The Week in Quantum Computing - September 30th 2024 - EU €65M, Q-Ctrl, Cat qubits and more
Issue #203
Quick Recap
This week in quantum computing, significant advancements were made in error correction and practical applications. Researchers led by Harald Putterman demonstrated a hardware-efficient quantum error correction method using concatenated bosonic qubits, achieving a minimum logical error per cycle of 1.65% for a distance-5 code. Q-CTRL and QCentroid have integrated their software platforms to streamline quantum optimization workflows, enhancing accessibility and boosting algorithm success on real hardware by 1000x. The European Union announced a €65 million investment in quantum chip research, part of a broader €200 million initiative aimed at advancing quantum technologies. This funding underscores the EU's commitment to leading in frontier technologies and enhancing Europe's innovation landscape. Additionally, a comprehensive survey by QuEra Computing revealed that 74.9% of nearly 1,000 respondents are optimistic about quantum computing's potential, despite concerns about cybersecurity, ethics, and job market disruptions.
Podcast available here:
Have you ever played music with a quantum device? Well, QuantumTech, the Ion Maidens and Moth Quantum made it happen last week at Twickenham in London. Next time… Wembley! The little screen on the top left, that was the qubit modifying the timbre and modulation of the synth that Thomas was playing like a boss.
The Week in Quantum Computing
HSBC Pioneers Quantum-Safe Tech for Tokenised Gold
The trial also addressed the threat of "store now, decrypt-later" (SNDL) cyber incidents. SNDL is a technique where malicious actors steal sensitive data with the intention of decrypting it later using powerful quantum computers that do not yet exist.
https://ift.tt/2otiuwx
Hardware-efficient quantum error correction using concatenated bosonic qubits
Researchers led by Harald Putterman have demonstrated a hardware-efficient quantum error correction method using concatenated bosonic qubits. The team, comprising 121 authors, utilized a microfabricated superconducting quantum circuit to create a logical qubit memory by concatenating encoded bosonic cat qubits with an outer repetition code of distance \(d=5\). This approach passively protects against bit flips and corrects phase-flip errors using ancilla transmons. The study found that the phase-flip correcting repetition code operates below threshold, with logical phase-flip error decreasing as code distance increases. The minimum logical error per cycle was 1.65% for the distance-5 code. These findings suggest that concatenated bosonic codes are promising for achieving fault-tolerant quantum computation.
Q-CTRL integrates with QCentroid to enhance quantum optimization workflows for customers
Q-CTRL has integrated its Fire Opal software with QCentroid to streamline quantum optimization workflows. This collaboration aims to simplify algorithm testing using no-code and API tools, enhancing accessibility to quantum computing. Fire Opal's AI-driven error suppression boosts algorithm success on real hardware by 1000x, facilitating large-scale problem-solving. The integration allows QCentroid users to leverage Fire Opal’s capabilities directly, including solving complex MaxCut optimization problems. Heather West from IDC praised the partnership for offering "frictionless quantum software." This integration marks a significant step in making quantum computing more practical and effective for businesses and researchers, promising to unlock new possibilities in the field. The main takeaway: Q-CTRL and QCentroid's partnership significantly lowers barriers to quantum computing adoption.
Hacking and Certifying Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) - Prof. Vadim Makarov @ QV3, DEF CON 32
At DEF CON 32's QV3 session, Prof. Vadim Makarov discussed the vulnerabilities and certification processes of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD). Makarov highlighted that while QKD promises theoretically unbreakable encryption, practical implementations can be susceptible to hacking. He demonstrated specific attack vectors and emphasized the need for rigorous certification standards to ensure security. "Even quantum systems are not immune to real-world flaws," Makarov stated. Institutions and companies involved in QKD development must prioritize robust testing and certification to safeguard against potential breaches. The main takeaway: Ensuring the security of QKD systems requires not just theoretical robustness but also practical, certified resilience against hacking.
EU invests €65 million in quantum chips
The European Union has announced a €65 million investment in quantum chip research through the Chips Joint Undertaking (Chips JU). This funding, part of a broader €200 million initiative over three years, aims to advance quantum computing and sensing technologies. The call for proposals, closing on January 21, 2025, seeks projects that will develop and manufacture quantum technologies, enhancing Europe's innovation landscape and establishing a supply chain for quantum chips. Real-world applications include optimizing logistics, accelerating drug discovery, enhancing cybersecurity, and improving AI algorithms. Interested organizations can apply via the Funding and Tender Opportunities portal and the Chips JU website. This initiative underscores the EU's commitment to leading in frontier technologies.
Quantum Computing: Opportunities, Concerns And Impact
Yuval Boger of QuEra Computing reports on a comprehensive survey involving nearly 1,000 respondents, revealing 74.9% optimism about quantum computing's potential despite significant concerns. Key issues include cybersecurity threats, ethical dilemmas, and job market disruptions. With 41 countries initiating national quantum programs, the focus is on technological leadership, economic growth, and national security. The survey highlights a preference for quantum computers from friendly trade partners over domestic systems. Boger emphasizes the urgent need for international collaboration on quantum-resistant cryptography, ethical guidelines, and equitable access. The main takeaway: Responsible innovation and governance are crucial to harness quantum computing's benefits while mitigating its risks.
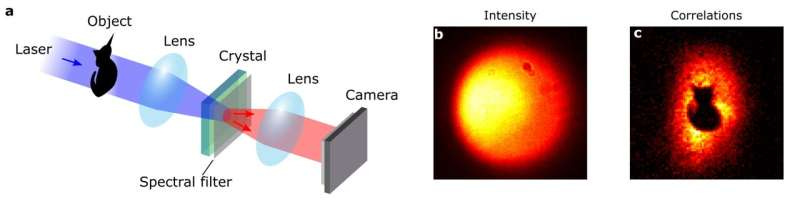
Sorbonne University Team Pioneers Quantum Imaging to Conceal Visual Data from Standard Cameras
Researchers from the Paris Institute of Nanoscience at Sorbonne University, led by Hugo Defienne and Ph.D. candidate Chloé Vernière, have developed a groundbreaking quantum imaging technique that hides images from standard cameras. By using entangled photons and a process called spontaneous parametric down-conversion (SPDC), they encoded images into the spatial correlations of photon pairs. Standard cameras only capture a uniform intensity image, but a single-photon sensitive camera and specialized algorithms can reconstruct the hidden image. "Entangled photons are fundamental to many applications," Vernière notes. This method holds promise for secure quantum communication and imaging through scattering media. The main takeaway: Quantum correlations can effectively conceal visual information from conventional imaging technologies.
World’s first observation of quantum entanglement in quarks
CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has achieved the first observation of quantum entanglement in quarks, as reported in *Nature*. This groundbreaking discovery was made by the ATLAS collaboration and confirmed by the CMS detector, both at the LHC. The experiments, conducted between 2015 and 2018, involved proton-proton collisions at 13 teraelectronvolts. ATLAS spokesperson Andreas Hoecker highlighted the significance, stating it "paves the way for new investigations." CMS spokesperson Patricia McBride noted the potential to test the Standard Model in new ways. This observation marks a significant milestone in quantum mechanics, opening avenues for advanced technological applications and deeper understanding of particle physics. The main takeaway: Quantum entanglement has now been observed in quarks, expanding the frontier of quantum physics research.
New Research Unveils a Scalable Path to Quantum Processors
In recent theoretical research, a team of physicists, led by University of Rhode Island professor Vanita Srinivasa, envisions a modular system for scaling quantum processors with a flexible way of linking qubits over long distances to enable them to work in concert to perform quantum operations. The ability to carry out such correlated or “entangling” operations between linked qubits is the basis of the enhanced power quantum computing holds compared with current computers. A new paper on their research, co-authored by Srinivasa, Jacob M. Taylor of the University of Maryland and the National Institute of Standards and Technology, and Jason R. Petta of the University of California, Los Angeles, was recently published in the journal PRX Quantum.
AI and Quantum Computing Form Strong Bond to Power Materials Discovery Innovation SandboxAQ, EY Researchers Report
A white paper by SandboxAQ and EY reveals the transformative potential of AI and quantum-inspired technologies in accelerating materials discovery, traditionally a slow and costly process. AI-driven simulations, combined with quantum mechanics, enable faster and more accurate predictions of material behavior, reducing the need for expensive lab experiments. This democratizes materials research, allowing smaller companies to compete in innovation and address challenges like battery degradation and energy storage. "AI and quantum computing hold particularly promising potential for the future of materials science," state the researchers. SandboxAQ’s platform integrates quantum chemistry toolkits with AI computation, making materials discovery faster and more cost-effective. The main takeaway: AI and quantum computing are revolutionizing materials discovery, democratizing access, and accelerating innovation.
Quantum Computing: Between Hope and Hype
In June, the White House announced a US/India workshop on quantum computing and post-quantum cryptography, hosted by UCLA and organized by Rafail Ostrovsky. Scott Aaronson delivered the opening talk, reflecting on his 25 years in quantum computing. He noted significant recent advancements, including Google’s use of the Kitaev surface code to extend logical qubit coherence and a Microsoft-Quantinuum collaboration achieving high-fidelity quantum operations. Aaronson emphasized the importance of 2-qubit gate fidelities reaching ~99.99% for fault-tolerant quantum computing. He urged immediate action on post-quantum cryptography, highlighting the field's transition from theoretical to practical. Aaronson concluded that quantum computing is now plausibly imminent, necessitating serious consideration and preparation. Main takeaway: Quantum computing is transitioning from theoretical promise to practical reality, demanding immediate attention to post-quantum cryptography.
Quantum Circle Summit 2024
The Quantum Circle Summit 2024, set for November 14 in Brussels, will be the first event in Belgium to gather over 200 international and local quantum computing experts. Key speakers include Julian Van Velzen (Capgemini), Stefan Walter (Fujitsu), and Maarit Palo (IBM). The summit will feature nine panelists discussing global and Belgian quantum technology landscapes. Jan Sonck, Quantum Ecosystem Manager, will explain the community's goals to accelerate quantum development in Belgium. The event aims to foster strategic investments and societal impact through quantum technology. "Let’s meet the future!" encapsulates the summit's forward-looking vision. The main takeaway: The summit is a pivotal step for Belgium's quantum technology ecosystem.
US Implements Controls on Quantum Computing and other Technologies
The U.S. Commerce Department announced new export controls on quantum computing, advanced semiconductors, and additive manufacturing technologies. These controls, effective November 5 for quantum technologies, include key equipment, materials, and software. Assistant Secretary Thea D. Rozman Kendler emphasized the importance of international coordination for national security. The rule stops short of requiring licenses for foreign nationals but mandates new disclosure requirements. Carl Williams, a quantum technology consultant, noted the burden on small companies due to these reporting requirements. The Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) seeks public comments on potential future license requirements. The main takeaway: The U.S. is tightening controls on critical technologies to safeguard national security while balancing industry impact.
Contribute your flagship quantum technology showcase to the quantum application hub.
A platform where the forefront of commercial quantum technology is not only displayed but experienced. This hub serves as a vital intersection for executives and policy makers, offering them a firsthand look at the state-of-the-art in commercial quantum technology.







Big thanks for mentioning our Quantum Circle Summit, taking place in Brussels on November 14.