The Week in Quantum Computing - September 25th
Issue #153
The Week in Quantum Computing. Brought to you by Sergio Gago (@piratecto).
Quick Recap
A VERY busy week indeed, full with conferences, papers dropped and news.
Government Support: Governments, such as the U.K., are actively supporting quantum hardware and software development, with the U.K. committing £2.5 billion over the next ten years.
Venture Capital: VC funding is available in the quantum sector, with examples like Oxford Ionics raising £40 million and Phasecraft securing £17.4 million in equity finance.
Funding for Quantum Hardware: Nanofiber Quantum Technologies Inc. raised $8.5 million in funding from venture capital investors.
Spain's Quantum Initiatives: Spain is investing €22 million in its Quantum Spain program to compete in quantum research and is collaborating with companies like IBM, Repsol, and Huawei.
Researchers have published a paper on Barren Plateaus in Quantum Ansätze, providing insights into quantum computing's limitations and potential improvements.
A study introduces SU(2) equivariant quantum circuit ansätze using spin networks, which could enhance quantum algorithm optimization.
French startup ColibriTD raised €1 million from the Earlybird fund to develop a quantum-as-a-service platform.
Cambridge startup Riverlane announced a "quantum decoder chip" for real-time error correction in quantum computing.
The University of Copenhagen received a DKK 49.5 million grant to establish a Quantum Technology Training Laboratory, promoting quantum education and research.
IBM launched a free online course on quantum-safe cryptography for developers to address the cybersecurity threats posed by quantum computing.
Intel is working on scaling its quantum computing technology to millions of error-correcting qubits to achieve a quantum advantage.
Signal Foundation is upgrading its Signal Protocol to quantum-safe cryptography, anticipating the threat of quantum computing to encryption.
Canada unveiled its first IBM Quantum System One computer with a 127-qubit processor.
Toshiba opened a Quantum Information Group in Cambridge, focusing on quantum cryptography, including Quantum Key Distribution (QKD).
Quantum Sensing is Cool
Sridhar Prabhu et. all have developed the amazing poster with the landscape of quantum sensing. Sometimes in the world of computing we get too fixated with algorithms, but sensing is really the king here!
https://zenodo.org/record/8350885
The Tweet of the week
The Week in Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing: Building A Startup In The Pre-Market Phase
According to figures published by Markets and Markets, revenues in the sector are expected to come in at around $899 million in 2023, rising to $4,375 million in 2028. The development of quantum hardware and software is something that governments are keen to encourage. For instance, the U.K. government sees Britain becoming a “quantum-enabled” country by 2033 and has committed £2.5 billion to supporting development over the next ten years.
So there is confidence and consequently, there is VC cash available. For instance, Oxford Ionics - a hardware company with 50 people on the payroll - has raised £40 million so far. Phasecraft - a software startup - has secured £17.4 million in equity finance, plus a further £3.7 million in grants.
Link: https://ift.tt/gJusloh
September 17, 2023 at 03:31PM
Nanofiber Quantum Technologies Raises $8.5 Million in Funding for Quantum Computing Hardware
Nanofiber Quantum Technologies Inc. (NanoQT) has secured $8.5 million in funding from leading venture capital investors, including Phoenix Venture Partners (PvP), the JAFCO Group Co Ltd, SPARX Group Co Ltd, Keio Innovation Initiative, Inc., and Waseda University Ventures.
Link: https://ift.tt/enpJ9SB
Inside Spain’s burgeoning quantum tech landscape
Spain plans to catapult itself into the global quantum research landscape through significant national investment. Its domestic R&D program, Quantum Spain, run by the Ministerio de Economía, supports this goal with a budget of 22 million euros until 2025. The Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC), one of Spain’s fourteen supercomputing centers, is set to house the country's first 30-qubit quantum computer. This initiative has been supported by quantum startup Qilimanjaro, formed by government center researchers. Victor Canivell, co-founder of Qilimanjaro, stressed that the Spanish government offers key support to spinoffs, though venture capital is significantly less present than in the U.S. Further, the BSC is working on tech transfer initiatives, using EU public funding to facilitate public-private collaborations with companies like IBM, Repsol, and Huawei. The key takeaway: Spain is strategically leveraging public institutions and funding to compete in the quantum race.
How to Buy a Quantum Computer
Quantum computers, utilizing quantum bits or qubits, present vast potential for advancements in various fields ranging from chemistry to finance to AI. These computational machines use principles of quantum mechanics for its processing; a departure from the use of bits by classical computers. Companies like D-wave and SpinQ are pioneering sales in quantum computers, despite the high costs (in millions) and specialized applications. Quantum annealing, performed by such machines, is particularly attractive for those requiring high security or involved in teaching. Considering the high expenditures, quantum computing is typically accessed as a service; cloud-based quantum computing (like IBM quantum experience) and circuit simulators serve as alternatives for owning actual quantum hardware. Despite the current developmental phase of quantum computing, future implications are colossal, especially in the field of cryptography and machine learning.
https://quantumzeitgeist.com/how-to-buy-a-quantum-computer/
Paper: The Adjoint Is All You Need: Characterizing Barren Plateaus in Quantum Ansätze
Enrico Fontana, Dylan Herman, Shouvanik Chakrabarti, Niraj Kumar, Romina Yalovetzky, Jamie Heredge, Shree Hari Sureshbabu, and Marco Pistoia have released a cutting-edge research paper on quantum computing. The study utilizes the representation theory of compact Lie groups to formulate a theory of Barren Plateaus (BPs) for parameterized quantum circuits, specifically in relation to their dynamical Lie algebra (DLA), a term deemed Lie algebra Supported Ansatz (LASA). Their innovative approach allows, for the first time, the ability to calculate the variance of the gradient of the cost function for non-trivial, subspace uncontrollable family of quantum circuits. The team proves that this variance scales inversely with the dimension of the DLA, aligning with previous numerical observations. The implications of their findings could lead to advancements in quantum computing. The key takeaway is a newly established connection between Barren Plateaus and the variance of the gradient of the cost function.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.07902v2
The French startup ColibriTD has raised €1 million in funding from the Earlybird fund to make quantum computing universally accessible
French startup, ColibriTD, has raised €1 million from the Earlybird fund in support of its goal to make quantum computing universally accessible. Run by co-founders Laurent Guiraud, a former Google and AWS product domain expert, and Hacène Goudjil, a corporate social responsibility professional, the team aims to create an end-to-end quantum computing platform. The funding will be utilised to develop a hardware-agnostic quantum-as-a-service platform, and strengthen hardware and academic partnerships. Initially focusing on aerospace applications, they plan to expand into the healthcare sector. Earlybird Venture Capital's Earlybird-X, alongside several business angels, led the funding round. Summing up, ColibriTD's funds aim to speed up the development of their quantum-as-a-service platform, promoting universal quantum computing accessibility.
Paper: All you need is spin: SU(2) equivariant variational quantum circuits based on spin networks
In a quantum computing breakthrough, researchers Richard D. P. East, Guillermo Alonso-Linaje, and Chae-Yeun Park have proposed SU(2) equivariant quantum circuit ansätze using spin networks to optimize variational algorithms' operational efficiency. By utilizing spin networks, their research introduces a natural building block for forming parameterized quantum circuits, with demonstrated effectiveness in resolving the SU(2) symmetric Heisenberg models' ground state problems. This report, funded by the Simons Foundation, applies a form of tensor network invariant under group transformation, providing a significant boost for quantum variational algorithms' performance. Notably, this construction is mathematically equivalent to existing models but easier to execute on quantum hardware. The key takeaway is that spin networks-based SU(2) equivariant variational quantum circuits could pave the way for quantum algorithm optimization, indicating wider application potential in real-world problems.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.07250v1
Cambridge chip designer Riverlane aims to be the next Arm with quantum game-changer
Cambridge start-up Riverlane, valued at £150m, announced a significant advance in quantum computing: a "quantum decoder chip" capable of real-time error correction. A spin-off from Cambridge University, Riverlane is seeking to equal Arm in chip design. Quantum computers are capable of dealing with complex issues beyond the scope of ordinary computers, prompting potential revolution across industries including healthcare, sustainable energy, materials science and logistics. Their wide application has been held back by high error rates rendering them unusable. Steve Brierley, CEO and founder of Riverlane, said the development of a decoder to detect and rectify errors in real-time was crucial. This achievement is viewed as potential turning point in commercializing quantum computing.
Podcast with Carmen Recio and Sergio Gago, from Moody’s Analytics
The Superposition Guy’s podcast recently hosted Carmen Recio and Sergio Gago from Moody's Analytics. During the discussion, they detailed the importance of quantum computing in financial risk modelling, machine learning, and optimization, with a focus on the intersection of quantum and artificial intelligence (AI). They also addressed the necessity for businesses to stay informed about how quantum computing can be integrated into existing processes. Gago, a former CTO turned quantum specialist and now Managing Director of AI and Quantum Computing at Moody's, underscored how companies often struggle to discern how different tech breakthroughs, such as quantum computing and AI, can synchronously enhance their operations. The key takeaway is the growing significance of quantum computing in the financial services industry and the increasing need to bridge the gap between quantum companies and end-users.
https://quantumcomputingreport.com/podcast-with-carmen-recio-and-sergio-gago-from-moodys-analytics/
The University of Copenhagen is Awarded a Quantum Technology Training Laboratory
The University of Copenhagen has been awarded a DKK 49.5 million grant from the A.P. Møller Foundation to establish a Quantum Technology Training Laboratory at the Niels Bohr Institute. The lab will form part of a new educational initiative, the "Center for Educational Quantum Advantage". Professors Anasua Chatterjee, Ferdinand Kuemmeth, Kim Splittorff, and Jan Thomsen initiated the new center, aiming to bolster Denmark's position in quantum physics. The lab's state-of-the-art infrastructure will provide hands-on experimentation experience with prototypes of quantum computers, modernizing the teaching framework and encouraging young talent to delve into quantum physics research. Rector Henrik C. Wegener expressed gratitude for the support, noting it's a "good day for the University of Copenhagen's students, researchers, and partners". Key takeaway: The development signifies a significant step in the promotion and development of quantum computing education and research.
AI and Quantum Computing’s role in shaping tomorrow’s hospitality and catering industry
The AI and quantum computing symbiosis has promising potential to significantly benefit the hospitality and catering industry. According to Grace Weaver of Hospitality and Catering News, AI’s data analysis capabilities can optimize operations, personalised customer experiences, and enhance security, while aiding with sustainability and inventory management. Quantum computing, meanwhile, can solve complex optimization issues related to workforce schedules and encryption, thus aiding in data security. By merging these technologies, businesses in the sector can leverage this synergy to offer more efficient, robust services making strides towards sustainability goals. Overall, the relationship between AI and quantum computing provides a roadmap for hospitality and catering industry’s response to evolving demands of modern consumers and climate change.
Rigetti Computing Awarded Five-Year Contract with Air Force Research Lab for Quantum Foundry Services
Rigetti Computing, a pioneer in full-stack quantum-classical computing, has been awarded a five-year Indefinite Delivery Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) contract by the Air Force Research Lab (AFRL). Rigetti will provide quantum foundry services, enhancing the research and development of quantum networking hardware. As per the agreement, Rigetti will offer quantum integrated circuits, quantum-limited amplifiers, cryogenic microwave components, and 9Q QPUs. Dr. Subodh Kulkarni, Rigetti CEO, highlighted the importance of the contract in bolstering their existing partnership with AFRL. Rigetti’s Fab-1, operational since 2016, has been instrumental in fabricating chips for internal R&D and academic research. This collaboration is expected to enhance Rigetti’s understanding of device and design level fabrication processes. The key takeaway is Rigetti's reinforced partnership with AFRL to further quantum computing research and industry applications.
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/rigetti-computing-awarded-five-contract-123000757.html
China, India race for 1,000-qubit quantum computers
China and India are locked in a race to develop 1,000-qubit quantum computers, a feat set to be achieved by IBM in the US this year. India, a latecomer in this field, approved a $730 million funding package for its National Quantum Mission (NQM) in April 2023, with a plan to deliver quantum computers with 50-1,000 physical qubits by 2031. Chinese tech firm Origin Quantum launched a 24-qubit computer, Benyuan Wuyuan 2, in 2021. It aims to launch a 72-qubit machine, Wukong, in 2023 and cross the 1,000-qubit threshold by 2025. Despite US sanctions on high-end tech exports to China, Origin Quantum has evaded impact since it sources chip production from Hefei government-owned Nexchip Semiconductor. The key takeaway is the global competition in the quantum computing landscape, with significant advancements expected soon.
https://asiatimes.com/2023/09/china-india-race-for-1000-qubit-quantum-computers/
University of Maryland and IonQ Celebrate Opening of QLab: A Hub for Quantum Computing Research
University of Maryland and quantum computing company IonQ have marked the opening of QLab, a dedicated hub for quantum computing research. This collaborative endeavor underscores a commitment to innovation in the thriving field of quantum technology, which has significant potential to reshape the future of computation. By establishing QLab, both institutions aim to provide an innovative platform that would accelerate the advancement of quantum technology. The key take-away is the growing industry-academic partnership trend aiming to fast-track quantum computing developments, as exemplified by the University of Maryland and IonQ's collaboration on QLab.
"Xanadu and KISTI Ignite Quantum Revolution with South Korea's First Quantum-Classical Hybrid Computing Platform"
Photonic quantum computing leader Xanadu and the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (KISTI) have joined forces to form South Korea's first quantum-classical hybrid computing infrastructure. The partnership will result in a software development kit (SDK) for a hybrid circuit, providing connectivity for various classical and quantum hardware platforms through KISTI's cloud services. Xanadu's open-source software library, PennyLane, and its Lightning quantum simulator will undergird the SDK. This partnership will equip South Korean researchers with hybrid computing resources, a critical aspect for advanced research. Xanadu's CEO, Christian Weedbrook, and KISTI's president, Dr. Kim Jaesoo, expressed mutual excitement about this next step in quantum computing evolution. The key takeaway is the importance of hybrid quantum-classical computing as a promising new frontier in technology.
NOVA LQ® Continuous Variable Quantum Key Distribution System
LuxQuanta is launching NOVA LQ®, a Continuous Variable Quantum Key Distribution System (CV-QKD) on the AWS marketplace. Deployed at computing nodes, this first-generation QKD system ensures secure keys distribution within metropolitan networks. Implementing the principles of quantum physics, it ensures encryption between remote transmitter (Alice) and receiver (Bob) environments, with security independent of adversarial computational capacity. NOVA LQ® integrates with existing optical fibre links without interfering with current data transmission. Its QKD technology uses coherent detection through conventional photodiodes, eliminating the need for single-photon detectors at receivers. It guarantees quantum-secure, future-proof, encryption and cost reduction. Currently, NOVA LQ® integrates with AWS Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2) instances hosted in AWS Edge devices. The key takeaway: LuxQuanta's NOVA LQ® offers a quantum-secure, cost-optimized and easily integrable CV-QKD system for metropolitan networks.
https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace/pp/prodview-v2sitofneqedw
Intel Expects Its Quantum Computing Approach to Leapfrog Rivals
Intel plans to use its conventional computing experience to overtake rivals in quantum computing with large qubit counts. The company is developing a successor to its 12-qubit Tunnel Falls quantum processor. Quantum computers leverage superposition and entanglement, inherent to qubits, to dramatically accelerate computations. To ensure computational stability, Intel is aiming to scale to millions of error-correcting qubits. According to Greg Lavender, Intel's Chief Technology Officer, their approach is promising but it's too early to declare success. Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger has showcased a 300mm silicon wafer with 24,000 total qubits at an event. However, this is contingent on improving qubit quality and reliability. The company is also developing technology, like its Horse Ridge processor, to control qubits efficiently. Key takeaway: Intel leverages its existing semiconductor manufacturing expertise for quantum advantage.
https://www.cnet.com/tech/computing/intel-expects-its-quantum-computing-approach-to-leapfrog-rivals/
The Signal Protocol used by 1+ billion people is getting a post-quantum makeover
The Signal Foundation has initiated an upgrade to its Signal Protocol, widely used by over a billion users via platforms like Signal, Google RCS, and WhatsApp for end-to-end message encryption. This reform entails a switch from X3DH, which depends on Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) cryptography, to a post-quantum encryption approach. The move anticipates the threat posed by quantum computing to conventional cryptographic protocols. ECDH relies on the mathematical principle of discrete logarithm problems relating to elliptic curves over integer fields. It creates unique asymmetric key pairs, making message decryption possible only with the correct private key. The upgrade highlights the continuous efforts necessary to maintain security amidst rapidly evolving technological landscapes.
Terra Quantum and Honda Research Institute Europe Develop Quantum ML Method for Disaster Routing
Terra Quantum, in collaboration with Honda Research Institute Europe (HRI-EU), has developed a hybrid quantum computing method to expedite escape times in emergency situations. These organizations evaluated hybrid quantum technologies' potential in optimising evacuation routes during emergencies and noted promising results in a simulated earthquake scenario. The quantum computing solution can adjust to numerous real-time variables and has shown commendable efficiency. Dr. Sebastian Schmitt, Principal Scientist at HRI-EU, highlighted the significance of this development, stating it represents a recognisable step towards problems potentially addressed by quantum technologies. Terra Quantum plans further development of the solution, aiming towards adaptable utilization in various city landscapes. The key takeaway is that hybrid quantum computing methods exhibit considerable potential in augmenting emergency response systems, contributing significantly to public safety.
EuRyQa - European infrastructure for Rydberg Quantum Computing
The EU-funded EuRyQa project aims to develop the next generation of scalable quantum computers using ultracold Rydberg atoms. Ultracold trapped atoms are promising for quantum computing, having shown potential in systems with over 200 qubits. The project aims to unite academic and industrial partners to develop 4 Rydberg platforms with 100-1,000 qubits, including three nationally funded platforms and a European startup. Furthermore, EuRyQa seeks to establish benchmarks and standards in this technology. Guido Pupillo is the project coordinator. A key goal is to produce a common quantum computing stack for Rydberg atoms leading to solutions for computational problems, a federated cloud service, and a blueprint for fault-tolerant quantum computing. The key takeaway is that EuRyQa represents a unified, Europe-wide effort to pioneer scalable, fault-tolerant quantum computing based on Rydberg atoms.
https://qt.eu/projects/computing/euryqa
Quantum Leap: Quantum Computing Nears Advantage Stage, Opening New Opportunities in Quantum Infrastructure Software
Quantum computing is nearing the "Quantum Advantage" stage, where quantum solutions are preferable over conventional systems for significant computational problems. This points towards the emergence of the Quantum Infrastructure Software segment, which creates opportunity for those providing enabling tools for this industry. Quantum computing teams are aligning with Cloud Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Application Software as a Service (SaaS) models, and hyperscalers like AWS, Microsoft and IBM are developing supporting platforms. A leader in this space, Q-CTRL, is pioneering Quantum Infrastructure Software, providing "middleware" to enhance the use of quantum computing hardware and streamline application development. It delivers value and convenience to algorithm developers and increases the value of hardware platforms by making them more user-friendly. Its solutions help stabilize hardware, reduce error, optimize system utility and ensure cross-compatibility, proofing quantum computing for long term growth.
SoftBank Teams Up with University of Tokyo to Fuse Quantum Computing & 5G, Pushing the Frontier of Digitalization
SoftBank and the University of Tokyo have initiated joint research to realize business application of quantum computers. To accomplish this, SoftBank has become a part of the Quantum Innovation Initiative Consortium (QII Consortium) operated by the University of Tokyo. The plan includes integrating the quantum computer, IBM Quantum System One, with technologies like 5G, IoT, and future 6G systems. The quantum computer is equipped with a 127-qubit processor and is installed at the Kawasaki Business Incubation Center. Executives from both organizations emphasized the rapid approach of quantum computer practical application and their intent to lead application development in this field. The significant takeaway is the accelerating convergence of quantum computing with mobile communication in a bid to drive societal digitalization.
Canada Welcomes its First IBM Quantum System One Computer
Canada has made significant strides in technology by unveiling its first IBM Quantum System One computer at IBM’s Bromont, Québec facility. The System One boasts a 127-qubit processor, offering increased consistency and reduced error rates compared to previous IBM quantum systems. IBM expects the technology to be beneficial for various Québec sectors, including the quantum innovation zone DistriQ and Technum Québec innovation zone. Their operations are facilitated through a partnership with Université de Sherbrooke. Québec’s Minister of Economy, Innovation, and Energy, Pierre Fitzgibbon, hailed the advancement as a major leap in Québec's quantum sciences ecosystem. The collaboration between IBM and the Québec government began in February 2022, further solidified in July 2023, along with a quantum working group focused on leveraging quantum computing for sustainability solutions. Key takeaway: Canada now features among countries at the forefront of the quantum computing revolution.
https://fagenwasanni.com/news/canada-welcomes-its-first-ibm-quantum-system-one-computer/265373/
IBM Launches Free Online Course on Quantum-Safe Cryptography for Developers
IBM has launched a free online course on quantum-safe cryptography on its Quantum Learning platform. Creators Michael Maximilien and Jennifer Janechek designed this course for developers keen on boosting application security. The program covers cryptographic hash functions, symmetric key cryptography, asymmetric key cryptography, and quantum-safe cryptography. It also includes interactive live code examples and multimodal lessons. The course aims to prepare developers for the evolving cybersecurity threats in the quantum era. As quantum computing matures, it could solve complex mathematical problems more rapidly than classical computing counterparts, thereby threatening the efficacy of today's cryptographic methods. Developers are urged to build competency in quantum-safe cryptography before standards materialize, to maintain security of applications. Key takeaway: As quantum computing advances, it's crucial for developers to adapt cryptography for continued data security.
https://quantumzeitgeist.com/ibm-free-online-course-quantum-safe-cryptography/
ParTec AG becomes a complete integrator of quantum computers in the Greater Munich area
ParTec AG, a leading modular supercomputing company, plans to become a full integrator of quantum computers with an initial €5 million investment in a factory in Munich. ParTec's qubit-agnostic solution relies on a component-based design, allowing it to work with technology providers to deliver comprehensive quantum solutions. Bernhard Frohwitter, CEO of ParTec AG, believes this innovative approach will lead to a strong market position, over the monolithic designs of other solutions. The company aims to launch its first quantum computer in 2024, with the new factory anticipated to start operations in the same year. ParTec continues to explore hybrid quantum computing in partnership with NVIDIA and Jülich Supercomputing Centre, and provides solutions for the Israeli National Quantum Initiative. The key takeaway: ParTec's modular approach to quantum computing integration positions it as a pioneering force in the burgeoning quantum market.
https://par-tec.com/complete-quantum-integrator/
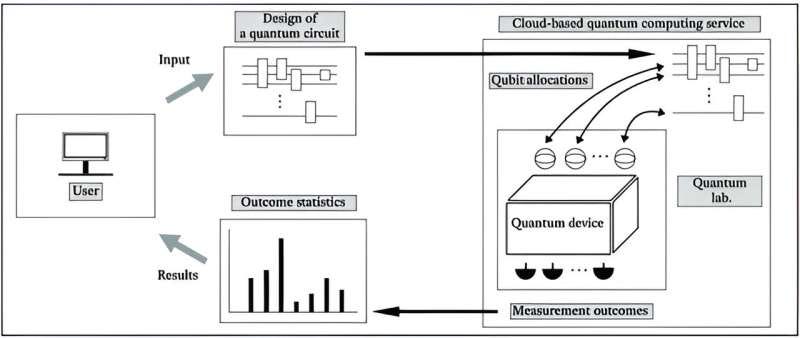
Can cloud-based quantum computing really offer a quantum advantage?
Jiheon Seong and Joonwoo Bae from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology have developed an entanglement witness circuit to detect qubit entanglement in cloud-based quantum computing services. With this, even without total control of the machine, users can detect entanglement— a critical factor for the quantum advantage. This solution addresses limitations in services such as IBMQ and IonQ, where users only have control over the input quantum circuit. The newly designed entanglement witnesses are based on a framework called EW 2.0, which offers double the efficiency in detecting entanglement. Thus, the research signifies a crucial step in leveraging the quantum advantage in cloud-based quantum computing. The key takeaway: effective quantum computing can be realized in cloud-based services with innovative solutions, such as the entanglement witness circuit.
https://phys.org/news/2023-09-cloud-based-quantum-advantage.html
Toshiba opens quantum computing lab in Cambridge
The Japanese tech titan, Toshiba, has inaugurated a Quantum Information Group in Cambridge, showcasing quantum cryptography technology to the public for the first time. This move signals Toshiba's commitment to leading advancements in the burgeoning field. Quantum Information Group, operating under Toshiba's R&D wing - Toshiba Research Europe Limited, focuses on quadrupling Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) transmission capacity. QKD is an ultra-secure encryption method that leverages the principles of quantum physics. As cyber threats level up, Toshiba's QKD aims at providing unhackable encryption that could revolutionize many sectors, including finance and healthcare. The main takeaway: Leading R&D in quantum cryptography, Toshiba has entered the promising quantum computing space with a focus on offering superior security solutions.
https://telecoms.com/523888/toshiba-opens-quantum-computing-lab-in-cambridge/