Materials and Systems Center (SQMS) designed and built the facility to unite scientific communities, industries and start-ups to advance quantum information science and technology. The facility features large dilution refrigerators for quantum computation, sensing, metrology, and communications. DOE Under Secretary for Science and Innovation, Geri Richmond, stated that the Quantum Garage will enable the scientific community to advance quantum technology and science. The facility will also serve as a training ground for the next generation of quantum computing scientists and engineers.
Who Is Investing In The $850 Billion Quantum Tech Market And Why
Quantum technology, though in its early stages, is projected to generate $850 billion in market value by 2040, according to Olivier Tonneau, partner at VC firm Quantonation. This prediction was shared during a webinar organized by The European Quantum Industry Consortium (QuIC), which highlighted the potential of quantum technologies. Among the innovations discussed were quantum sensing technology from Exail Technologies, a photonic quantum computer from Quandela, and a quantum-based software platform from Multiverse Computing. Despite the challenges, the quantum tech market is expected to grow significantly, driven by a rapidly expanding ecosystem of startups and established institutions.
Build your quantum network
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is being embraced by CIOs and network administrators as a strategic decision to bolster the security of digital communications in data centers. The technology is being trialed as a fundamental element in proactive data defense. The simplest architecture for QKD systems is point-to-point, involving two parties, Alice (sender) and Bob (receiver), connected by a direct communication link. The quantum states are transmitted via this link, encoded with bits of information to generate a key. Commercially available quantum devices, offered by a range of vendors, can be incorporated into existing network architecture. However, there is a distance limitation of roughly 100 kilometers due to photon losses. The European Telecom Standards Institute (ETSI) is currently discussing standards for QKD systems.
https://quantumguru.medium.com/build-your-quantum-network-a826bc7b98cc
Wavemaker, Liftt co-lead $4.7m round in Singapore’s Entropica Labs
Wavemaker and Liftt co-led a $4.7 million funding round for a Entropica Labs. This financial injection will enable the firm to further its developments and innovations by providing developers and users with tools that can design and run quantum circuits and algorithms that are resilient to errors.. The involvement of Wavemaker and Liftt underscores the growing interest and investment in quantum technology across Asia's startup ecosystem.
https://www.techinasia.com/wavemaker-liftt-colead-47m-round-sg-quantum-software-firm
Quantum computer: French start-up Quandela raises 50 million euros
French start-up Quandela has successfully raised 50 million euros in funding for its quantum computing initiatives. The notable achievement highlights the growing interest and investment in the field of quantum technology. The funds will likely be utilized to advance Quandela's research and development efforts, propelling the company further into the forefront of the quantum computing industry.
D-Wave Supports New Congressional Legislation Designed to Expand U.S. Quantum Program
D-Wave Quantum Inc., a global leader in quantum computing systems, has announced its support for legislation aimed at expanding the National Quantum Initiative (NQI) in the US. The legislation aims to boost commercialization efforts, support industry engagement within US quantum programs, and encourage the development of near-term quantum applications. The company's CEO, Dr. Alan Baratz, has urged Congress to reauthorize and expand the NQI to keep pace with global leaders like Japan, the UK, Australia, and Germany. The legislation could accelerate the development of quantum applications that could solve complex public-sector problems, such as optimizing global supply chains and infrastructure, and enhancing sustainability.
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/d-wave-supports-congressional-legislation-120000045.html
Paper: Hacking Cryptographic Protocols with Advanced Variational Quantum Attacks
A recent paper by Borja Aizpurua, Pablo Bermejo, Josu Etxezarreta Martinez, and Roman Orus presents an improved approach to Variational Quantum Attack Algorithms (VQAA) on cryptographic protocols. Their method offers robust quantum attacks on cryptographic algorithms, notably more efficient and requiring fewer qubits than previous strategies. Simulations of these attacks have been implemented on symmetric-key protocols like S-DES, S-AES, and Blowfish, with a classic simulation of an 8-qubit quantum computer able to find a 32-bit Blowfish instance's secret key with 24 times fewer iterations than a brute-force attack. The authors' work also suggests potential future improvements, bringing us closer to assessing the vulnerability of large-size classical cryptographic protocols with Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) devices.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.02986v1
Paper: Quantum Communications
Michal Hajdušek and Rodney Van Meter have published a paper / book titled "Quantum Communications". The work, supported by the Simons Foundation, discusses the advancing field of quantum technologies, underlining its growing attention from governments, private companies, investors, and the public. The authors emphasize that information processing and communication using individual quantum systems are no longer theoretical but are becoming commonplace in labs and startups globally. The paper that serves as a textbook, part of the Q-Leap Education project's Quantum Academy of Science and Technology, aimed at educating future quantum engineers. The main emphasis is on quantum networks, with the work suitable for undergraduate students with diverse backgrounds.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.02367v1
Quantum computing the next (very) cold war? US lawmakers want to blow billions to outrun China, Russia
US lawmakers, led by Frank Lucas and Zoe Lofgren, are concerned about falling behind Russia and China in quantum computing. They have introduced a bill proposing billions in spending to accelerate quantum computing systems development. China and Russia are actively developing quantum computing test beds, with a Chinese group claiming a 176 qubit quantum computer online. The proposed bill, HR6213, reauthorizes the Quantum Initiative Act and calls for the US government to take steps to accelerate US development in quantum systems. The bill requests over $3 billion between 2024 and 2028. Despite uncertainty around the bill's approval, the US has made strides in quantum computing, with IBM planning to spend $100 million on a 100,000 qubit quantum-centric supercomputer. The quantum race is on, with the US poised to invest heavily to maintain its technological edge.
https://www.theregister.com/2023/11/07/us_lawmakers_quantum/
MonarQ: A quantum computer in service of research
Calcul Québec, a provider of infrastructure for the Canadian academic research ecosystem, is managing a new quantum computer, MonarQ. MonarQ, which features 24 superconducting qubits, will be accessible to researchers for exploratory science. This aligns with Calcul Québec's mission to make technology accessible and understandable for researchers, and to actively participate in the use and application of their infrastructure in research. The organization also has a dedicated research services development team, formed in 2022, to meet the needs of the Humanities and Social Sciences research community and implement quantum computing services. MonarQ's acquisition signifies a major step towards quantum service development, providing an affordable platform for fundamental quantum computing research.
https://www.innovationnewsnetwork.com/monarq-quantum-computer-service-research/39474/
IQM launches IQM Radiance – a 150-qubit system paving the way to quantum advantage
IQM Quantum Computers has introduced a quantum computing platform, IQM Radiance, which includes a roadmap for a 150-qubit system aimed at achieving quantum advantage. The system is designed for businesses, high-performance computing centers, data centers, and government agencies. Dr. Jan Goetz, CEO and Co-founder of IQM Quantum Computers, highlights the potential of quantum computing in machine learning, cybersecurity, energy grid optimization, and chemical research. IQM Radiance starts as a 54-qubit system, with availability targeted for 2024, and an upgrade to a 150-qubit system planned for 2025. Dr. Björn Pötter, Head of Product at IQM, emphasizes the significant head start businesses can gain through the acquisition of IQM Radiance. The company's proven technical capabilities include a successful partnership with VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, delivering a 20-qubit quantum computer.
Best practices for portfolio optimization by quantum computing, experimented on real quantum devices
Researchers from Scientific Reports have successfully solved portfolio optimization problems using the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) on real quantum computers. The team's work focused on defining the best hyperparameters for portfolio optimization by VQE. The study found a strong dependence on solution quality upon the size of the quantum computer and correct hyperparameters. With optimal settings, quantum algorithms on real devices achieved solutions close to exact with a high convergence rate towards classical solutions. Results from different real quantum devices also revealed the relationship between solution quality and quantum processor size. These findings affirm the potential for quantum computing to solve complex financial problems more efficiently as quantum hardware continues to develop.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-45392-w
2025, el año para promover la computación cuántica
BBVA, the only Spanish bank among over 300 global experts and organizations, is urging UNESCO to declare 2025 the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology. The initiative is expected to foster significant advancements in areas related to the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals, such as non-polluting energy development, climate action, and sustainable economic growth. Quantum science and technology have been instrumental in transformative developments like transistors and lasers, and are anticipated to revolutionize complex system modeling, ultra-secure communications, and the development of medical treatments, new materials, and more efficient, sustainable energy batteries. The quantum year aims to inspire professionals to realize these advancements in the coming decades.
https://www.bbva.com/es/innovacion/2025-el-ano-para-promover-la-computacion-cuantica/
IonQ files for $500M mixed shelf, CFO emphasizes it is for potential M&A
Quantum computer maker IonQ (NYSE:IONQ) has filed for a $500M mixed shelf, as announced in its Q3 earnings report. The filing includes common stock, preferred stock, debt securities, warrants, depositary shares, subscription rights, purchase contracts, and units. Despite a sequential quarterly fall, IonQ raised full-year revenue and bookings guidance. CFO Thomas Kramer clarified that the filing is not due to a need for funds but to fund potential M&A and strategic growth. IonQ’s quantum computer, IonQ Forte, has a capacity of 29 algorithmic qubits. The company's stock closed 1.6% lower at $11.23. Kramer's statement indicates the company's proactive approach towards potential growth opportunities.
QEC23: Six key takeaways on the state of quantum error correction
The QEC23 conference in Sydney highlighted the rapid progression in Quantum Error Correction (QEC). The field has moved from theoretical to practical, with over half the talks presenting results from new QEC experiments. Notably, Google's Mike Newman discussed the suppression of logical errors by expanding the surface code. The conference also spotlighted the fast-paced progress in neutral atom qubits, with significant results presented by Dolev Bluvstein of Harvard University. Other key insights included the rising interest in erasure qubits and real-time decoding, and the shift towards a circuit-centric approach with Floquet codes. The discussions underscored the central role of QEC in advancing fault-tolerant quantum computing.
https://www.riverlane.com/blog/qec23-six-key-takeaways-on-the-state-of-quantum-error-correction
Microsoft and Photonic join forces on the path to quantum at scal with a $100m investment
Microsoft and Photonic Inc. have announced a strategic co-innovation collaboration to advance quantum networking and computing. Photonic's unique architecture, which employs silicon spin qubits with a spin-photon interface, will be integrated into Microsoft's Azure Quantum Elements. The partnership aims to address three stages of quantum networking: delivering entanglement between two separate quantum devices, creating a quantum repeater that can capture and hold quantum information, and developing a reliable quantum repeater that is operational with Azure cloud. Jason Zander, Executive Vice President of Strategic Missions and Technologies at Microsoft, and Dr. Stephanie Simmons, founder and Chief Quantum Officer of Photonic, highlighted the significance of the collaboration in accelerating scientific discovery and innovation in quantum computing. The partnership represents a notable stride towards the realization of a global quantum internet.