The Week in Quantum Computing. Brought to you by Sergio Gago (@piratecto).
Quick Recap
This week in quantum computing: Quantum Inspired! If you don’t get good qubits just simulate them! The main public companies such as D-Wave, IonQ, Rigetti, and Quantum Computing Inc. reported regular losses for 2022, with higher losses expected in 2023. QURECA launched the Qureka! Box to educate high school and undergraduate students about quantum computing. Research papers explored heuristics for the 3-SAT problem and a framework for demonstrating practical quantum advantage. Quantum Source, a photonic quantum computing startup, extended its seed round to $27 million, while Quanscient raised €3.9 million to accelerate product development. D-Wave announced a breakthrough in quantum annealing, and Moderna partnered with IBM to apply AI and quantum computing to mRNA technology.
In other news, the Indian Cabinet approved the National Quantum Mission to scale up scientific and industrial R&D for quantum technologies. ETH Zurich researchers achieved the heaviest Schrödinger cat by putting a small crystal into a superposition of two oscillation states. A talent crunch in quantum computing has led to a search for the right courses to address the growing demand for skilled professionals. Ericsson and the Canadian government invested $470 million CAD in a five-year R&D partnership that includes quantum computing.
Are Financial Institutions really investing in Quantum? Moody’s in partnership with Corininum research will release during May a report that will shed some light on the real numbers. Asking the real players in the industry. And I will be giving you glimpses of what we have found. If you want access to the report let me know!
The Article of the week
Forbes, together with their technology council (a paid membership to be able to publish about specific topics) has published an article that deserves good attention
15 Significant Ways Quantum Computing Could Soon Impact Society
I am the first one willing (and working towards) a bright quantum future. I also deeply respect many of the authors who made these claims. However I think it is important to add some light into them, specifically when sayin "could impact soon”.
1. Breaking Current Encryption Schemes
True. But the consensus does not think Y2Q will happen before 2030, and most likely beyond that. So “soon” is an overstatement. Plus “current” can mean anything. Today we only know how to break RSA / Diffi-Hellman based asymetric cryptographic protocols.
2. Better Securing Sensitive Data
Partially True. Technologies like QKD can improve (and in principle, fully secure) data in transit provided you have the right channel. There is still a lot of work to do for that with companies like LuxQuanta fighting to advance it. But the claim of “the combination between quantum computing and blockchain” sounds a bit too much.
3. ‘Breaking’ The Blockchain
False. As said in point oner, we only know how to break Asymmetric cryptography and still, it will take some time to do it. we don’t know how to break hashes or any other type of symmetric signatures. While there is people trying to use Grover-like algorithms with some claims on SHA-1, there is nothing (that I know of) that proves the contrary.
4. Modeling Chemical Reactions For Drug Development
True. Chemistry is potentially one of the key use cases. In this very newsletter there are examples on cases with quantum inspired techniques that can help a lot here.
5. Enhancing Drug Discovery And Personalized Medicine
True. Same as before.
6. Improving AI Capabilities
Partially True. Let’s not go into “what would happen if we merge GPT4 with Quantum” because then I’ll start laughing so hard I won’t be able to keep writing. However the question of “What ML can do for quantum” is very relevant and useful. using ML for tomography for example is a key case that could speed up QC development. Likewise you can use ML for error correction.
7. Optimizing Investment Portfolios
True. But today there is no quantum advantage in this case, or it is not clear when we will get this quantum advantage. Yes, you can model Markovtitz style portfolios and run them with hundreds (or thousands) of assets, but it is not clear how they compare with state of the art modeling algorithms. (But this is a very active field of research and a potential for “business advantage”).
8. Safe Computing Of Encrypted Data
False. This points mentions. PQC and Homomorphic encryption as the keys for safe computing. That is true and fully agree… but it has nothing to do with quantum. Remember: Post Quantum Cryptography refers to classical algorithms that you use on your classical laptop, that are, in principle (and today) resistant to the algorithms we know.
9. Democratizing Generative AI
False. The claim is about the capacity of QCs to handle high volume of data and transactions. That is simply not true and not be “soon” when that happens. QCs are very specific (and expensive) machines that serve for very niche experiments. That is the opposite of “democratizing” anything. Can you play with Quantum Convolutional networks? Yes. Can you mimic transformers? Yes. Can you build an LLM with a quantum computer? No. (But those interested, I recommend you taking a look at Lambeq)
10. Enabling True Real-Time Reporting
False. Even though there is no specific proof on where this claim comes from. I suspect it may come from the fact that we can do “Quantum Teleportation”, which does not mean you can teleport information faster than the speed of light unfortunately (Einstein 1 - Quantum Hypist 0). Then it goes about digital twins (which is a great concept that works) but not with quantum computers!
11. Discovering New Materials
True. Because we can model atoms and molecules better and faster, we can model how they interact. This could help us build better batteries, solar panels, or fertilizers. In general, any problem where we have to simulate large complex systems, and where today the only option is using HPC. (Hopefully you see now the tendency… Is it an HPC Problem? → Could be a potential QC problem. It is not an HPC Problem? It does not require playing with entanglement or interference? —> you can do it with a QC but you won’t get far).
12. Improving Weather Forecasting
True. Because you can improve certain ML algorithms and potentially get better (and more) simulations, you can potentially forecast complex systems better. Whether they are weather related, or credit risk!
13. Enabling Hyper-Personalized Shopping Experiences
Partially True. In the same fashion as before, you will be able to build classifiers with better accuracy at scale for some cases. But in order to beat the current systems we need much more development. Today QCs can run only on very small datasets with a limited amount of features (that would AI practitioners laugh at them with the dimensionality they use). But it is a great reason to continue researching in this direction.
14. Optimizing Traffic Flows
Partially True. For the same reasons as portfolio optimization and and other ML problem. Traffic flows can be reducted to a certain type of NP problems (whether they are TSPs, MaxCuts, 3SATs or Knapsacks). While we don’t have a NP-Hard / NP-Complete quantum algorithm today that proves advantage there, you could find business advantages and it is an area with a lot of research.
15. Combating Climate Change
Partially False. Claiming that QC is the key to combat climate change is a big overstatement. We are at the very beginning of the potential applications in chemistry (the molecules or materials we can simulate today are not that big and we can solve them with big computers, or HPC). But it is true that once we have QCs big enough and with decent error correction, this could lead to better materials, better energy utilization and other efficiencies. Which in turn will be helpful to combat climate change. But saying that using QCs “soon” helps combat climate change has pretty much the same effect of you individually taking the public transport instead of your car (which you should anyways!)
In short: Be careful with the claims you read. Make sure they have sources that you can verify and take it with a pinch of salt. Quantum Computers are going to be a revolution, but there are still many, many questions to resolve and work to do. The field needs people, funding and joint research and collaboration between industry and academia. But for the right reasons, not for finding ROI today.
What advice would you give to a C-suite executive evaluating what to do about quantum computing?
Dr. Faisal Kamran - internationally-renowned technology strategist and sustainability expert, working as Principal Technology Analyst for Sony Electronics - shares the four crucial steps he'd advise for execs looking to stay ahead of the competition and drive innovation.
The Week in Quantum Computing
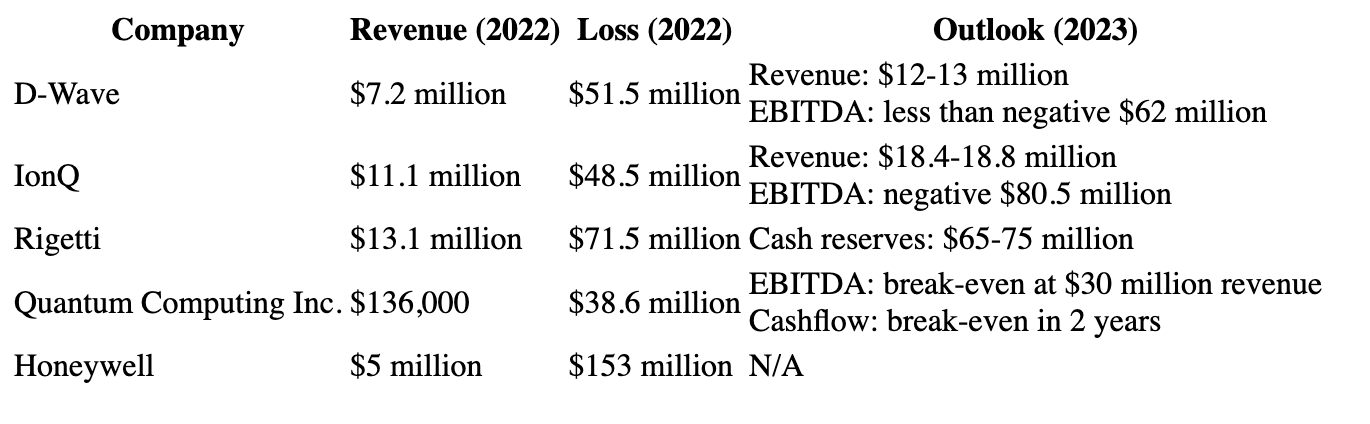
Q4 2022 quantum computing results: D-Wave, IonQ, Rigetti, Quantum Computing Inc., & Quantinuum
The four publicly-listed pure-play quantum computing companies, IonQ, D-Wave, Rigetti, and Quantum Computing Inc., all posted regular losses in 2022. Revenue varied between the companies, with D-Wave and IonQ posting the highest figures at $7.2 million and $11.1 million respectively. Honeywell's Quantinuum unit posted the highest losses at $153 million, while Quantum Computing Inc. had the lowest revenue figure of $136,000. All companies expect to record higher losses in 2023, with D-Wave and Quantum Computing Inc. predicting break-even points within the year. Rigetti will look to raise additional funds in late 2024 or early 2025.
Link: https://ift.tt/g9HObZS
April 16, 2023 at 10:30PM
Heuristics for Quantum Computing Dealing with 3-SAT
The SAT problem is maybe one of the most famous NP-complete problems. This paper deals with the 3-SAT problem. We follow a sort of incremental strategy to save computational costs with respect to the classical quantum computing approach. We present an heuristics that leads this strategy, improving the performance of the purely random incremental scheme. We finally validate our approach by means of a thorough empirical study. […]
We presented an algorithm which, inspired by Grover´s one, has improved the amount of quantum computational resources by a significant ratio. For this algorithm to be designed, we described a sort of incremental strategy over the sets of clauses that conforms to the 3-SAT formula under scope. The aim of this process is, on the one hand, to use the advantages of Grover´s modified algorithm and, on the other hand, to choose an appropriate conforming order (within this incremental scheme) such that the assumptions required for Grover’s modified algorithm to be used are as useful as possible. This last issue led us to define an heuristics for the set of clauses to be added to the previously described incremental scheme.
Link: https://ift.tt/p4YhIZw
April 17, 2023 at 08:30AM
QURECA Launches the Qureka! Box on World Quantum Day to Celebrate Quantum Technology Education and Outreach
QURECA, the leading company in quantum training and resourcing, is proud to announce the launch of the Qureka! Box on World Quantum Day. The Qureka! Box is designed to introduce to high school and undergraduate students, as well as the general public, the fascinating world of quantum computing.
The box features interactive game-based hands-on teaching and learning tools in quantum computing promoting maximum engagement and interest while ensuring that nobody is left behind. The box provides a complete set of tools that minimizes the need for abstract imagination.
Link: https://ift.tt/lnqUzBQ
April 17, 2023 at 12:30PM
Title:A Framework for Demonstrating Practical Quantum Advantage: Racing Quantum against Classical Generative Models
Generative modeling has seen a rising interest in both classical and quantum machine learning, and it represents a promising candidate to obtain a practical quantum advantage in the near term. In this study, we build over a proposed framework for evaluating the generalization performance of generative models, and we establish the first quantitative comparative race towards practical quantum advantage (PQA) between classical and quantum generative models, namely Quantum Circuit Born Machines (QCBMs), Transformers (TFs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Networks (WGANs). After defining four types of PQAs scenarios, we focus on what we refer to as potential PQA, aiming to compare quantum models with the best-known classical algorithms for the task at hand. We let the models race on a well-defined and application-relevant competition setting, where we illustrate and demonstrate our framework on 20 variables (qubits) generative modeling task. Our results suggest that QCBMs are more efficient in the data-limited regime than the other state-of-the-art classical generative models. Such a feature is highly desirable in a wide range of real-world applications where the available data is scarce.
Link: https://ift.tt/ZlhH7ui
April 17, 2023 at 12:30PM
Waiting for quantum computers to arrive, software engineers get creative
OAKLAND, Calif., April 17 (Reuters) - Quantum computers promise to be millions of times faster than today's fastest supercomputers, potentially revolutionizing everything from medical research to the way people solve problems of climate change. […] Lacking quantum computers that customers can use today to get an advantage over classical computers, these startups are developing a new breed of software inspired by algorithms used in quantum physics, a branch of science that studies the fundamental building blocks of nature.
Link: https://ift.tt/Rt2pi0x
April 17, 2023 at 09:31PM
Quantum light source goes fully on-chip, bringing scalability to the quantum cloud
"Our breakthrough allowed us to shrink the source size by a factor of more than 1,000, allowing reproducibility, stability over a longer time, scaling, and potentially mass-production. All these characteristics are required for real-world applications such as quantum processors," says Prof. Dr.
Link: https://ift.tt/8zrLjGi
April 17, 2023 at 10:32PM
Quantum Computing Market Expected to Reach US$ 4.85 Billion by 2030 | CAGR 31.3% [PDF Version]
Quantum Computing Market Research Report By Application (Optimization, Machine Learning, Simulation & Others), By Product Type (Hardware, Software, & Services)EINPresswire.
Link: https://ift.tt/5bWrsel
April 18, 2023 at 06:31AM
Overcoming Supply Chain Challenges with Quantum Computing
The global supply chain is an intricate web of interconnected businesses and organizations that spans the world. It plays a critical role in ensuring that goods and services are delivered to customers on time and at the right price. However, the supply chain is not without its challenges. From unpredictable demand to logistical issues, there are many factors that can disrupt the flow of goods and services. Fortunately, quantum computing is emerging as a technology that can help address many of these challenges. In this article, we will explore how quantum computing can help overcome supply chain challenges and revolutionize the industry.
Link: https://ift.tt/Fe693LI
April 18, 2023 at 04:31PM
QC Ware Launches Promethium, Enabling Faster and More Accurate Pharmaceutical, Chemical and Materials Discovery
New SaaS chemistry simulation software with intuitive user interface will make more powerful computational tools easily accessible to the chemistry community. PALO ALTO, Calif.
Link: https://ift.tt/yUBJvop
April 18, 2023 at 10:33PM
15 Significant Ways Quantum Computing Could Soon Impact Society
Many of us are awed by what technology can do today, but quantum computing is poised to make exponential changes to a multitude of functions across industries and entities, which could radically change how we live and work.
Link: https://ift.tt/mrUJQku
April 19, 2023 at 04:31PM
Photonic quantum computing startup Quantum Source extends Seed round to $27 million
Quantum Source was founded in 2021 and is led by co-founders CEO Oded Melamed (CEO), Gil Semo (VP of R&D), Prof. Barak Dayan (Chief Scientist), and Dan Charash (Chairman).
Link: https://ift.tt/zB2bUEn
April 19, 2023 at 04:31PM
Fujitsu and BSC collaborate to advance research in personalized medicine and quantum computing
Dual collaboration agreement will promote the development of projects to exploit clinical data and simulate quantum computers Barcelona Supercomputing Center, Fujitsu Limited The Barcelona Supercomputing Center – Centro Nacional de Supercomputación (BSC-CNS) and Fujitsu Limited will sign a dual
Link: https://ift.tt/8uER7bS
April 19, 2023 at 04:31P
Application-Oriented Performance Benchmarks for Quantum Computing
In this work, we introduce an open-source suite of quantum application-oriented performance benchmarks that is designed to measure the effectiveness of quantum computing hardware at executing quantum applications. These benchmarks probe a quantum computer's performance on various algorithms and small applications as the problem size is varied, by mapping out the fidelity of the results as a function of circuit width and depth using the framework of volumetric benchmarking. In addition to estimating the fidelity of results generated by quantum execution, the suite is designed to benchmark certain aspects of the execution pipeline in order to provide end users with a practical measure of both the quality of and the time to solution. Our methodology is constructed to anticipate advances in quantum computing hardware that are likely to emerge in the next five years. This benchmarking suite is designed to be readily accessible to a broad audience of users and provides benchmarks that correspond to many well-known quantum computing algorithms.
Link: https://ift.tt/WxJSCF7
April 19, 2023 at 08:31PM
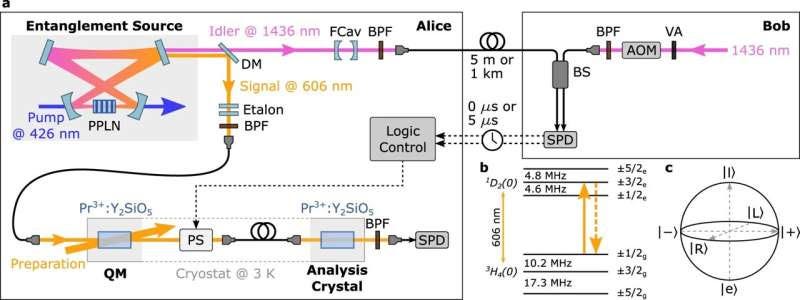
Long-distance quantum teleportation enabled by multiplexed quantum memories
Experimental set-up. a Entangled photon pairs are generated at Alice. Signal photons are routed to a Pr-doped crystal, while the idler photons are sent towards Bob either through a 5 m or a 1 km long optical fiber.
Link: https://ift.tt/dSGkfDt
April 19, 2023 at 08:31PM
Quanscient raises €3.9 million to help bring products to market faster with its quantum computing-powered solution
Quanscient, the Finnish cloud and quantum computing-powered multiphysics simulation technology provider has raised €3.9 million. The Seed funding came from Maki.vc and will be used to further accelerate product development and expansion.
Link: https://ift.tt/64FMQkp
April 20, 2023 at 09:31AM
Rock, Paper, Scissors: Searching for Stronger Nonlocality Using Quantum Computers
The 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Alain Aspect, John Clauser, and Anton Zeilinger for their works on "quantum nonlocality" in quantum mechanics. Quantum nonlocality is a phenomenon where connected particles can affect each other instantly, regardless of the distance separated.
Link: https://ift.tt/8yGbsk5
April 20, 2023 at 09:31AM
Cabinet approves National Quantum Mission to scale-up scientific & industrial R&D for quantum technologies
National Quantum Mission received cabinet approval at a total cost of Rs. 6003.65 crore, to scale up scientific and industrial R&D, for accelerating Quantum Technology led economic growth and leverage India into a leading nation in the area
Link: https://ift.tt/ztg0uiG
April 20, 2023 at 01:31PM
Quantum Annealing Breakthrough: D-Wave’s 5,000 Qubit Processor Shows Faster Coherent Dynamics Than Classical Computing.
D-Wave Quantum Inc. has achieved another major breakthrough in quantum computing. In a peer-reviewed study published on April 19, 2023, the company reported the largest programmable quantum simulation to date.
Link: https://ift.tt/l9CBkfK
April 20, 2023 at 05:30PM
Heaviest Schrödinger cat achieved by putting a small crystal into a superposition of two oscillation states
Scientists at ETH Zurich have made progress in creating heavier Schrödinger cats, which can be alive (top) and dead (bottom) at the same time. Credit: ETH Zurich Even if you are not a quantum physicist, you will most likely have heard of Schrödinger's famous cat.
Link: https://ift.tt/Tmx1Nkj
April 21, 2023 at 12:30PM
Moderna teams up with IBM to put AI, quantum computing to work on mRNA technology used in vaccines
Moderna and IBM are teaming up to use generative artificial intelligence and quantum computing to advance mRNA technology, the development at the core of the company’s Covid vaccine. The companies said they signed an agreement that would allow Moderna to access IBM’s quantum computing systems and generative AI model. The agreement comes as Moderna navigates its post-pandemic boom driven by its mRNA Covid vaccine.
Link: https://ift.tt/mC9Xacu
April 21, 2023 at 06:33PM
Talent crunch: Finding the right quantum computing course
When it comes to picking up new skills in tech, most employees would go online to learn and develop fundamentals of understanding a particular skill or technology. Some of the most sought-after skills in tech today are in the field of cybersecurity, cloud management, and app development.
Link: https://ift.tt/Caj45ui
April 21, 2023 at 06:33PM
Ericsson, Government of Canada Includes Quantum in $470 Million (CAD) R&D Investment
Ericsson and the Canadian government's CAD 470 million, five-year research and development partnership will cover quantum computing.
Link: https://ift.tt/zvONYEM
April 21, 2023 at 10:32PM







Re. 3. ‘Breaking’ The Blockchain:
"False. ... there is nothing (that I know of) that proves the contrary."
The quantum threat to blockchain is more nuanced. Bitcoin blockchain uses different types of addresses with different threat profiles. Older addresses are public key based (p2pk) and are vulnerable to quantum attack. Old addresses contain 4 million BTC or over 25% of all bitcoins. At the current price it is over $156B.
Newer addresses (post-2010) are hash-based (such as p2pkh addresses) and are immune to quantum attacks, but only if the funds never moved out. If even a small amount of funds moved from this address type, the public key is revealed and is vulnerable to quantum attack.
Deloitte has a good article about this issue: https://www2.deloitte.com/nl/nl/pages/innovatie/artikelen/quantum-computers-and-the-bitcoin-blockchain.html
More detailed analysis quantum vulnerability of different blockchain technologies is available in this paper: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-32701-6.pdf
PS. Thanks for sharing your insights on a panel at QuantumTech'23 in Boston!