The Week in Quantum Computing - September 23th 2024 - TU Delft, Quantinuum, Airbus, Qiskit, Q-Ctrl
Issue #202 + Podcast!
Quick Recap
Too busy? Listen to the (AI Generated) podcast instead! (It may contain traces or errors and hyperexcitement)
This week, Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) made a significant breakthrough in quantum data storage by utilizing the spin state of Titanium-47's nucleus. This innovative approach, led by Professor Sander Otte and first author Lukas Veldman, could greatly enhance the security of quantum computing applications. Meanwhile, Equal1 CEO Jason Lynch highlighted the potential of quantum computing to address Ireland’s data center energy consumption issues. TNO launched the Qu-STAR project in collaboration with Airbus to advance the quantum internet via space, aiming to overcome the limitations of ground networks. At the same time, Alice & Bob and Thales partner to provide solutions to the aerospace industry. Oxford Ionics, in partnership with the University of Oxford, achieved a world record in quantum state preparation and measurement fidelity, marking a significant improvement in quantum system reliability. IBM introduced the Qiskit Functions Catalog to simplify quantum computing development. With Q-CTRL integrating Fire Opal, a performance-management software into those systems. While Finland’s IQM scaled up quantum computer production to meet rising demand, enhancing quantum application development. Quantinuum has teleported a logical qubit and has also published a great article on their advances in Quantum Natural Language Processing that explain how to encode text into qubits. Atom has received $10M additional funding.
The Week in Quantum Computing
Safest place for storing quantum data might be atom's nucleus
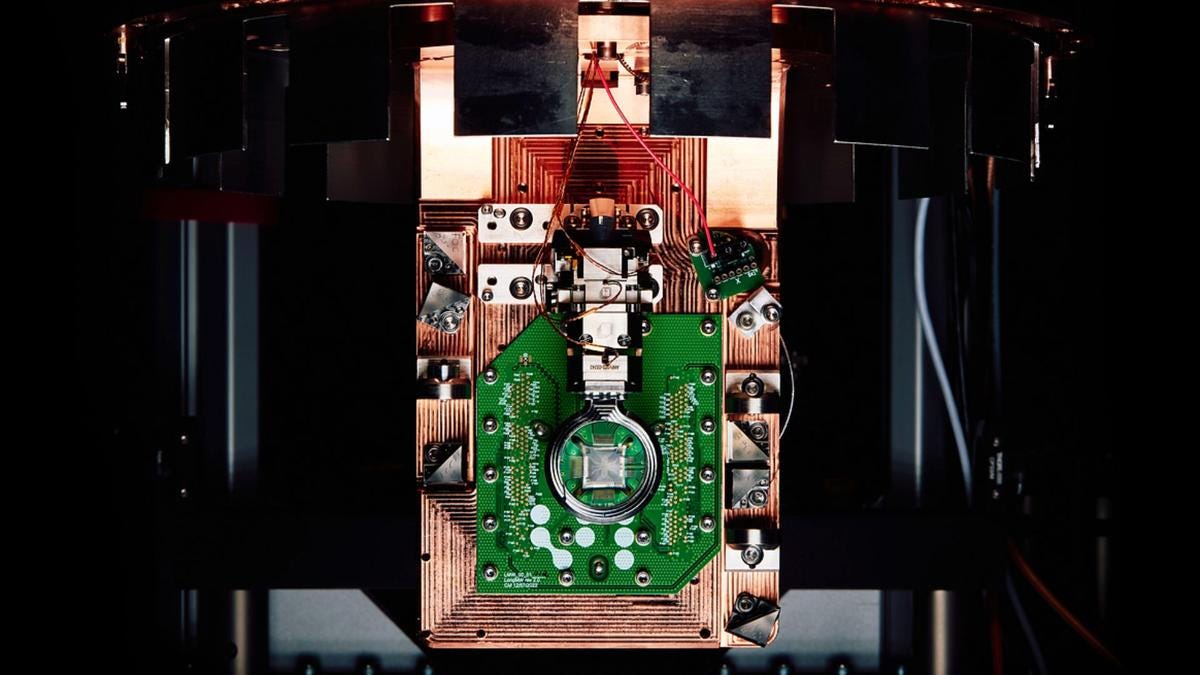
Researchers at Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) have pioneered a method to store and retrieve quantum data using the spin state of an atom's nucleus, specifically Titanium-47 (Ti-47). By creating a 'quantum wobble' with a voltage pulse, they aligned the nucleus' spin with its orbiting electrons, enabling data access via a scanning tunneling microscope. "This experiment gives humans influence on the state of matter on an unimaginably small scale," stated Professor Sander Otte. First author Lukas Veldman highlighted the innovative approach, noting, "Both spins wobbled together for a fraction of a microsecond." This breakthrough could significantly enhance the security of quantum computing applications. The main takeaway: Atom's nucleus could be the safest place for quantum data storage.
Quantum chips can solve Ireland’s data-centre problem, says Equal1 CEO Jason Lynch
Equal1 CEO Jason Lynch asserts that quantum computing can address Ireland’s data centre energy consumption issues and position the country as a leader in sustainable technology. Lynch emphasizes, "We need to look at this as an investment in the jobs of the future." Equal1, founded six years ago, has raised €35 million and is preparing for a new fundraising round in the tens of millions. Their UnityQ technology, the first hybrid quantum-classical silicon-on-chip, aims to integrate quantum power into existing systems. Lynch highlights that quantum solutions could reduce AI energy consumption by 20 times, benefiting sectors like pharma. The main takeaway: Embracing quantum computing could revolutionize Ireland’s data centres and foster technological leadership.
TNO launches Qu-STAR to pioneer quantum internet via space
TNO has launched the Qu-STAR project to advance the quantum internet via space, addressing the limitations of ground networks that restrict quantum information exchange to a few hundred kilometers. Collaborating with Airbus Central Research and Technology, TNO aims to design a global quantum internet architecture, leveraging the Netherlands' expertise in quantum technology, free space optics, and photonics. The initiative will contribute to the Quantum Internet Alliance and its Special Interest Group on Space. Kees Buijsrogge, TNO Space Director, emphasized the importance of a collaborative, open approach to achieve significant technological advancements. The main takeaway: Qu-STAR aims to overcome current quantum internet limitations by utilizing satellite technology for global connectivity.
https://news.satnews.com/2024/09/15/tno-launches-qu-star-to-pioneer-quantum-internet-via-space/
Oxford Ionics sets new world record, slashes quantum errors by 1,300%
Oxford Ionics, in collaboration with the University of Oxford’s physics department, has achieved a world record in quantum state preparation and measurement (SPAM) fidelity, reaching 99.9993%. This new protocol reduces SPAM errors by 1,300%, marking a 13-fold improvement over previous methods. The protocol combines standard SPAM techniques with mid-circuit non-demolition (QND) measurements, allowing for real-time error detection without interrupting calculations. Tested on three different qubit encodings in a single trapped 137Ba+ ion, the protocol demonstrated the lowest reported SPAM infidelities. "The world records set by Oxford Ionics bring it one step closer to delivering quantum computers capable of widespread commercial impact," the study authors noted. This breakthrough significantly enhances the reliability of quantum systems.
https://interestingengineering.com/science/oxford-ionics-sets-new-world-record
Preparing for a Quantum-safe Tomorrow
The "Preparing for a Quantum-safe Tomorrow" roundtable, held on July 3, 2024, in Zürich as part of the Point Zero Forum, addressed the imminent threat quantum computing poses to current cryptographic systems. Moderated by Thomas Moser of the Swiss National Bank, the session featured experts like Raphael Auer (BIS), Marco Brenner (IBM), and Klaus Ensslin (ETH Zurich). The discussion emphasized the urgency of transitioning to quantum-resistant cryptosystems to protect financial infrastructures. Key action points for organizations were proposed to ensure security against quantum threats. As Moser highlighted, "The transition to quantum-resistant cryptosystems is not just necessary but urgent." The main takeaway: Financial institutions must act now to safeguard against future quantum computing threats.
https://www.elevandi.io/insights/preparing-for-a-quantum-safe-tomorrow
IBM makes developing for quantum computers easier with the Qiskit Functions Catalog
IBM has launched the Qiskit Functions Catalog to simplify quantum computing development by abstracting complex tasks. Jay Gambetta, IBM’s VP of Quantum Programs, likens this to the transformative impact of putting quantum computers on the cloud. The catalog includes contributions from partners like Qedma, Q-CTRL, Algorithmiq, and QunaSys, focusing on error mitigation and chemistry applications. IBM also introduced Benchpress, a benchmarking tool showing Qiskit’s superior performance, being 13 times faster at transpiling circuits compared to competitors. Gambetta emphasizes that this innovation will broaden quantum computing’s accessibility, moving from physicists to computer scientists. The main takeaway: IBM’s Qiskit Functions Catalog aims to democratize quantum computing by making it more accessible and efficient for developers.
Finland’s IQM has now produced 30 full-stack quantum computers
Finland’s IQM has produced 30 full-stack quantum computers since its founding in 2018. Its Espoo facility, operational since 2021, can manufacture up to 20 quantum computers annually and houses Europe’s only private quantum chip factory. Co-CEO Mikko Välimäki highlighted the goal of reducing costs to broaden market access. IQM plans to expand with a new facility in Grenoble, France, by 2027. The company has delivered six on-premise quantum computers globally and was selected by Amazon Braket for its 20-qubit IQM Garnet in Stockholm. Välimäki stated, “We are the first quantum computer manufacturer with the goal of taking quantum computers to a much wider market.”
https://thenextweb.com/news/finlands-iqm-produced-30-full-stack-quantum-computers
Q-CTRL’s Fire Opal Among First Qiskit Functions Delivering Utility-Scale Performance to the Global Quantum Developer Community
Q-CTRL has launched Fire Opal, a performance-management software, as one of the first Qiskit Functions to deliver utility-scale performance on IBM Quantum systems. This integration aims to simplify quantum application development and enhance performance management. Michael J. Biercuk, CEO of Q-CTRL, highlighted the significance of this step in maturing the industry. Jay Gambetta of IBM emphasized the ease of leveraging quantum optimization in workflows. The Fire Opal Performance Management function uses AI-driven error suppression, while the Optimization Solver addresses utility-scale problems. Clients like Cleveland Clinic and SoftBank have already validated its efficacy.
Quantum Computing Playbook: A Guide to Tapping Quantum’s Trillion Dollar Economic Potential
Quantum computing is projected to generate over $1 trillion in economic impact by 2035, transforming industries like finance, pharmaceuticals, and AI. Companies such as IBM, Google, Microsoft, and Quantinuum are leading advancements in quantum processors. Despite its potential, the field faces challenges in hardware and software development, workforce shortages, and regulatory needs. Richard Feynman’s early recognition of classical computing limitations and Shor’s algorithm for factoring large numbers highlight quantum computing’s foundational breakthroughs. Collaboration among companies, academia, and governments is crucial for building a robust quantum ecosystem. As Matt Swayne notes, "Quantum computing is rapidly emerging as a transformative technology." The main takeaway: Quantum computing holds immense promise but requires overcoming significant hurdles to realize its full potential.
Quantum Computing: Commercial Revenue to Near $10bn Globally by 2030
A Juniper Research study forecasts quantum technology commercial revenue will surge from $2.7 billion in 2024 to $9.4 billion by 2030, despite only 300 quantum computers being deployed by then. The study highlights quantum-hybrid solutions as key to maximizing returns, predicting a modest 6% ROI by 2030 with over $29 billion in investments. Quantum cloud solutions are identified as the strongest immediate revenue opportunity due to the limited number of quantum computers. Quantum encryption technologies, particularly quantum key distribution, are expected to provide the fastest ROI, crucial for sectors like banking and finance. The research includes a comprehensive market assessment and forecasts for 60 countries. The main takeaway: Quantum-hybrid solutions will drive early commercial success in quantum computing.
https://www.emsnow.com/uantum-computing-commercial-revenue-to-near-10bn-globally-by-2030/
Technical perspective: By the end of the decade, we will deliver universal, fully fault-tolerant quantum computing
Quantinuum, led by Dr. Harry Buhrman and Dr. Chris Langer, announced an accelerated hardware roadmap aiming to deliver a fully fault-tolerant and universal quantum computer by the decade's end. The upcoming Quantinuum Helios™, powered by Honeywell, will surpass classical capabilities by 2025, paving the way for the fifth-generation Quantinuum Apollo™. Apollo will feature thousands of physical qubits, physical error rates below 10^-4, and logical error rates potentially as low as 10^-10. Leveraging advanced Quantum Error Correction (QEC) codes, Apollo promises significant efficiency gains and fault-tolerant quantum advantage. "Apollo promises fault-tolerant quantum advantage sooner, with fewer resources," stated the announcement. The main takeaway: Quantinuum is accelerating towards a fault-tolerant quantum future.
A new path for Kyber on the web
Google's Chrome team, including David Adrian, David Benjamin, Bob Beck, and Devon O'Brien, announced the transition from the experimental Kyber post-quantum key exchange to the standardized Module Lattice Key Encapsulation Mechanism (ML-KEM). This shift follows the finalization of Kyber by NIST, now renamed ML-KEM, and its integration into Google's BoringSSL cryptography library. Chrome 131 will adopt ML-KEM, replacing Kyber768+X25519 with ML-KEM768+X25519 (codepoint 0x11EC). The team emphasized the importance of avoiding non-standard algorithm ossification and ensuring seamless post-quantum security. David Adrian stated, "We’re excited to continue to improve security for Chrome users, against both current and future computers." The main takeaway is Chrome's commitment to advancing post-quantum cryptographic security.
https://security.googleblog.com/2024/09/a-new-path-for-kyber-on-web.html
Resource-efficient photonic quantum computation with high-dimensional cluster states
Researchers Ohad Lib and Yaron Bromberg have advanced photonic quantum computation by generating high-dimensional cluster states, as reported in *Nature Photonics* on September 16, 2024. They achieved cluster states with over nine qubits at a rate of 100 Hz by encoding multiple qubits on each photon through high-dimensional spatial encoding. This method significantly reduces computation duration by enabling instantaneous feedforward between qubits encoded in the same photon. Their work addresses the challenge of generating large cluster states efficiently, a critical step towards scalable, fault-tolerant quantum computation. As Lib and Bromberg state, this "paves the way for resource-efficient measurement-based quantum computation using high-dimensional entanglement." The main takeaway is the potential for more efficient and scalable photonic quantum computing.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-024-01524-w
Quantum Brilliance, ParityQC Awarded Contract to Develop Mobile Quantum Computer by 2027
HALLE, Germany, Sept. 18, 2024 — Quantum Brilliance and ParityQC have announced that they have been awarded a joint contract by Germany’s Cyber Agency (Cyberagentur) to develop the world’s first mobile quantum computer by 2027.
The QB/ParityQC strategic partnership was one of three bids selected for the €35 million project, the largest research amount ever awarded by Cyberagentur. The project’s goal is to make a mobile quantum computer for use in defense, security and civilian applications and is designed to keep Germany at the forefront of technological innovation.
Link: https://ift.tt/QcCs0l8
Colorado’s multimillion dollar investment in quantum gets 70-acre campus in Arvada
Two months after winning a $40.5 million federal grant to invest in a quantum computing hub in Colorado, members of a local consortium have acquired a 70-acre property in Arvada, attracted millions more in funding commitments, and, on Monday, put shovels to the ground.
https://ift.tt/VD3oqwU
Scalable and interpretable quantum natural language processing: an implementation on trapped ions
We present the first implementation of text-level quantum natural language processing, a field where quantum computing and AI have found a fruitful intersection. We focus on the QDisCoCirc model, which is underpinned by a compositional approach to rendering AI interpretable: the behaviour of the whole can be understood in terms of the behaviour of parts, and the way they are put together. Interpretability is crucial for understanding the unwanted behaviours of AI. By leveraging the compositional structure in the model's architecture, we introduce a novel setup which enables 'compositional generalisation': we classically train components which are then composed to generate larger test instances, the evaluation of which asymptotically requires a quantum computer. Another key advantage of our approach is that it bypasses the trainability challenges arising in quantum machine learning. The main task that we consider is the model-native task of question-answering, and we handcraft toy scale data that serves as a proving ground. We demonstrate an experiment on Quantinuum's H1-1 trapped-ion quantum processor, which constitutes the first proof of concept implementation of scalable compositional QNLP. We also provide resource estimates for classically simulating the model. The compositional structure allows us to inspect and interpret the word embeddings the model learns for each word, as well as the way in which they interact. This improves our understanding of how it tackles the question-answering task. As an initial comparison with classical baselines, we considered transformer and LSTM models, as well as GPT-4, none of which succeeded at compositional generalisation.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.08777
Cryptomathic and PQShield form strategic alliance to offer PQC solutions for code signing and data protection in compliance with latest NIST and CNSA recommendations
OXFORD, England and AARHUS, Denmark, Sept. 19, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- Cryptomathic, an acknowledged security software provider for advanced key management solutions with numerous innovations in cryptographic agility, and PQShield, a cybersecurity company specializing in quantum-resistant cryptographic solutions, have agreed a strategic alliance that will enable clients from various industries to transition to Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC) and comply with migration mandates from CNSA 2.0 and also implement the recently approved NIST algorithms.
With the CNSA 2.0 requirements and also with the recent release of FIPS 203, FIPS 204 and FIPS 205, which specify algorithms derived from CRYSTALS-Dilithium, CRYSTALS-KYBER and SPHINCS+, the migration to Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC) is now a reality for a many organizations. Organizations are faced with challenges when navigating the transition to PQC, as it impacts a wide range of use cases from signing of device firmware and secure boot, to network and application security, where meticulous management of the involved cryptographic keys and their life cycles through the transition is more important than ever. As organizations consider their options and estimate development efforts, this represents a unique opportunity to strengthen their cybersecurity.
https://ift.tt/i9pS2RM
Upstate N.Y. Gets Nearly $30M for Quantum Computing, Tech
The Northeast Regional Defense Technology Hub has received a $27.4 million grant from the U.S. Department of Defense. The money will go to semiconductor and technology research at upstate universities and research institutions. The U.S. Department of Defense has awarded a $27.4 million grant to boost semiconductor and other technology research and workforce training at Upstate New York universities and research institutions. U.S. Senate Majority Leader Charles Schumer, D-NY, announced the grant Wednesday for the New York-based Northeast Regional Defense Technology Hub (NORDTECH). Schumer said the money will support four projects in New York led by NY CREATES, Cornell, RIT and other Upstate research labs focused on semiconductors, quantum computing and other technology critical maintaining the nation’s edge in the defense industry.
Alice & Bob And Thales Develop Quantum Algorithms For Next Generation Aerospace Equipment
Alice & Bob and Thales have embarked on a collaborative project to develop quantum algorithms for the next generation of aerospace equipment, focusing on simulations for radars and antennas. This partnership aims to leverage fault-tolerant quantum computers (FTQCs) to potentially revolutionize the aerospace industry by accelerating electromagnetic simulations, thereby optimizing the design of airborne equipment. Supported by the i-Démo Régions project, which is part of France's 2030 plan with a budget of 2.6 million euros over three years, this initiative seeks to position France as a leader in quantum technology development. The collaboration draws on the combined expertise of Alice & Bob, Thales, and Inria, with Inria providing programming and compilation tools for the quantum algorithms. These algorithms will be tested on FTQC quantum calculator demonstrators by Alice & Bob, while Thales will define use cases and benchmark algorithm performance. This project not only aims to advance the technological capabilities of aerospace equipment but also to assess the resources and timeline needed for the industrialization and scaling of these quantum solutions. The partnership represents a significant step towards harnessing the power of quantum computing in the aerospace sector, with the potential to make France a frontrunner in the field of mature quantum technology
https://ift.tt/ijrfk9l
Quantinuum High-fidelity teleportation of a logical qubit using transversal gates and lattice surgery
Quantum entanglement and the teleportation of a quantum state across the processor are key ingredients in quantum computing. The fragility of the quantum states, however, requires error correction codes to ensure their faithful processing. Using a trapped-ion platform consisting of up to 30 trapped ions, the Quantinuum H2 quantum processor, Ryan-Anderson et al. demonstrate the fault-tolerant teleportation of quantum states. The implemented error-correcting color code effectively stabilizes the qubits, allowing quantum teleportation to be carried out in a fault-tolerant manner. Quantum state teleportation is commonly used in designs for large-scale quantum computers. Using Quantinuum’s H2 trapped-ion quantum processor, we demonstrate fault-tolerant state teleportation circuits for a quantum error correction code—specifically the Steane code. The circuits use up to 30 qubits at the physical level and employ real-time quantum error correction. We conducted experiments on several variations of logical teleportation circuits using both transversal gates and lattice surgery. We measured the logical process fidelity to be 0.975 ± 0.002 for the transversal teleportation implementation and 0.851 ± 0.009 for the lattice surgery teleportation implementation as well as 0.989 ± 0.002 for an implementation of Knill-style quantum error correction.
https://ift.tt/w2yxFft
QCentroid and QPerfect Partner to Accelerate Enterprise Quantum Computing
Strasbourg, 19 September – QCentroid, the pioneering Quantum-as-a-Service platform provider, and QPerfect, a leading European deep-tech company specializing in quantum computing solutions, today announced a partnership to make quantum computing more accessible and practical for businesses. This collaboration combines QCentroid’s powerful Quantum Ops platform with QPerfect’s unique virtual quantum computer, MIMIQ 1.0, to deliver an unparalleled quantum experience to enterprises. By integrating MIMIQ’s capabilities into the QCentroid platform, businesses can now seamlessly access, test, customize, benchmark, and deploy quantum applications at an unprecedented scale.
https://qcentroid.xyz/news/qcentroid-and-qperfect-partner-to-accelerate-enterprise-quantum-computing/
Differentiating quantum error correction, suppression, and mitigation
Q-Ctrl has released an article that discusses the three key strategies to address noise and errors in quantum computing: error suppression, error mitigation, and quantum error correction (QEC). Each serving a different purpose in enhancing quantum hardware performance.
Error Suppression focuses on preventing errors during quantum operations by leveraging techniques from quantum control to build resilience into hardware. This approach is deterministic and involves optimizing quantum gates and idle qubit states to minimize interference. It improves algorithmic performance by reducing error rates and can be integrated directly into quantum firmware.
Error Mitigation handles errors through postprocessing by running variations of a quantum algorithm, then combining results to correct for inaccuracies. While powerful, it comes with significant overhead, as algorithms must be run multiple times to extract correct outcomes.
Quantum Error Correction (QEC) encodes qubit information across multiple qubits to detect and correct errors during computation. This method offers a more comprehensive error correction framework but requires a large number of physical qubits for a single logical qubit, making it less practical in current systems.
The article suggests that combining these methods—especially error suppression with QEC—offers a path to more reliable quantum computation.
https://ift.tt/EVkcpxy
Talking quantum circuits - Interpretable and scalable quantum natural language processing
Large language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT are having an impact on society across many walks of life. However, as users have become more familiar with this new technology, they have also become increasingly aware of deep-seated and systemic problems that come with AI systems built around LLM’s.
“How can quantum structures and quantum computers contribute to the effectiveness of AI?”
In previous work we have made notable advances in answering this question, and this article is based on our most recent work in the new papers [arXiv:2406.17583, arXiv:2408.06061], and most notably the experiment in [arXiv:2409.08777].
https://ift.tt/XBgvCmn
Helium-3 in the Quantum Technology Supply Chain
Helium-3 (He-3) is critical to quantum technology, especially in cryogenic systems that maintain the ultra-low temperatures required for quantum coherence. It plays a pivotal role in stabilizing quantum systems, particularly in superconducting quantum computers where He-3 has the highest criticality, with no viable alternatives. As quantum technologies scale, the demand for He-3 increases, leading to concerns about its limited supply on Earth. This has prompted interest in lunar mining as a potential solution. The availability of He-3 will be key to the future growth and success of the quantum computing industry.
https://ift.tt/EfDFKCR
D-Wave and Staque Announce Strategic Partnership to Accelerate Annealing Quantum Computing Adoption Across the Middle East
PALO ALTO, Calif. & CALGARY, Alberta, September 20, 2024--(BUSINESS WIRE)--D-Wave Quantum Inc. (NYSE: QBTS) ("D-Wave" or the "Company"), a leader in quantum computing systems, software, and services and the world’s first commercial supplier of quantum computers, and Staque, a leading consulting and development practice in AI, blockchain and quantum computing, announced a new strategic partnership aimed at accelerating the commercial adoption of annealing quantum computing across the Middle East. The partnership was revealed at Qubits UAE in Dubai, a half-day version of D-Wave’s annual Qubits user conference, which is showcasing "success powered by quantum" through business optimization use cases, progress in quantum-fueled AI technology, and demonstrations of annealing quantum computing performance over classical computing.
https://ift.tt/r9HITA3
Atom Computing Secures $10M from PensionDanmark to Boost Quantum Expansion in Denmark
Sept. 20, 2024 — PensionDanmark has invested 10 million dollars in the American quantum computing company Atom Computing, which is on its way to establishing itself in Denmark for the benefit of the Danish quantum environment.
“Quantum computers can open up a whole new world of solutions, and with this investment, we give our members the opportunity to share in the returns from this potential paradigm shift to the benefit of their pension savings,” said Peter Stensgaard Mørch, CEO of PensionDanmark.
https://ift.tt/sF3Kh0C